Eval
Principles
Agents eval:
- Start early.
- Source realistic tasks from failures.
- Define unambiguous, robust success criteria.
- Design graders thoughtfully and combine multiple types (code-based, model-based, human).
- Make sure the problems are hard enough for model.
- Iterate on evaluations to improve signal-to-noise ratio.
- Read transcripts (记录).
- Pick framework:
Agent Failure
智能体的失败通常不是系统崩溃, 而是质量的细微退化, 源于模型权重、训练数据和环境交互的复杂相互作用. 这些失败是隐晦的:
- Algorithm bias.
- Factual hallucination.
- Concept drift: 性能随时间推移而下降, 无法发现新问题.
- Emergent unintended behaviors.
Targets
- Effectiveness: goal achievement.
- Efficiency: operational cost.
- Robustness: reliability.
- Safety and alignment: trustworthiness.
Methods
| Method | 👍 Strengths | 👎 Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Metrics | Objective, scalable, efficient | May not capture full capabilities |
| LLM-as-a-Judge | Consistent, scalable, efficient | May overlook intermediate steps, limited by LLM capabilities |
| Human Evaluation | Captures nuanced behavior | Subjective, time-consuming, expensive, difficult to scale |
Metrics
Regression
- String-based similarity: ROUGE, BLEU.
- Embedding-based similarity: BERTScore, cosine similarity.
- Task-specific benchmarks.
Performance
- Latency: P50, P90, P99.
- Error rate.
Cost
- Tokens per task.
- API cost per run.
Effectiveness
- Task completion rate.
- Tool usage frequency.
Quality
- Correctness.
- Accuracy.
- Relevance.
- Trajectory adherence.
LLM
Robust pairwise comparison:
You are an expert evaluator for a customer support chatbot.
Your goal is to assess which of two responses is more helpful, polite, and correct.
[User Query]
"Hi, my order #12345 hasn't arrived yet."
[Answer A]
"I can see that order #12345 is currently out for delivery and should arrive by 5 PM today."
[Answer B]
"Order #12345 is on the truck. It will be there by 5."
Please evaluate which answer is better. Compare them on correctness, helpfulness, and tone.
Provide reasoning and output final decision in JSON object with "winner" key ("A", "B", or "tie") and "rationale" key.
Critic agent:
1. Based on the trace, was the initial plan logical?
2. Was the {tool_A} tool the correct first choice, or should another tool have been used?
3. Were the arguments correct and properly formatted?
Human
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL):
- Domain expertise: 领域专业知识.
- Interpreting nuance: 解释细微差别.
- Golden set: 将生产故障转化为测试用例.
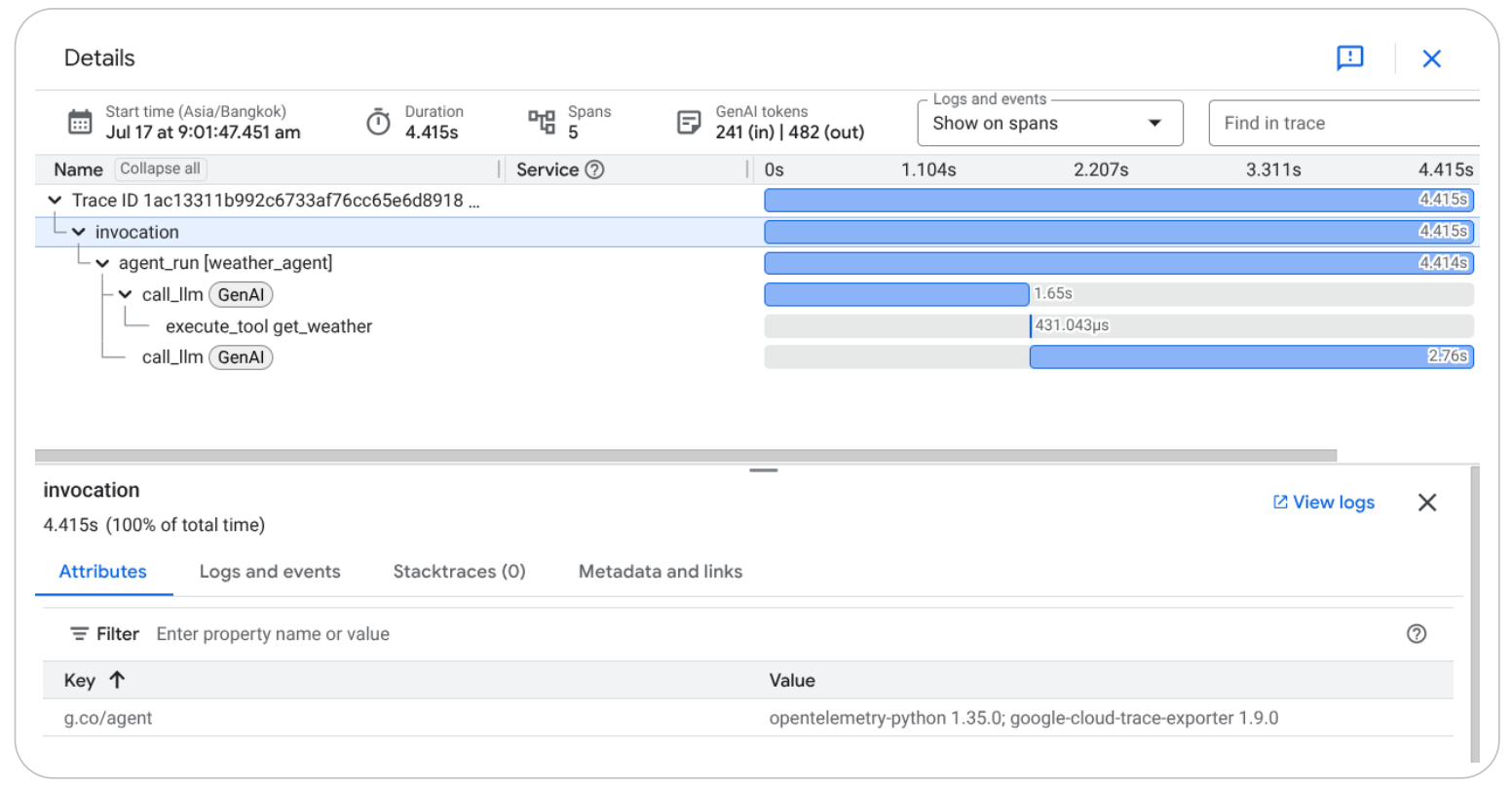
Trace
When building agents, trace is the source of truth:
- Debugging becomes trace analysis
- Testing becomes eval-driven
- Can't set breakpoints in reasoning
- Performance optimization changes: task success rate, reasoning quality, tool usage efficiency
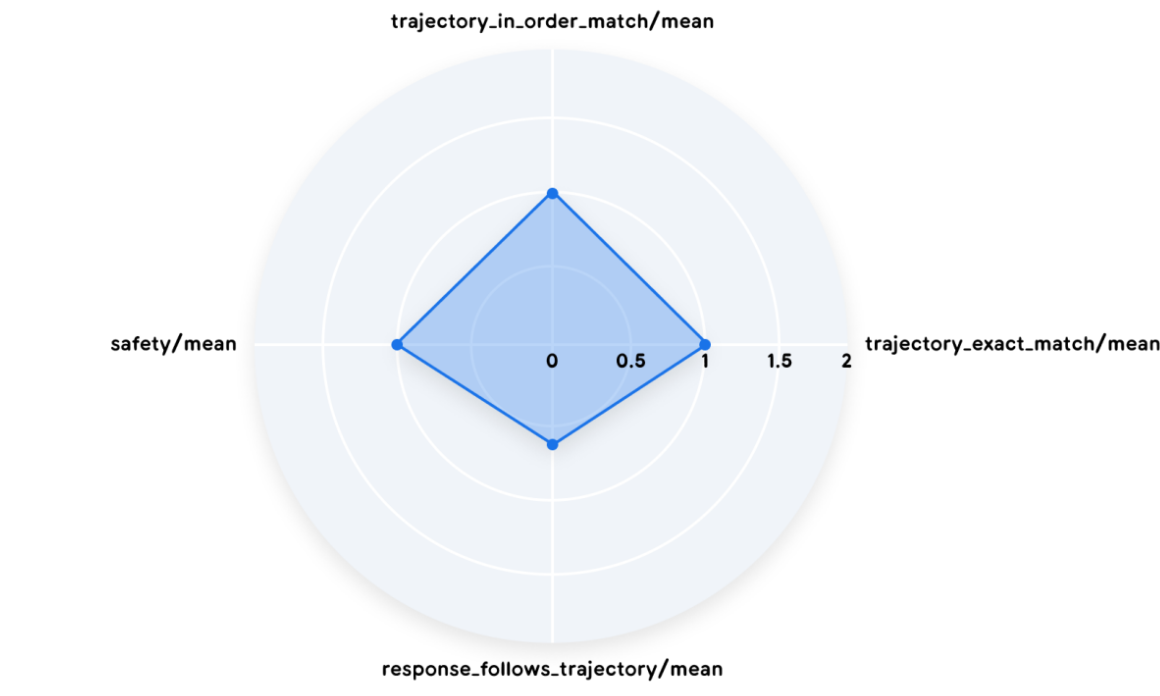
Trajectory
Trajectory is equally important as final response:
- Exact match: produce trajectory that perfectly mirrors ideal solution.
- In-order match: complete expected trajectory, while accommodating extra, un-penalized actions.
- Any-order match: include all necessary actions.
- Precision: relevant tool calls.
- Recall: essential tool calls.
Trajectory Score
- Response match score.
- Tool trajectory score.
Benchmarks
- Aggregate: Don’t obsess over a 1-2% lead on one benchmark, focus on specific and comprehensive domain.
- Relative: Compare within the same model family or lab, how did the score change from v1 to v2?
- Verify: The only benchmark that matters at the end of the day is your workload.
References
- Agent evaluation whitepaper.
- Agent quality whitepaper.
- Claude Opus 4.5 system card.
- Autonomous agents benchmark.