Authentication
Cookie
- First request header -> without cookie.
- First response header ->
Set-Cookie: numberto client. - Client store identification number for specific site into cookies files.
- Second request header ->
Cookie: number. (extract identification number for specific site from cookies files). - Function: create User Session Layer on top of stateless HTTP.
用户能够更改自己的 Cookie 值 (client side), 因此不可将超过权限的数据保存在 Cookie 中 (如权限信息), 防止用户越权.
HTTP
HTTP basic authentication is 401 authentication:
- 客户端向服务器请求数据:
Get /index.html HTTP/1.0
Host:www.google.com
- 服务器向客户端发送验证请求代码
401WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm="google.com"
HTTP/1.0 401 Unauthorized
Server: SokEvo/1.0
WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm="google.com"
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: xxx
- 当符合 HTTP/1.0 或 HTTP/1.1 的客户端收到 401 返回值时, 将自动弹出一个登录窗口, 要求用户输入用户名和密码.
- 用户输入用户名和密码后, 将用户名及密码以 BASE64 加密方式加密, 并将密文放入前一条请求信息中
- 服务器收到上述请求信息后, 将 Authorization 字段后的用户信息取出/解密, 将解密后的用户名及密码与用户数据库进行比较验证
Get /index.html HTTP/1.0
Host: www.google.com
Authorization: Basic d2XXXXXXXXXn==
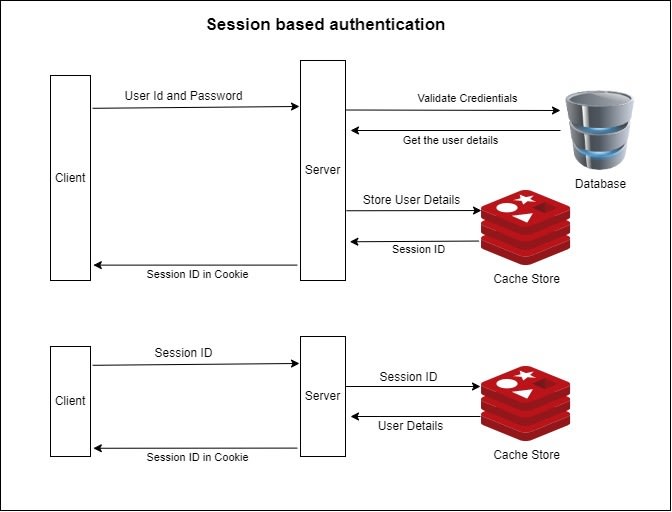
Session Cookie
HTTP 协议是一个无状态的协议,
服务器不会知道到底是哪一台浏览器访问了它,
因此需要一个标识用来让服务器区分不同的浏览器.
Cookie 就是这个管理服务器与客户端之间状态的标识.
Response header with Set-Cookie, Request header with Cookie.
浏览器第一次访问服务端, 服务端就会创建一次 Session, 在会话中保存标识该浏览器的信息. Session 缓存在服务端, Cookie 缓存在客户端, 他们都由服务端生成, 实现 HTTP 协议的状态.
- 客户端发送登录信息 (ID, Password).
- 服务器收到客户端首次请求并验证成功后,
会在服务器端创建 Session 并保存唯一的标识字符串 Session ID (Key-Value Store),
在 Response Header 中设置
Set-Cookie: <Session ID>. - 客户端后续发送请求都需在 Request Header 中设置:
Cookie: <Session ID>. - 服务器根据
<Session ID>进行用户验证, 利用 Session Cookie 机制可以简单地实现用户登录状态验证, 保护需要登录权限才能访问的路由服务. Max-Agepriority higher thanExpires. When both tonull, cookie become session cookie.
Set-Cookie: username=tazimi; domain=tazimi.dev; Expires=Wed, 21 Oct 2022 08:00:00
Set-Cookie: username=tazimi; domain=tazimi.dev; path=/blog
Set-Cookie: username=tazimi; domain=tazimi.dev; path=/blog; Secure; HttpOnly
Set-Cookie: username=tazimi; domain=github.com
Set-Cookie: height=100; domain=me.github.com
Set-Cookie: weight=100; domain=me.github.com
- 认证方式局限于在浏览器 (Cookie).
- 非 HTTPS 协议下使用 Cookie, 容易受到 CSRF 跨站点请求伪造攻击.
- Session ID 不包含具体用户信息, 需要 Key-Value Store (e.g. Redis) 持久化, 在分布式环境下需要在每个服务器上都备份, 占用了大量的存储空间.
Session authentication with Lucia in Next.js:
signUpfunction.signInfunction.getAuthfunction.signOutfunction.- Protected routes
AuthenticatedLayout. - Authorization in UI
RootLayout.
SingUp React Server Component:
// src/features/auth/actions/sign-up.ts
'use server'
import { generateId } from 'lucia'
import { cookies } from 'next/headers'
import { redirect } from 'next/navigation'
import { Argon2id } from 'oslo/password'
import { lucia } from '@/lib/lucia'
import { prisma } from '@/lib/prisma'
async function signUp(formData: FormData) {
const formDataRaw = {
firstName: formData.get('firstName') as string,
lastName: formData.get('lastName') as string,
email: formData.get('email') as string,
password: formData.get('password') as string,
confirmPassword: formData.get('confirmPassword') as string,
}
if (formDataRaw.password !== formDataRaw.confirmPassword)
throw new Error('Passwords do not match')
// TODO: add validation yourself
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
try {
const hashedPassword = await new Argon2id().hash(
formDataRaw.password
)
const userId = generateId(15)
await prisma.user.create({
data: {
id: userId,
firstName: formDataRaw.firstName,
lastName: formDataRaw.lastName,
email: formDataRaw.email,
hashedPassword,
},
})
const session = await lucia.createSession(userId, {})
const sessionCookie = lucia.createSessionCookie(session.id)
cookies().set(
sessionCookie.name,
sessionCookie.value,
sessionCookie.attributes
)
} catch (error) {
// TODO: add error feedback yourself
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
// TODO: add error handling if user email is already taken
// The Road to Next
}
redirect('/dashboard')
}
export { signUp }
SingIn React Server Component:
// src/features/auth/actions/sign-in.ts
'use server'
import { cookies } from 'next/headers'
import { redirect } from 'next/navigation'
import { Argon2id } from 'oslo/password'
import { lucia } from '@/lib/lucia'
import { prisma } from '@/lib/prisma'
async function signIn(formData: FormData) {
const formDataRaw = {
email: formData.get('email') as string,
password: formData.get('password') as string,
}
// TODO: add validation yourself
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
try {
const user = await prisma.user.findUnique({
where: { email: formDataRaw.email },
})
if (!user) {
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
throw new Error('Incorrect email or password')
}
const validPassword = await new Argon2id().verify(
user.hashedPassword,
formDataRaw.password
)
if (!validPassword) {
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
throw new Error('Incorrect email or password')
}
const session = await lucia.createSession(user.id, {})
const sessionCookie = lucia.createSessionCookie(session.id)
cookies().set(
sessionCookie.name,
sessionCookie.value,
sessionCookie.attributes
)
} catch (error) {
// TODO: add error feedback yourself
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
}
redirect('/dashboard')
}
export { signIn }
getAuth function:
// src/features/auth/queries/get-auth.ts
import type { Session, User } from 'lucia'
import { cookies } from 'next/headers'
import { cache } from 'react'
import { lucia } from '@/lib/lucia'
export const getAuth = cache(
async (): Promise<
{ user: User, session: Session } | { user: null, session: null }
> => {
const sessionId
= cookies().get(lucia.sessionCookieName)?.value ?? null
if (!sessionId) {
return {
user: null,
session: null,
}
}
const result = await lucia.validateSession(sessionId)
try {
if (result.session && result.session.fresh) {
const sessionCookie = lucia.createSessionCookie(
result.session.id
)
cookies().set(
sessionCookie.name,
sessionCookie.value,
sessionCookie.attributes
)
}
if (!result.session) {
const sessionCookie = lucia.createBlankSessionCookie()
cookies().set(
sessionCookie.name,
sessionCookie.value,
sessionCookie.attributes
)
}
} catch {}
return result
}
)
SingOut React Server Component:
// src/features/auth/actions/sign-out.ts
'use server'
import { cookies } from 'next/headers'
import { redirect } from 'next/navigation'
import { lucia } from '@/lib/lucia'
import { getAuth } from '../queries/get-auth'
export async function signOut(_formData: FormData) {
const { session } = await getAuth()
if (!session)
redirect('/sign-in')
await lucia.invalidateSession(session.id)
const sessionCookie = lucia.createBlankSessionCookie()
cookies().set(
sessionCookie.name,
sessionCookie.value,
sessionCookie.attributes
)
redirect('/sign-in')
}
Protected routes:
// src/app/(authenticated)/layout.tsx
// - src/app/(authenticated)/dashboard/page.tsx
// - src/app/(authenticated)/account/page.tsx
// - and more ...
import { redirect } from 'next/navigation'
import { getAuth } from '@/features/auth/queries/get-auth'
export default async function AuthenticatedLayout({
children,
}: Readonly<{
children: React.ReactNode
}>) {
const { user } = await getAuth()
if (!user)
redirect('/sign-in')
return <>{children}</>
}
Authorization UI:
// src/app/layout.tsx
import Link from 'next/link'
import { getAuth } from '@/features/auth/queries/get-auth'
export default function RootLayout() {
const { user } = await getAuth()
const appNav = (
<>
<li>
<Link href="/">LOGO</Link>
</li>
{user && (
<li>
<Link href="/dashboard">Dashboard</Link>
</li>
)}
</>
)
const authNav = user
? (
<li>
<form action={signOut}>
<button type="submit">Sign Out</button>
</form>
</li>
)
: (
<>
<li>
<Link href="/sign-up">Sign Up</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link href="/sign-in">Sign In</Link>
</li>
</>
)
}
Token
- 客户端发送登录信息 (ID, Password).
- 服务端收到请求验证成功后, 服务端会签发一个 Token (包含用户信息) 并发送给客户端.
- 客户端收到 Token 后存储到 Cookie 或 Local Storage,
客户端每次向服务端请求都需在 Request Header 中设置:
Authorization: <Token>. - 服务端收到请求并验证 Token, 成功发送资源 (鉴权成功), 不成功发送 401 错误代码 (鉴权失败).
- 多端兼容性: Token 认证不局限于浏览器 (Cookie).
- 安全性: 不使用 Cookie 可以规避 CSRF 攻击.
- 灵活性: Token 中包含了用户信息, 不需要 Key-Value Store 持久化, 分布式友好. 服务器端变成无状态, 服务器端只需要根据定义的规则校验 Token 合法性. 上述两点使得 Token Authentication 具有更好的扩展性.
- Token 认证 (加密解密过程) 比 Session Cookie 更消耗性能.
- Token (包含用户信息) 比 Session ID 大, 更占带宽.
- 不保存 Session 状态, 无法中止或更改 Token 权限, Token 到期前会始终有效, 存在盗用风险:
- Token 有效期应短.
- Token 应使用 HTTPS 协议.
- 对于重要权限, 需使用二次验证 (Two Factor Authentication).
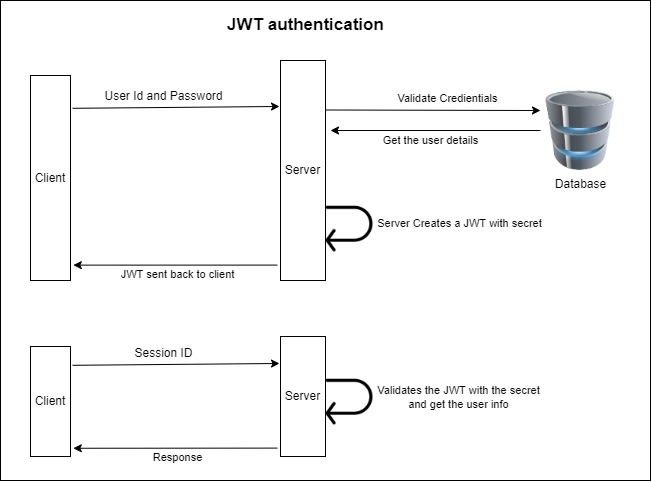
JSON Web Token
JSON Web Tokens is small, object-friendly (compared to SAML, Security Assertion Markup Language Tokens) and security for public/private key pair (compared to SWT, Simple Web Tokens):
- 基于 Token 的解决方案中最常用的是 JWT.
- 服务器认证用户密码以后, 生成一个 JSON 对象并签名加密后作为 Token 返回给用户.
- JSON 对象包含用户信息, 用户身份, 令牌过期时间等:
- Header: 明文 Base64 编码 JSON 对象, 描述 JWT 的元数据.
一般为 Token 的加密算法和 Token 的类型, 如
{"alg": "HS256","typ": "JWT"}. - Payload: 明文 Base64 编码 JSOn 对象, 存放实际数据. 有 7 个官方字段和部分定义私有字段, 一般存放用户名, 用户身份, JWT 描述字段.
- Signature: 对 Header 和 Payload 的签名, 利用签名验证信息的正确性, 防止数据篡改. 签名需要服务端保存的密钥.
- Header: 明文 Base64 编码 JSON 对象, 描述 JWT 的元数据.
一般为 Token 的加密算法和 Token 的类型, 如
- 把三个部分拼成一个字符串, 每个部分之间用
.分隔:HeaderBase64.PayloadBase64.Signature. - 业务接口用来鉴权的 token 为
access token. 越是权限敏感的业务,access token有效期足够短, 以避免被盗用. - 一个专门生成
access token的 token, 称为refresh token.refresh token用来获取access token, 有效期更长, 通过独立服务和严格的请求方式增加安全性.
- JWT 默认是不加密.
- JWT 不加密的情况下, 不能将秘密数据写入 JWT.
- JWT 可以加密, 生成原始 Token 以后, 可以用密钥再加密一次.
- JWT 不仅可用于认证, 也可用于交换信息. 有效使用 JWT, 可以降低服务器查询数据库的次数.
- 不保存 Session 状态, 无法中止或更改 Token 权限, Token 到期前会始终有效, 存在盗用风险:
- JWT 有效期应短.
- JWT 应使用 HTTPS 协议.
- 对于重要权限, 需使用二次验证 (Two Factor Authentication).
Client
- HTTP request with credential data (email/password) for first request, get token data or error code from first response.
- Intercept token to
fetch/axiosrequest headers for rest requests- Sent requests with token data.
- Logout whenever token data inspire or deleted.
- Store token in
Redux/Vuexglobal state. - Store token in
localStorage/sessionStorage.
OAuth
OAuth (Open Authorization) 是一个开放标准, 作用于第三方授权和第三方访问. 用户数据的所有者告诉系统, 同意授权第三方应用进入系统, 获取这些数据. 系统从而产生一个短期进入令牌 (Token), 用来代替密码供第三方应用使用.
第三方应用申请令牌之前, 都必须先到系统备案, 说明自己的身份, 然后会拿到两个身份识别码: Client ID 和 Client Secret. 这是为了防止令牌被滥用, 没有备案过的第三方应用拿不到令牌 (Token).
OAuth Token 特征:
- 授权短 (Short Expire Time).
- 可撤销 (Revoke).
- 权限小 (Scope).
- 在 GitHub Developer Settings 中备案第三方应用, 拿到属于它的客户端 ID 和客户端密钥 (3rd-Party Server vs Resource Owner)
- 在自己的第三方网站提供一个 GitHub 登录链接,
用户点击该链接后会跳转到 GitHub OAuth API
https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize/?client_id=${clientID}. - 用户跳转到 GitHub, 通过验证并同意使用 GitHub 身份登录第三方网站, 此时就会带着授权码 Code 跳回第三方网站.
- 第三方网站收到授权码, 利用授权码, 客户端 ID, 客户端密钥向 GitHub 请求
access_token令牌https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token?client_id=${clientID}&client_secret=${clientSecret}&code=${code}(3rd-Party Server vs Authorization Server) - 第三方网站收到令牌, 可以暂时拥有 GitHub 一些请求的权限比如用户信息,
https://api.github.com/user?access_token=${accessToken}或者 Request HeaderAuthorization: token ${accessToken}. 可以构建第三方网站自己的 Token, 做进一步相关鉴权操作 (如 Session Cookie). (3rd-Party Server vs Resource Server)
2.0
OAuth 2.0 允许自动更新令牌. 资源所有者颁发令牌时一次性颁发两个令牌, 一个用于获取数据 (Access Token), 另一个用于获取新的令牌 (Refresh Token). 令牌到期前, 第三方网站使用 Refresh Token 发请求更新令牌:
https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token
?client_id=CLIENT_ID
&client_secret=CLIENT_SECRET
&grant_type=refresh_token
&refresh_token=REFRESH_TOKEN
Single Sign On
单点登录 (SSO) 要求不同域下的系统一次登录, 全线通用,
通常由独立的 SSO 系统记录登录状态, 下发 ticket,
各业务系统配合存储和认证 ticket:
- 用户访问系统 1 的受保护资源, 系统 1 发现用户未登录, 跳转至
SSO认证中心, 并将自己的地址作为参数. SSO认证中心发现用户未登录, 将用户引导至登录页面.- 用户输入用户名密码提交登录申请.
SSO认证中心校验用户信息, 创建用户与SSO认证中心之间的会话, 称为全局会话, 同时创建授权令牌.SSO认证中心带着令牌跳转会最初的请求地址 (系统 1).- 系统 1 拿到令牌, 去
SSO认证中心校验令牌是否有效. SSO认证中心校验令牌, 返回有效, 注册系统 1 .- 系统 1 使用该令牌创建与用户的会话, 称为局部会话, 返回受保护资源.
- 用户访问系统 2 的受保护资源.
- 系统 2 发现用户未登录, 跳转至
SSO认证中心, 并将自己的地址作为参数. SSO认证中心发现用户已登录, 跳转回系统 2 的地址, 并附上令牌.- 系统 2 拿到令牌, 去
SSO认证中心校验令牌是否有效. SSO认证中心校验令牌, 返回有效, 注册系统 2 .- 系统 2 使用该令牌创建与用户的局部会话, 返回受保护资源.
用户登录成功之后,
用户与 SSO 认证中心建立的会话称为全局会话,
用户与各个子系统建立的会话称为局部会话,
局部会话建立之后, 用户访问子系统受保护资源将不再通过 SSO 认证中心:
- 局部会话存在, 全局会话一定存在.
- 全局会话存在, 局部会话不一定存在.
- 全局会话销毁, 局部会话必须销毁.
References
- Modern guide to OAuth.