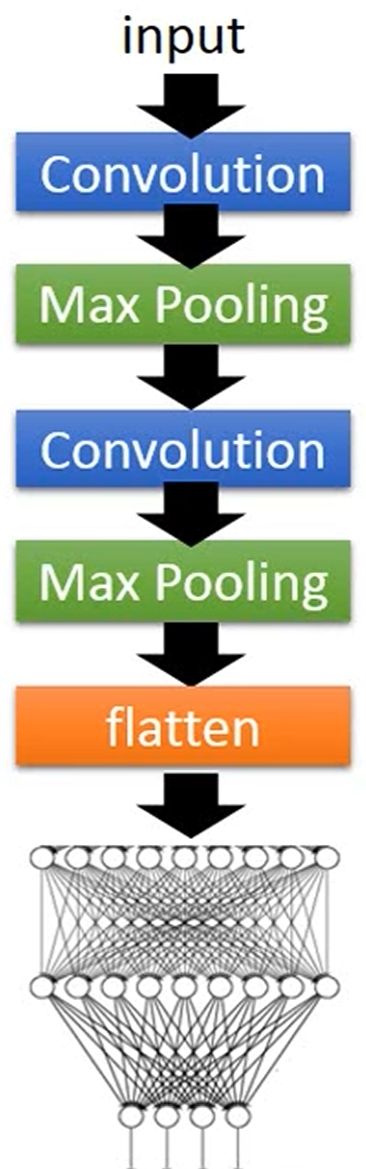
Convolutional Neural Networks
CNNs are a class of deep neural networks, most commonly applied to analyzing visual imagery. They are also known as ConvNets:
- Input Layer (输入层): raw pixel values of an image.
- Hidden Layers (隐藏层):
- Convolutional Layer (卷积层): find patterns in regions of the input, and passing the results to the next layer.
- Pooling Layer (池化层): down-samples the input representation, reducing its dimensionality.
- Fully Connected Layer (全连接层): compute the class scores, resulting in a volume of size , where each of the numbers represents a class.
- Output Layer (输出层): class scores.
# Load the data and split it between train and test sets
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
# Scale images to the [0, 1] range
x_train = x_train.astype("float32") / 255
x_test = x_test.astype("float32") / 255
# Make sure images have shape (28, 28, 1)
x_train = np.expand_dims(x_train, -1)
x_test = np.expand_dims(x_test, -1)
print("x_train shape:", x_train.shape)
print("y_train shape:", y_train.shape)
print(x_train.shape[0], "train samples")
print(x_test.shape[0], "test samples")
# Model parameters
num_classes = 10
input_shape = (28, 28, 1)
model = keras.Sequential(
[
keras.layers.Input(shape=input_shape),
keras.layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation="relu"),
keras.layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation="relu"),
keras.layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)),
keras.layers.Conv2D(128, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation="relu"),
keras.layers.Conv2D(128, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation="relu"),
keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D(),
keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
keras.layers.Dense(num_classes, activation="softmax"),
]
)
model.compile(
loss=keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossEntropy(),
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-3),
metrics=[
keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name="acc"),
],
)
# Train
batch_size = 128
epochs = 20
callbacks = [
keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath="model_at_epoch_{epoch}.keras"),
keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor="val_loss", patience=2),
]
model.fit(
x_train,
y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
validation_split=0.15,
callbacks=callbacks,
)
score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=0)
# Save model
model.save("final_model.keras")
# Predict
predictions = model.predict(x_test)
Convolution
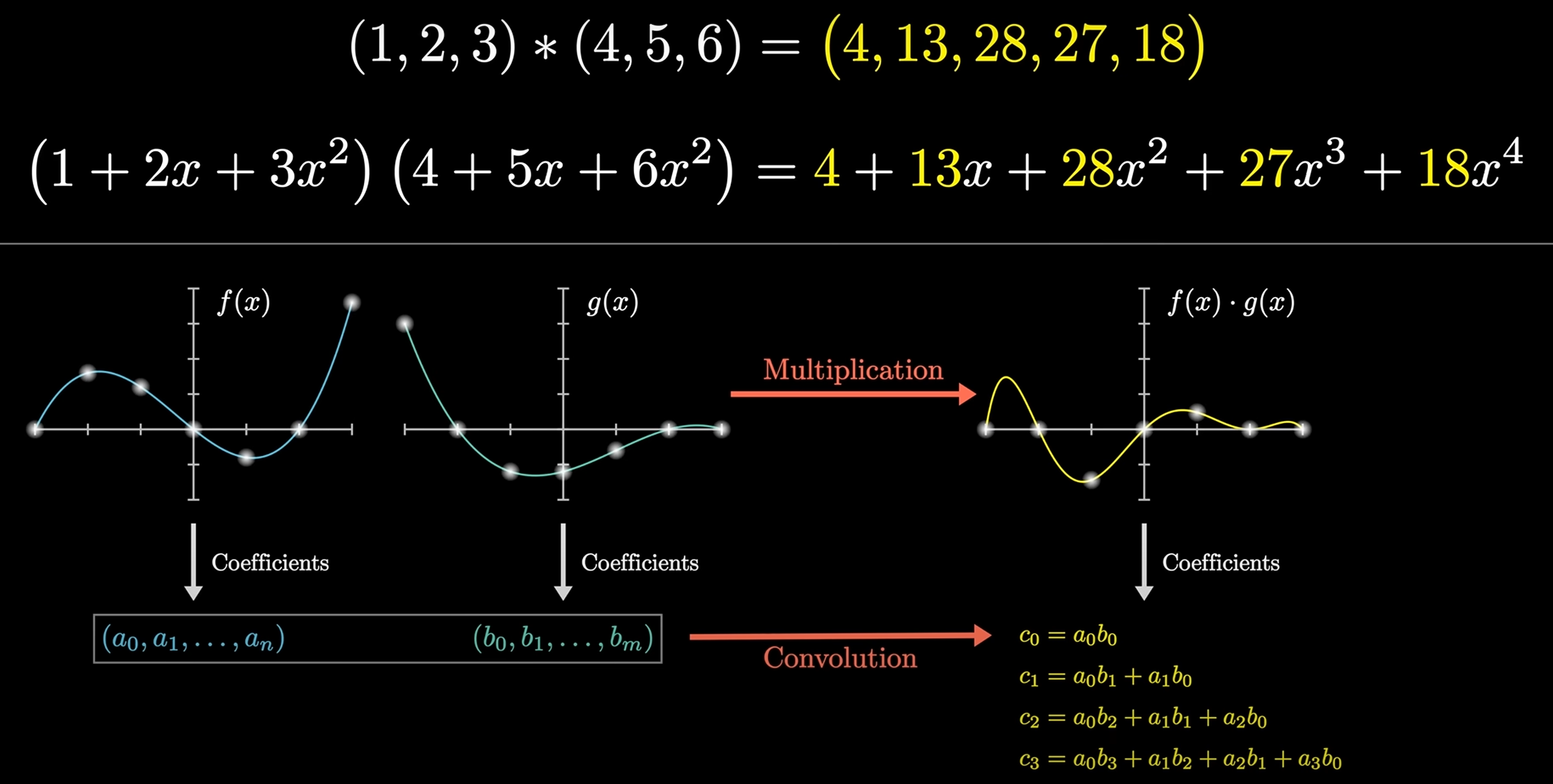
Convolution is a mathematical operation that combines two functions to produce a third function:
Given and , then: , e.g. . 上述计算可以转换为多项式相乘的形式:
可以运用快速傅里叶变换 (FFT) 以 的时间复杂度求解 的值, 从而实现快速卷积运算.
For matrix:
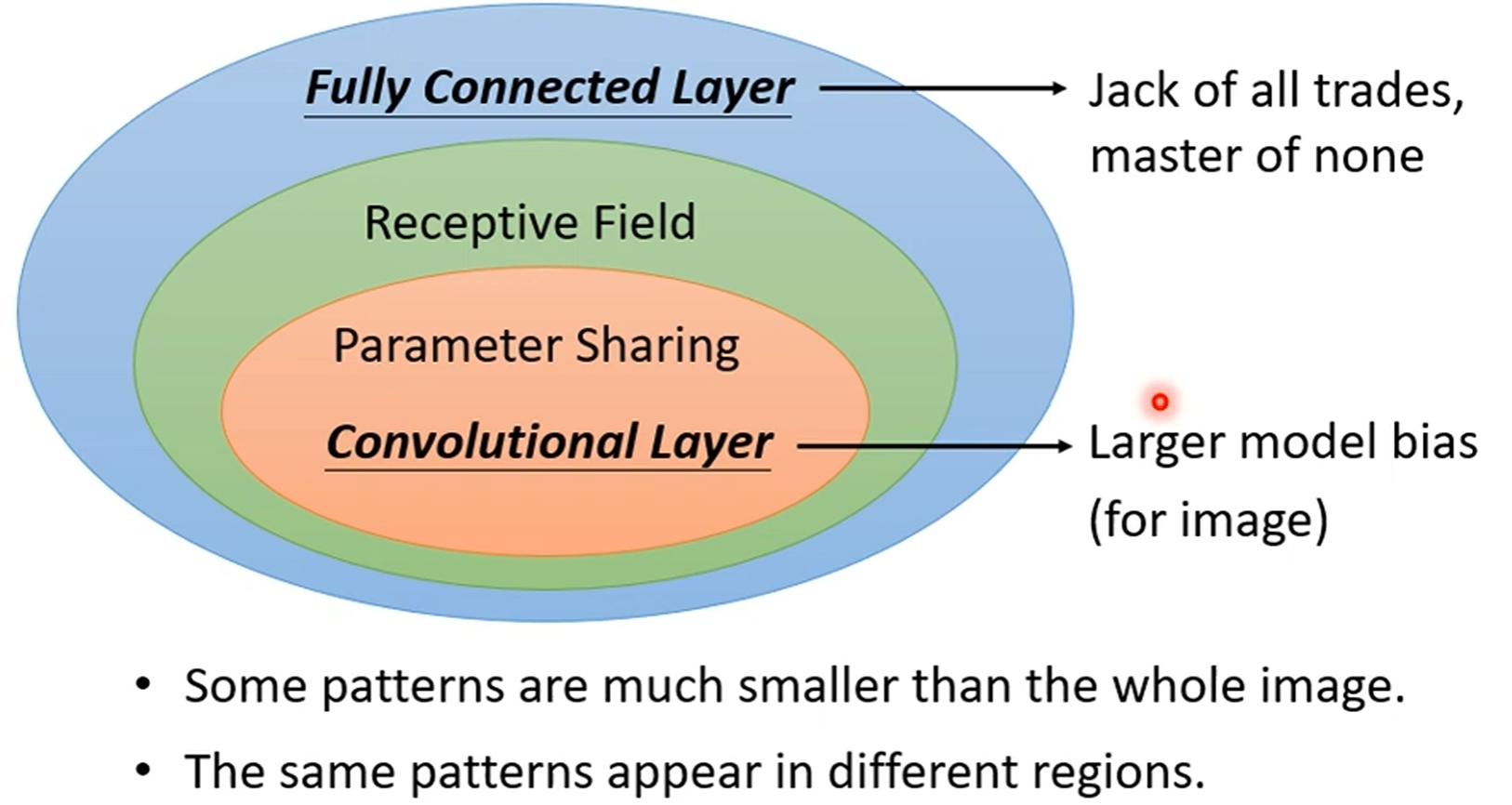
Convolutional Layer
Convolutional Layer is the first layer to extract features from an input image. The layer's parameters consist of a set of learnable filters (or kernels), which have a small receptive field but extend through full depth of input volume.
Pooling Layer
Pooling Layer is used to reduce the spatial dimensions of the input volume. It helps to reduce the amount of parameters and computation in the network, and hence to also control overfitting.
Fully Connected Layer
Fully Connected Layer is a traditional Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) layer. It is used to compute the class scores, resulting in a volume of size , where each of the numbers represents a class.
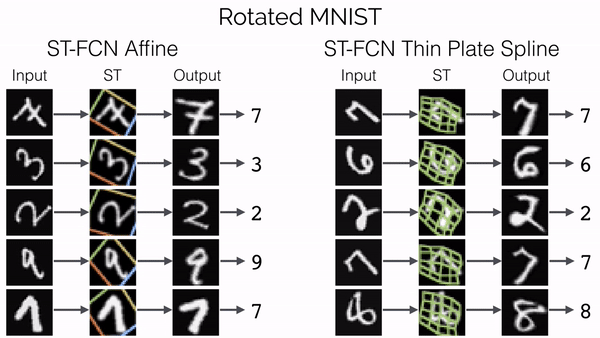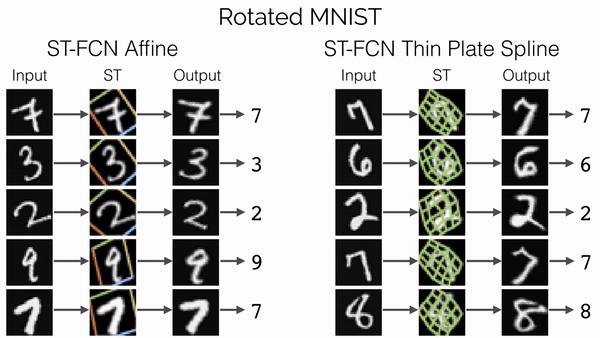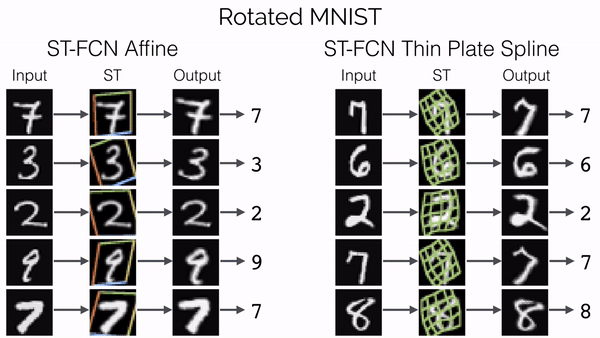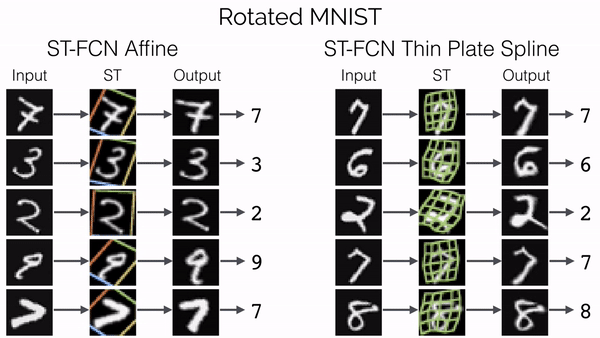
Spatial Transformer Networks
传统的池化方式 (Max Pooling/Average Pooling) 所带来卷积网络的位移不变性和旋转不变性只是局部的和固定的, 且池化并不擅长处理其它形式的仿射变换.
Spatial transformer networks (STNs) allow a neural network to learn how to perform spatial transformations on the input image in order to enhance the geometric invariance of the model. STNs 可以学习一种变换, 这种变换可以将仿射变换后的图像进行矫正, 保证 CNNs 在输入图像发生变换时, 仍然能够保持稳定的输出 (可视为总是输入未变换的图像).