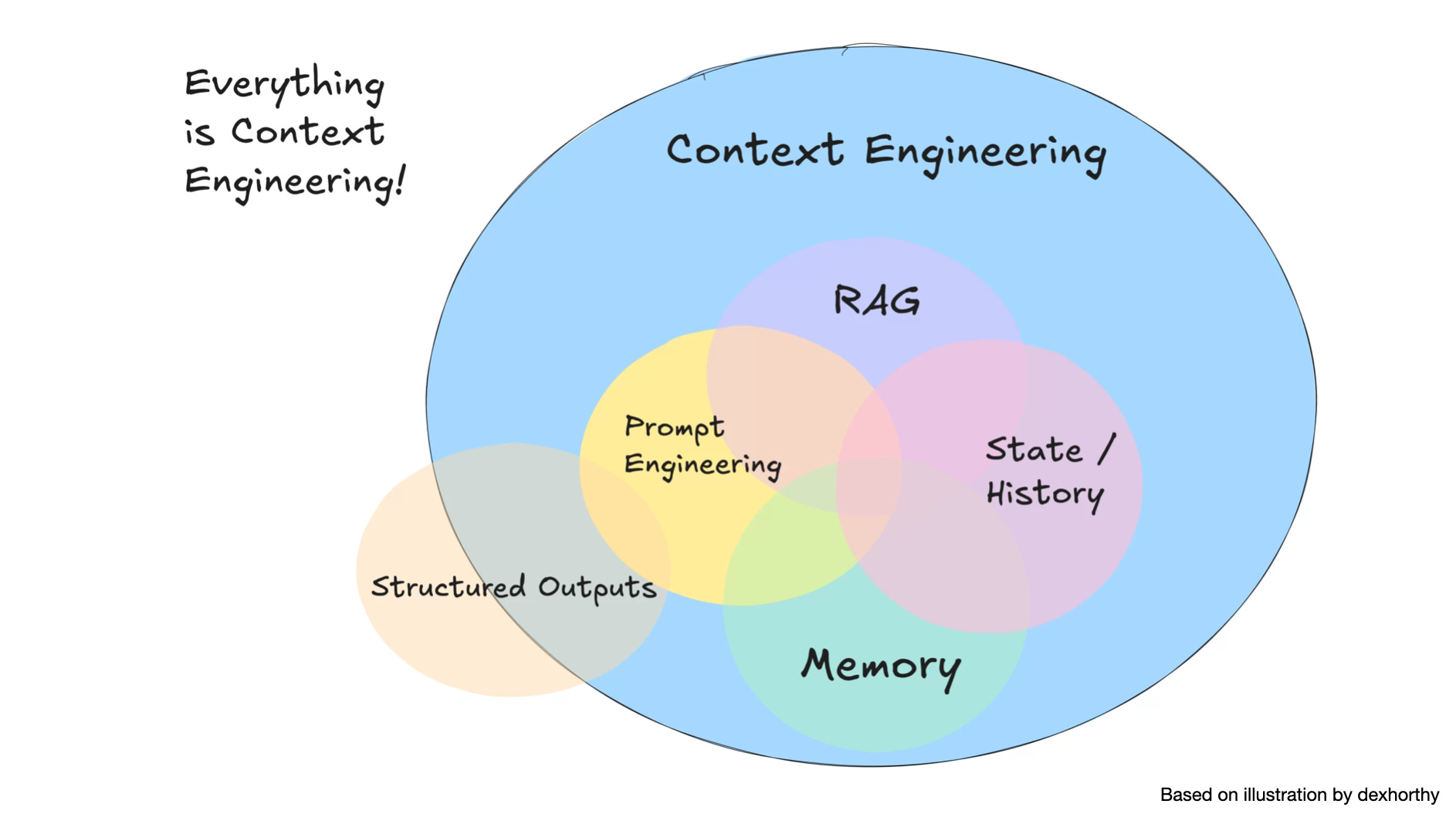
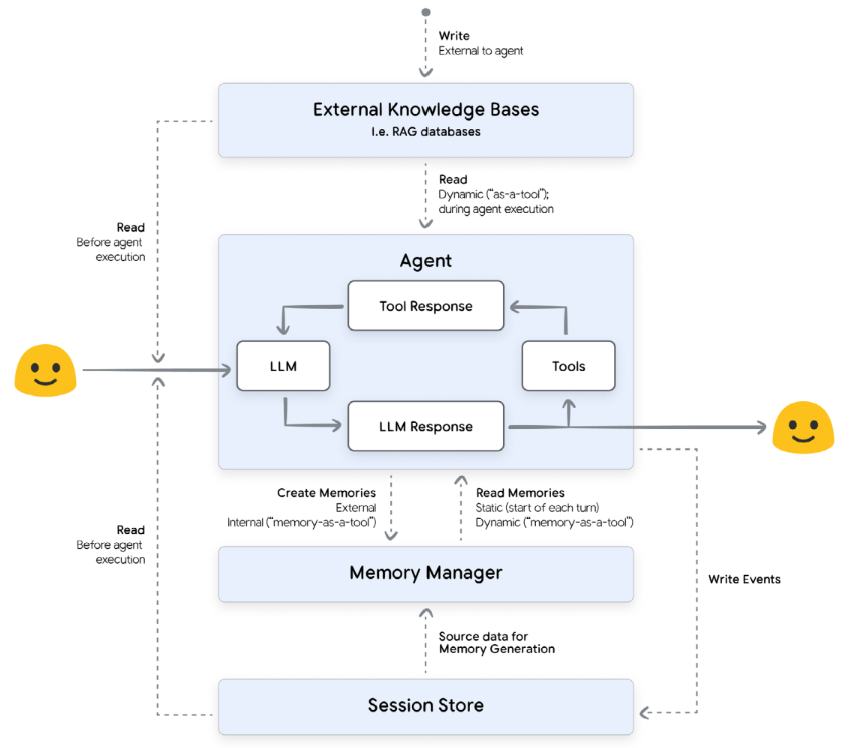
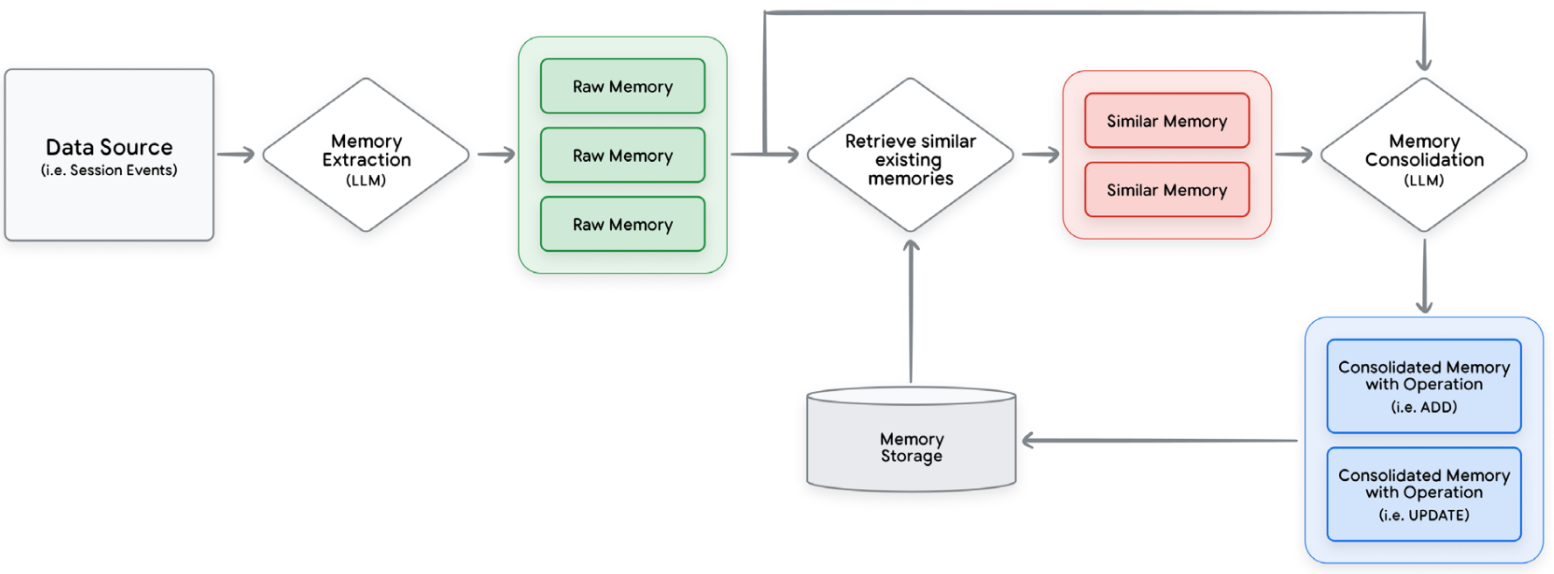
Context
注意力计算复杂度是 , 且是稀疏的 (模型不会均匀地关注所有输入):
- 上下文窗口受硬件边界限制.
- 有效上下文小于标称上下文: coding agent 只能有效利用其中的 10-15 .
Lost in the middle: 中间内容容易被忽略, 更关注开头和结尾.
Engineering
LLM 并未统一利用其上下文,
它们的准确性和可靠性会随着输入令牌数量的增加而下降,
称之为上下文腐烂 (Context Rot).
因此, 仅仅在模型的上下文中拥有相关信息是不够的:
信息的呈现方式对性能有显著影响.
这凸显了 上下文工程 的必要性,
优化相关信息的数量并最小化不相关上下文以实现可靠的性能:
- System instructions.
- Tool definitions.
- Few-shot examples.
- User prompt.
- Conversation history.
- Short-term memory.
- Long-term memory.
- External knowledge.
- Tool outputs.
- Subagent outputs.
- Artifacts.
Plan
Planning with files in Manus:
- Design around KV-cache:
- 稳定内容放前面: system prompt, tool definitions.
- 动态内容放后面: chat history, user input.
- 避免在稳定前缀中插入可变内容: e.g. 禁止在 system prompt 中插入时间戳.
- Plan is required
- Files are memory
- Don't get few-shotted: get rid of repetitive actions
- Manipulate attention through recitation
Start of context: [Original goal - far away, forgotten]
...many tool calls...
End of context: [Recently read task_plan.md - gets ATTENTION!]
Cache
Treat context as append-only log, not editable document:
| Anti-Pattern | Effect | Cost Multiplier |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic system prompt | 100% cache miss | 20-50x |
| Sliding window | 100% cache miss | 30-50x |
| Message compression | Invalidates from replacement point | 5-15x |
| Message editing | Invalidates from edit point | 10-30x |
| Multi-agent full mesh | Context explosion | 3-4x (vs single agent) |
MCP 服务器可通过 notifications/tools/list_changed 随时更改提供的工具列表.
在长对话中响应此通知可能会导致代价高昂的缓存未命中.
Reduction
减少上下文中的信息量:
- Keep-N: 只保留前 N 个字符或关键片段作为预览, 原始完整内容被移除.
- 总结摘要: 使用 LLM 对整段内容进行总结摘要, 保留关键信息, 丢弃细节.
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain.agents.middleware import SummarizationMiddleware
agent = create_agent(
model="gpt-4o",
middleware=[
SummarizationMiddleware(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
max_tokens_before_summary=4000, # 4000 tokens 时触发摘要
messages_to_keep=20, # 摘要后保留最后 20 条消息
),
],
)
Offloading
原始完整内容被卸载到外部存储 (e.g. 文件系统, 数据库), 消息中只保留最小必要的引用 (e.g 文件路径, UUID). 当需要完整内容时, 可以通过引用重新加载.
Isolation
通过多智能体架构 (Multi-Agent), 将上下文拆分到不同的子智能体中. 主智能体编写任务指令, 子智能体的整个上下文仅由该指令组成, 主智能体只需要最终结果.
Session
Immediate dialogue history and working memory for single and continuous conversation.
Events
Chronological history:
- User input.
- Agent response.
- Tool call.
- Tool output.
State
Working memory and scratchpad stores and updates dynamic details during conversation.
Compression
由于上下文窗口限制、API 费用、生成延迟、生成质量等因素, 过多的上下文会显著增加成本、延迟、噪声和误差, 需要对会话进行压缩:
- Keep last N turns.
- Token-based truncation.
- Recursive summarization.
- Trigger: count, time, event.
Memory
System
- Repeatable memory loop: inject → reason → distill → consolidate.
- Enforce precedence: current user message > session context > memory.
Manager
- Extraction: distill key information.
- Consolidation: merge and deduplicate.
- Storage: persist to database.
- Retrieval: fetch relevant memories.
Consolidation
记忆管理最复杂的部分:
- Duplication.
- Conflict: low confidence.
- Irrelevance: time-based decay.
- Evolution.
Trigger
- Session completion.
- Turn cadence: e.g. every 5 turns.
- Real-time: every single turn.
- Explicit command:
remember this.
Retrieval
- Relevance: semantic similarity.
- Recency: time-based decay.
- Importance.
Personalization
Meta-prompting for memory extraction:
You are a [USE CASE] agent whose goal is [GOAL].
What information would be important to keep in working memory during a single session?
List both fixed attributes (always needed) and inferred attributes (derived from user behavior or context).
Evaluation
- Precision: 准确率.
- Recall: 召回率.
- F1 score: 准确率与召回率的调和平均值.
- Latency.
Dynamic Discovery
Dynamic context discovery:
- 工具响应 -> 文件.
- 终端会话 -> 文件.
- 上下文压缩时引用对话历史.
- 按需加载.
- 渐进式披露.
References
- Context engineering whitepaper.
- Memory system.