Cascading
CSS Working Group
- CSS working group: CSS WG.
- W3C standard types:
- ED:
Editor's Draft. - FPWD:
First Public Working Draft. - WD:
Working Draft. - CR:
Candidate Recommendation. - PR:
Proposed Recommendation. - REC: a W3C
Recommendationis a W3C Technical Report.
- ED:
Order
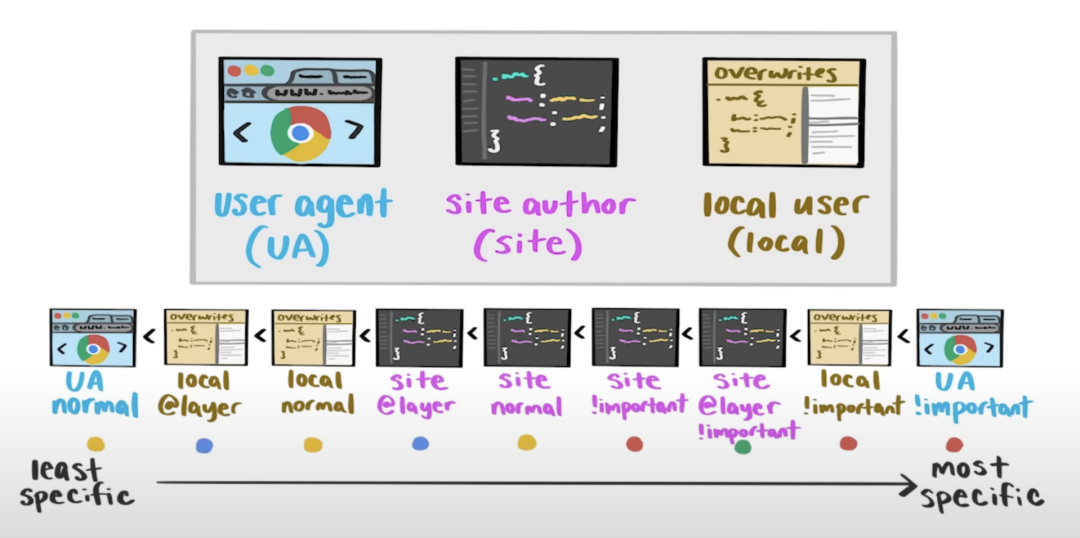
- Inherit styles.
- User agent normal styles.
- User normal styles.
- Author
@layernormal styles. - Author normal styles.
- Animation styles.
- Author
!importantstyles. - Author
@layer!importantstyles. - User
!importantstyles. - User agent
!importantstyles. - Transition styles.
Transition > Animation > Normal >
@layer> User > User Agent > Inherit
Important Styles Reversion
- 级联水平高的 styles 应用 !important 后, 其优先级变低.
- 级联水平低的 styles 应用 !important 后, 其优先级变高.
Layer
Formal Syntax
@layer formal syntax:
@layer base;
@layer theme, layout, components, utilities;
@layer base {
html {
font-size: 1rem;
}
}
@layer {
html {
font-size: 1rem;
}
}
@layer reset, externals, base, components, utilities;
@import 'reset.css' layer(reset);
@import 'carousel.css' layer(externals);
@import 'map.css' layer(externals);
<link rel="stylesheet" href="reset.css" layer="reset" media="supports(at-rule(@layer))" />
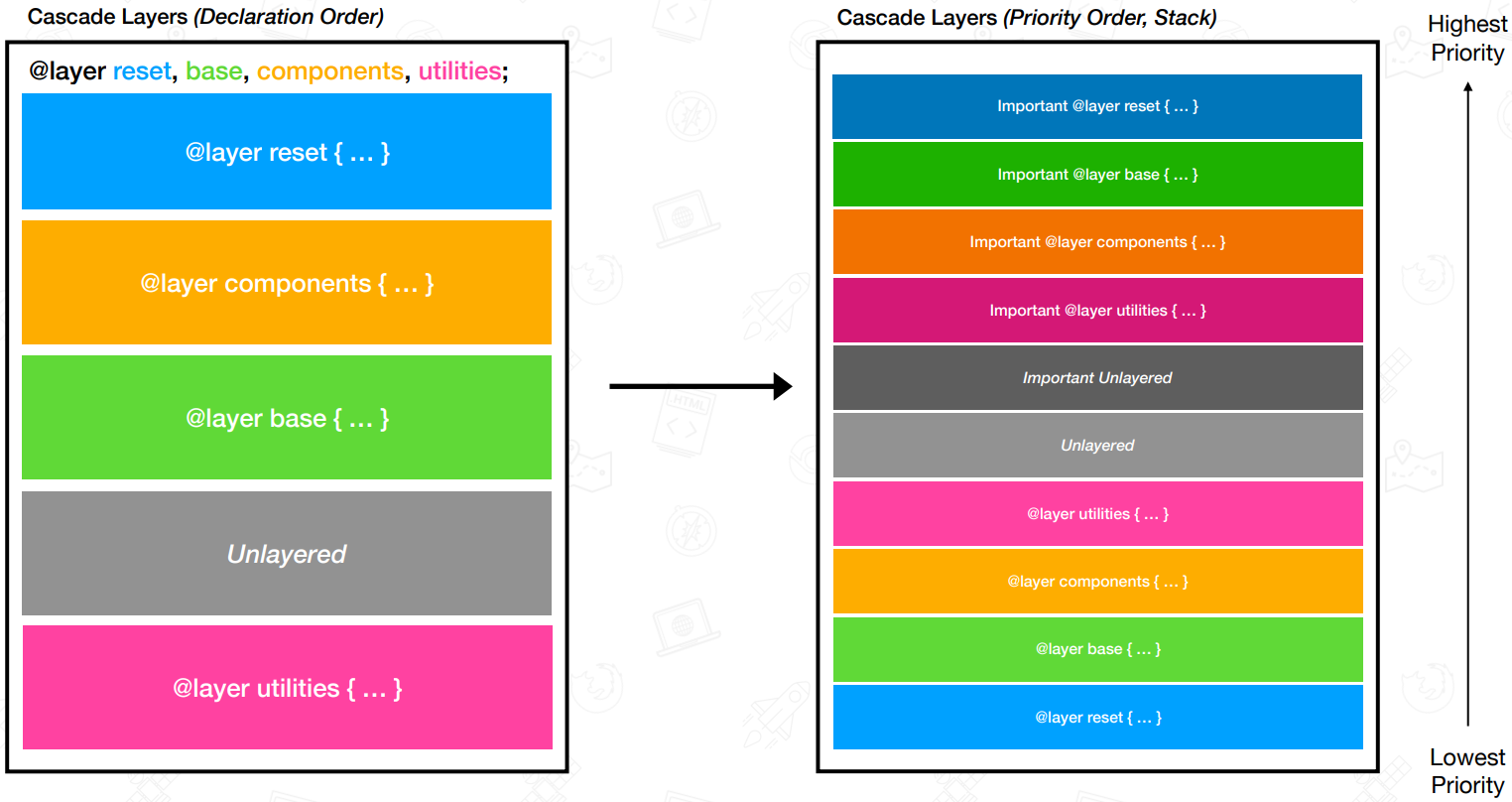
Priority
/* utilities > components > layout > theme */
@layer theme, layout, components, utilities;
/* c > c.d > a > a.b */
@layer a {
p {
color: red;
}
@layer b {
p {
color: green;
}
}
}
@layer c {
p {
color: orange;
}
@layer d {
p {
color: blue;
}
}
}
Scope
- 局部上下文: 生效元素必须为
@scope的子元素 - 规则完整性: 规则中的每一行代码, 必须属于一个完整的规则, 不能是一条单独的 CSS 声明.
<section class="scope-root">
<h3>Scope Root</h3>
<p>Paragraph 1</p>
<!-- Selected -->
<img src="image.jpg" alt="Image" />
<p>Paragraph 2</p>
<figure class="scope-limit">
<!-- Not selected -->
<img src="image.jpg" alt="Image" />
<figcaption>Figure Caption</figcaption>
</figure>
</section>
<style>
@scope (.scope-root) to (.scope-limit) {
img {
background-color: red;
}
/* stylelint-disable-next-line no-duplicate-selectors */
& img {
background-color: red;
}
:scope img {
background-color: red;
}
}
</style>
When two elements have equal specificity, the one whose scope root is closer to the matched element wins:
<div class="sidebar">
<div class="container">
<h2 class="title">Hello</h2>
</div>
</div>
<style>
@scope (.container) {
.title {
color: green;
}
}
/* The <h2 > is closer to .container than to .sidebar so 'color: green' wins. */
@scope (.sidebar) {
.title {
color: red;
}
}
</style>
Nesting
ul {
& + & {
font-weight: bold;
color: red;
}
}
Specificity
Specificity
(Selector Priority) has 4 bits,
thousands, hundreds, tens, ones 0000:
- Thousands: inline-style.
- Hundreds: ID selector (实际开发中一般用
[id="Id"]代替优先级过高的 ID selector). - Tens: class selector, attribute selector, pseudo class(
:). - Ones: type selector, pseudo element(
::).
Zero Specificity
- Universal selector (
*), combinators (+,>,~,a b) and:where()have no effect on specificity. :not()/:is()/:has()have no effect on specificity, but selectors in it have effect on specificity.
<!-- specificity: 1000 -->
<h1 style="color: black">Hello</h1>
/* specificity: 0001 */
h1 {
color: red;
}
/* specificity: 0100 */
#id {
color: green;
}
/* specificity: 0003 */
h1 + p::first-letter {
color: blue;
}
/* specificity: 0022 */
li > a[href*='link-url'] > .inline-warning {
color: yellow;
}
/* specificity: 0023 */
div li:nth-child(2) a:hover,
div li:nth-child(2) a:focus {
border: 10px dashed black;
}
/* specificity: 0024 */
div div li:nth-child(2) a:hover,
div div li:nth-child(2) a:focus {
border: 10px solid black;
}
/* specificity: 0033 */
div div .nav:nth-child(2) a:hover,
div div .nav:nth-child(2) a:focus {
border: 10px double black;
}
/* specificity: 0101 */
#outer a {
background-color: red;
}
/* specificity: 0104 */
#outer div ul li a {
color: yellow;
}
/* specificity: 0113 */
#outer div ul .nav a {
color: white;
}
/* specificity: 0201 */
#outer #inner a {
background-color: blue;
}
Styles for a directly targeted element will always take precedence over inherited styles, regardless of the specificity of the inherited rule:
#parent {
color: green;
}
/* <h1> element will be purple */
h1 {
color: purple;
}
Increasing specificity by duplicating selector:
.my-class.my-class.my-class span {
/* 0-3-1 */
color: white;
}
:is(.my-class.my-class.my-class, span) {
/* 0-3-0 */
color: white;
}
Inheritance
- Most CSS properties that affect the text node are inherited properties: color, font-size, font-family, etc.
- Most CSS properties that affect the element node are non-inherited properties.
- When the
unsetvalue is set on an inherited property, it resets the property value to its inherited value. unsetvalue resets a non-inherited property to itsinitialvalue.revertreverses the CSS default values to the browser user-agent styles.
Inheritable Properties:
- visibility
- cursor
- color
- direction
- font-family
- font-size
- font-style
- font-variant
- font-weight
- font
- line-height
- letter-spacing
- word-spacing
- white-space
- text-align
- text-indent
- text-transform
- border-collapse
- border-spacing
- caption-side
- empty-cells
- list-style-image
- list-style-position
- list-style-type
- list-style
- orphans
- quotes
- widows