DOM
- DOM Level 0.
- DOM Level 1:
- DOM Core.
- DOM XML.
- DOM HTML.
- DOM Level 2:
- DOM2 Core.
- DOM2 XML.
- DOM2 HTML.
- DOM2 Views.
- DOM2 StyleSheets.
- DOM2 CSS.
- DOM2 CSS 2.
- DOM2 Events.
- DOM2 UIEvents.
- DOM2 MouseEvents.
- DOM2 MutationEvents (Deprecated).
- DOM2 HTMLEvents.
- DOM2 Range.
- DOM2 Traversal.
- DOM Level 3:
- DOM3 Core.
- DOM3 XML.
- DOM3 Events.
- DOM3 UIEvents.
- DOM3 MouseEvents.
- DOM3 MutationEvents (Deprecated).
- DOM3 MutationNameEvents.
- DOM3 TextEvents.
- DOM3 Load and Save.
- DOM3 Load and Save Async.
- DOM3 Validation.
- DOM3 XPath.
const hasXmlDom = document.implementation.hasFeature('XML', '1.0')
const hasHtmlDom = document.implementation.hasFeature('HTML', '1.0')
Nodes
document.createElement('nodeName')
document.createTextNode('String')
document.getElementById(id)
document.getElementsByName(elementName)
document.getElementsByTagName(tagName)
document.getElementsByClassName(className) // HTML5
document.querySelector(cssSelector) // Selectors API
document.querySelectorAll(cssSelector) // Selectors API
element.getAttribute(attrName) // get default HTML attribute
element.setAttribute(attrName, attrValue)
element.removeAttribute(attrName)
element.compareDocumentPosition(element)
element.contains(element)
element.isSameNode(element) // Same node reference
element.isEqualNode(element) // Same nodeName/nodeValue/attributes/childNodes
element.matches(cssSelector)
element.closest(cssSelector) // Returns closest ancestor matching selector
element.cloneNode()
element.normalize()
element.before(...elements)
element.after(...elements)
element.replaceWith(...elements)
element.remove()
parentElement.hasChildNodes()
parentElement.appendChild(childElement)
parentElement.append(childElements)
parentElement.insertBefore(newChild, targetChild)
parentElement.replaceChild(newChild, targetChild)
parentElement.replaceChildren(children)
parentElement.removeChild(child)
function showAlert(type, message, duration = 3) {
const div = document.createElement('div')
div.className = type
div.appendChild(document.createTextNode(message))
container.insertBefore(div, form)
setTimeout(() => div.remove(), duration * 1000)
}
Node Type
Node 除包括元素结点 (tag) 外,
包括许多其它结点 (甚至空格符视作一个结点),
需借助 nodeType 找出目标结点.
| Node Type | Node Representation | Node Name | Node Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ELEMENT_NODE | Tag Name | null |
| 2 | ATTRIBUTE_NODE | Attr Name | Attr Value |
| 3 | TEXT_NODE | #text | Text |
| 4 | CDATA_SECTION_NODE | #cdata-section | CDATA Section |
| 5 | ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE | ||
| 6 | ENTITY_NODE | ||
| 8 | COMMENT_NODE | #comment | Comment |
| 9 | DOCUMENT_NODE | #document | null |
| 10 | DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE | html/xml | null |
| 11 | DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE | #document-fragment | null |
| 12 | NOTATION_NODE |
const type = node.nodeType
const name = node.nodeName
const value = node.nodeValue
if (someNode.nodeType === Node.ELEMENT_NODE)
alert('Node is an element.')
Attribute
const id = element.attributes.getNamedItem('id').nodeValue
const id = element.attributes.id.nodeValue
element.attributes.id.nodeValue = 'someOtherId'
const oldAttr = element.attributes.removeNamedItem('id')
element.attributes.setNamedItem(newAttr)
const attr = document.createAttribute('align')
attr.value = 'left'
element.setAttributeNode(attr)
alert(element.attributes.align.value) // "left"
alert(element.getAttributeNode('align').value) // "left"
alert(element.getAttribute('align')) // "left"
Further reading: DOM properties reflection on HTML attributes.
Text
Text node methods:
- appendData(text): 向节点末尾添加文本 text.
- deleteData(offset, count): 从位置 offset 开始删除 count 个字符.
- insertData(offset, text): 在位置 offset 插入 text.
- replaceData(offset, count, text): 用 text 替换从位置 offset 到 offset + count 的文本.
- splitText(offset): 在位置 offset 将当前文本节点拆分为两个文本节点.
- substringData(offset, count): 提取从位置 offset 到 offset + count 的文本.
Normalize text nodes:
const element = document.createElement('div')
element.className = 'message'
const textNode = document.createTextNode('Hello world!')
const anotherTextNode = document.createTextNode('Yippee!')
element.appendChild(textNode)
element.appendChild(anotherTextNode)
document.body.appendChild(element)
alert(element.childNodes.length) // 2
element.normalize()
alert(element.childNodes.length) // 1
alert(element.firstChild.nodeValue) // "Hello world!Yippee!"
Split text nodes:
const element = document.createElement('div')
element.className = 'message'
const textNode = document.createTextNode('Hello world!')
element.appendChild(textNode)
document.body.appendChild(element)
const newNode = element.firstChild.splitText(5)
alert(element.firstChild.nodeValue) // "Hello"
alert(newNode.nodeValue) // " world!"
alert(element.childNodes.length) // 2
textContent:- Security: Doesn’t parse HTML.
- Performance: Including
<script>and<style>text content.
innerText:- Doesn't parse HTML.
- Only show human-readable text content
innerTextcare CSS styles, readinnerTextvalue will triggerreflow.
innerHTML:- Do parse HTML.
const textContent = element.textContent
const innerHTML = element.innerHTML
// eslint-disable-next-line unicorn/prefer-dom-node-text-content -- API example
const innerText = element.innerText
Document
document node (#document):
alert(document.nodeType) // 9
alert(document.nodeName) // "#document"
alert(document.nodeValue) // null
const html = document.documentElement
const doctype = document.doctype
const head = document.head // HTML5 head.
const body = document.body
const title = document.title // 可修改.
const domain = document.domain // 可设置同源域名.
const url = document.URL
const referer = document.referer
const charSet = document.characterSet // HTML5 characterSet.
const anchors = documents.anchors
const images = documents.images
const links = documents.links
const forms = documents.forms
const formElements = documents.forms[0].elements // 第一个表单内的所有字段
// HTML5 compatMode:
if (document.compatMode === 'CSS1Compat')
console.log('Standards mode')
else if (document.compatMode === 'BackCompat')
console.log('Quirks mode')
document.getElementById(id)
document.getElementsByName(name)
document.getElementsByTagName(tagName)
document.getElementsByClassName(className) // HTML5
document.querySelector(cssSelector) // Selectors API
document.querySelectorAll(cssSelector) // Selectors API
document.write()
document.writeln()
Document Type
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-// W3C// DTD HTML 4.01// EN" "http:// www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
console.log(document.doctype.name) // "html"
console.log(document.nodeType) // 10
console.log(document.doctype.nodeName) // "html"
console.log(document.doctype.nodeValue) // null
console.log(document.doctype.publicId) // "-// W3C// DTD HTML 4.01// EN"
console.log(document.doctype.systemId) // "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd"
const doctype = document.implementation.createDocumentType(
'html',
'-// W3C// DTD HTML 4.01// EN',
'http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd'
)
const doc = document.implementation.createDocument(
'http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml',
'html',
doctype
)
Document Fragment
减少 DOM 操作次数, 减少页面渲染次数:
const frag = document.createDocumentFragment()
let p
let t
p = document.createElement('p')
t = document.createTextNode('first paragraph')
p.appendChild(t)
frag.appendChild(p)
p = document.createElement('p')
t = document.createTextNode('second paragraph')
p.appendChild(t)
frag.appendChild(p)
// 只渲染一次HTML页面
document.body.appendChild(frag)
克隆节点进行处理, 处理完毕后再替换原节点:
const oldNode = document.getElementById('result')
const clone = oldNode.cloneNode(true)
// work with the clone
// when you're done:
oldNode.parentNode.replaceChild(clone, oldNode)
Parse HTML:
const range = document.createRange()
const parse = range.createContextualFragment.bind(range)
parse(`<ol>
<li>a</li>
<li>b</li>
</ol>
<ol>
<li>c</li>
<li>d</li>
</ol>`)
function parseHTML(string) {
const context = document.implementation.createHTMLDocument()
// Set the base href for the created document so any parsed elements with URLs
// are based on the document's URL
const base = context.createElement('base')
base.href = document.location.href
context.head.appendChild(base)
context.body.innerHTML = string
return context.body.children
}
Manipulation
Append
| Method | Node | HTML | Text | IE | Event Listeners | Secure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| append | Yes | No | Yes | No | Preserves | Yes |
| appendChild | Yes | No | No | Yes | Preserves | Yes |
| innerHTML | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Loses | Careful |
| insertAdjacentHTML | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Preserves | Careful |
const testDiv = document.getElementById('testDiv')
const para = document.createElement('p')
testDiv.appendChild(para)
const txt = document.createTextNode('Hello World')
para.appendChild(txt)
innerHTML: non-concrete, including all types of childNodes:
div.innerHTML = '<p>Test<em>test</em>Test.</p>'
// <div>
// <p>Test<em>test</em>Test.</p>
// </div>
innerHTML performance:
// BAD
for (const value of values)
ul.innerHTML += `<li>${value}</li>` // 别这样做!
// GOOD
let itemsHtml = ''
for (const value of values)
itemsHtml += `<li>${value}</li>`
ul.innerHTML = itemsHtml
// BEST
ul.innerHTML = values.map(value => `<li>${value}</li>`).join('')
Insert
// Append
el.appendChild(newEl)
// Prepend
el.insertBefore(newEl, el.firstChild)
// InsertBefore
el.parentNode.insertBefore(newEl, el)
// InsertAfter
function insertAfter(newElement, targetElement) {
const parent = targetElement.parentNode
if (parent.lastChild === targetElement)
parent.appendChild(newElement)
else
parent.insertBefore(newElement, targetElement.nextSibling)
}
insertAdjacentHTML/insertAdjacentText:
- beforebegin: 插入前一个兄弟节点.
- afterbegin: 插入第一个子节点.
- beforeend: 插入最后一个子节点.
- afterend: 插入下一个兄弟节点.
// 4 positions:
//
// <!-- beforebegin -->
// <p>
// <!-- afterbegin -->
// foo
// <!-- beforeend -->
// </p>
// <!-- afterend -->
const p = document.querySelector('p')
p.insertAdjacentHTML('beforebegin', '<a></a>')
p.insertAdjacentText('afterbegin', 'foo')
// simply be moved element, not copied element
p.insertAdjacentElement('beforebegin', link)
Replace
node.replaceChild(document.createTextNode(text), node.firstChild)
node.replaceChildren(...nodeList)
Remove
// 删除第一个子节点
const formerFirstChild = someNode.removeChild(someNode.firstChild)
// 删除最后一个子节点
const formerLastChild = someNode.removeChild(someNode.lastChild)
while (div.firstChild)
div.removeChild(div.firstChild)
// Remove self
el.parentNode.removeChild(el)
el.remove()
Traverse
const parent = node.parentNode
const children = node.childNodes
const first = node.firstChild
const last = node.lastChild
const previous = node.previousSibling
const next = node.nextSibling
node.matches(selector)
Element Traversal API:
navigation properties listed above refer to all nodes.
For instance,
in childNodes can see both text nodes, element nodes, and even comment nodes.
const count = el.childElementCount
const parent = el.parentElement
const children = el.children
const first = el.firstElementChild
const last = el.lastElementChild
const previous = el.previousElementSibling
const next = el.nextElementSibling
el.matches(selector)
NodeList is iterable:
const elements = document.querySelectorAll('div')
for (const element of elements)
console.log(element)
const div = document.getElementById('div1')
function filter(node) {
return node.tagName.toLowerCase() === 'li'
? NodeFilter.FILTER_ACCEPT
: NodeFilter.FILTER_SKIP
}
const iterator = document.createNodeIterator(
div,
NodeFilter.SHOW_ELEMENT,
filter,
false
)
for (
let node = iterator.nextNode();
node !== null;
node = iterator.nextNode()
)
console.log(node.tagName) // 输出标签名
const div = document.getElementById('div1')
const walker = document.createTreeWalker(
div,
NodeFilter.SHOW_ELEMENT,
null,
false
)
walker.firstChild() // 前往<p>
walker.nextSibling() // 前往<ul>
for (
let node = walker.firstChild();
node !== null;
node = walker.nextSibling()
)
console.log(node.tagName) // 遍历 <li>
NodeFilter.acceptNode()FILTER_REJECT:- For
NodeIterator, this flag is synonymous withFILTER_SKIP. - For
TreeWalker, child nodes are also rejected.
- For
TreeWalkerhas more methods:firstChild.lastChild.previousSibling.nextSibling.
Attributes
HTML attributes 设置对应的 DOM properties 初始值:
alert(div.getAttribute('id')) // "myDiv" default div.id
alert(div.getAttribute('class')) // "bd" default div.class
div.setAttribute('id', 'someOtherId')
div.setAttribute('class', 'ft')
div.removeAttribute('id')
div.removeAttribute('class')
// `data-src`
console.log(el.dataset.src)
Select
startContainer: 范围起点所在的节点 (选区中第一个子节点的父节点).startOffset: 范围起点在 startContainer 中的偏移量.endContainer: 范围终点所在的节点 (选区中最后一个子节点的父节点).endOffset: 范围起点在 startContainer 中的偏移量.commonAncestorContainer: 文档中以startContainer和endContainer为后代的最深的节点.setStartBefore(refNode): 把范围的起点设置到 refNode 之前, 从而让 refNode 成为选区的第一个子节点.setStartAfter(refNode): 把范围的起点设置到 refNode 之后, 从而将 refNode 排除在选区之外, 让其下一个同胞节点成为选区的第一个子节点.setEndBefore(refNode): 把范围的终点设置到 refNode 之前, 从而将 refNode 排除在选区之外, 让其上一个同胞节点成为选区的最后一个子节点.setEndAfter(refNode): 把范围的终点设置到 refNode 之后, 从而让 refNode 成为选区的最后一个子节点.setStart(refNode, offset).setEnd(refNode, offset).deleteContents(): remove.extractContents(): remove and return.cloneContents(): clone.insertNode(node): 在范围选区的开始位置插入一个节点.surroundContents(node): 插入包含范围的内容.collapse(boolean): 范围折叠.compareBoundaryPoints(Range.HOW, sourceRange): 确定范围之间是否存在公共的边界 (起点或终点).
<!doctype html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="p1"><b>Hello</b> world!</p>
</body>
</html>
const p1 = document.getElementById('p1')
const helloNode = p1.firstChild.firstChild
const worldNode = p1.lastChild
const range = document.createRange()
range.setStart(helloNode, 2)
range.setEnd(worldNode, 3)
const fragment1 = range.cloneContents() // clone
const fragment2 = range.extractContents() // remove and return
p1.parentNode.appendChild(fragment1)
p1.parentNode.appendChild(fragment2)
const p1 = document.getElementById('p1')
const helloNode = p1.firstChild.firstChild
const worldNode = p1.lastChild
const range = document.createRange()
const span = document.createElement('span')
span.style.color = 'red'
span.appendChild(document.createTextNode('Inserted text'))
range.setStart(helloNode, 2)
range.setEnd(worldNode, 3)
range.insertNode(span)
// <p id="p1"><b>He<span style="color: red">Inserted text</span>llo</b> world</p>
const p1 = document.getElementById('p1')
const helloNode = p1.firstChild.firstChild
const worldNode = p1.lastChild
const range = document.createRange()
const span = document.createElement('span')
span.style.backgroundColor = 'yellow'
range.selectNode(helloNode)
range.surroundContents(span)
// <p><b><span style="background-color:yellow">Hello</span></b> world!</p>
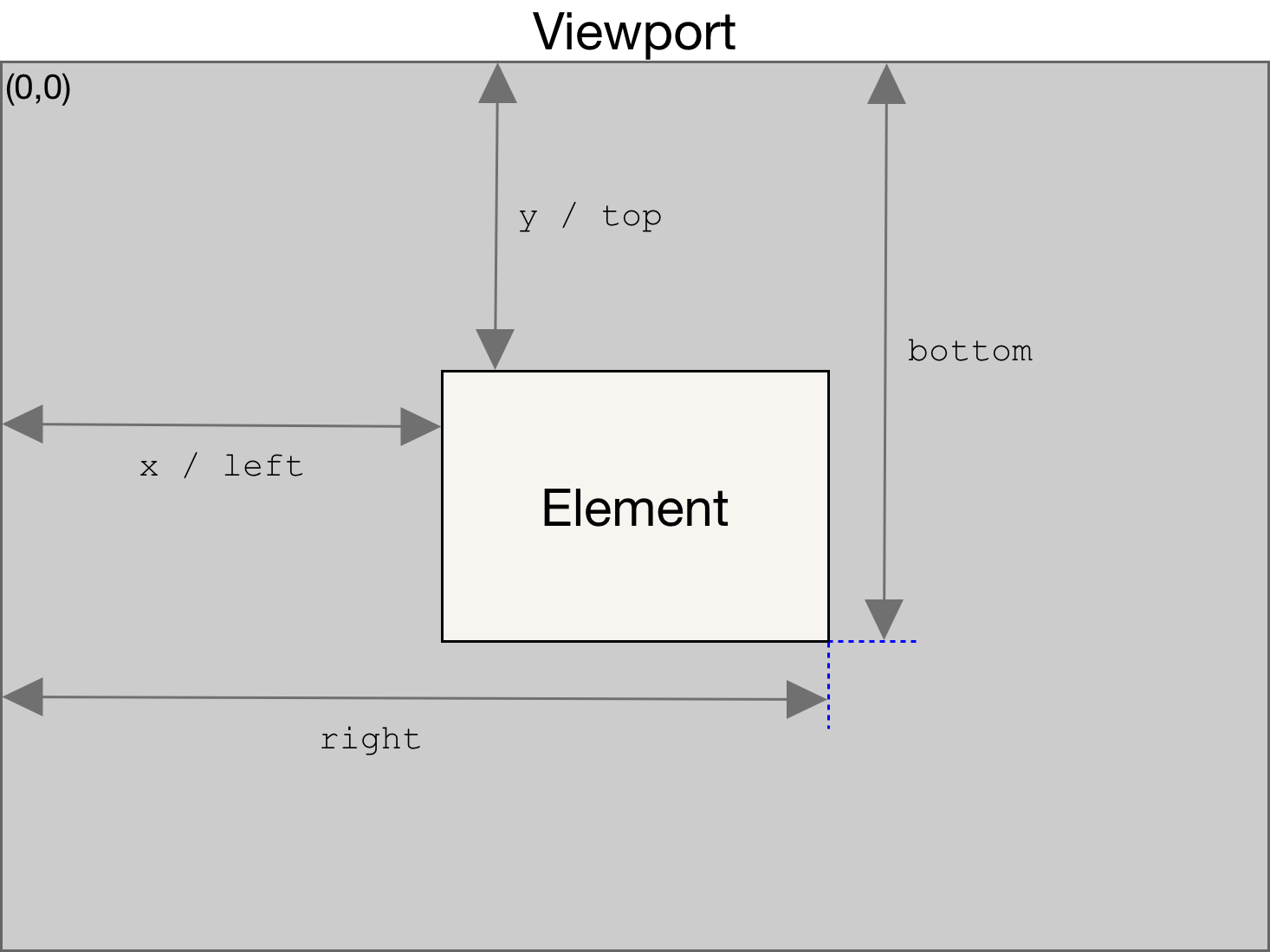
Geometry
Dimensions
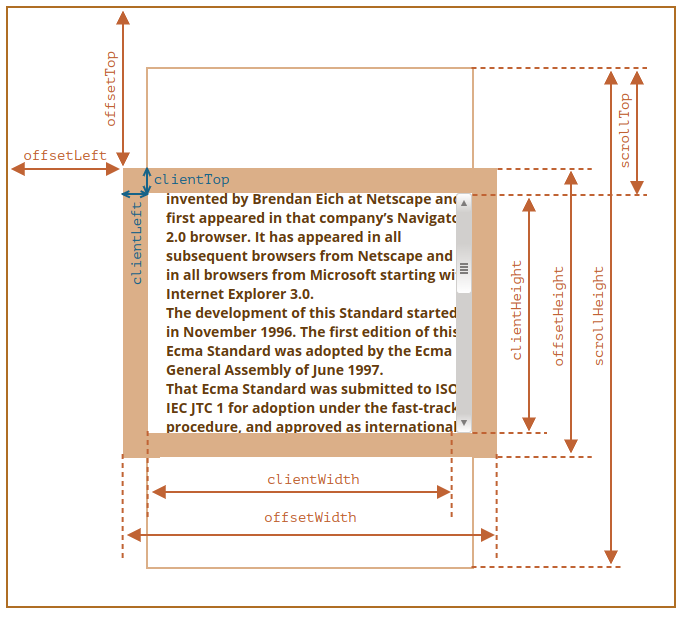
- outerHeight: 整个浏览器窗口的大小, 包括窗口标题/工具栏/状态栏等.
- innerHeight: DOM 视口的大小, 包括滚动条.
- offsetHeight: 整个可视区域大小, 包括 border 和 scrollbar 在内 (content + padding + border).
- clientHeight: 内部可视区域大小 (content + padding).
- scrollHeight: 元素内容的高度, 包括溢出部分.
// const supportInnerWidth = window.innerWidth !== undefined;
// const supportInnerHeight = window.innerHeight !== undefined;
// const isCSS1Compat = (document.compatMode || '') === 'CSS1Compat';
const width
= window.innerWidth
|| document.documentElement.clientWidth
|| document.body.clientWidth
const height
= window.innerHeight
|| document.documentElement.clientHeight
|| document.body.clientHeight
// 缩放到 100×100
window.resizeTo(100, 100)
// 缩放到 200×150
window.resizeBy(100, 50)
// 缩放到 300×300
window.resizeTo(300, 300)
In case of transforms, the offsetWidth and offsetHeight returns the layout width and height (all the same), while getBoundingClientRect() returns the rendering width and height.
getBoundingClientRect:
function isElementInViewport(el) {
const { top, height, left, width } = el.getBoundingClientRect()
const w
= window.innerWidth
|| document.documentElement.clientWidth
|| document.body.clientWidth
const h
= window.innerHeight
|| document.documentElement.clientHeight
|| document.body.clientHeight
return top <= h && top + height >= 0 && left <= w && left + width >= 0
}
Position
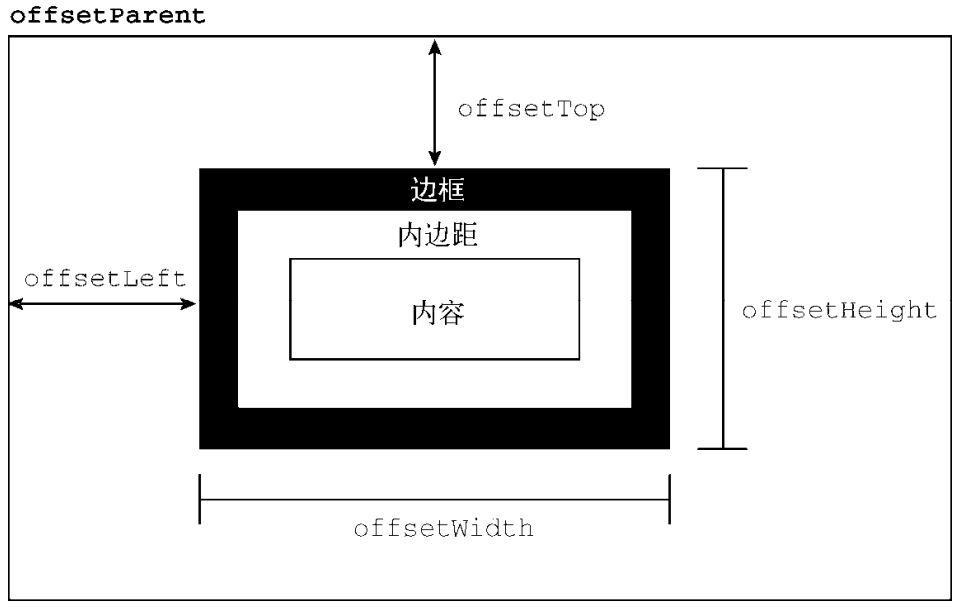
- offsetLeft/offsetTop: 表示该元素的左上角 (边框外边缘) 与已定位的父容器 (offsetParent 对象) 左上角的距离.
- clientLeft/clientTop:
表示该元素 padding 至 margin 的距离,
始终等于
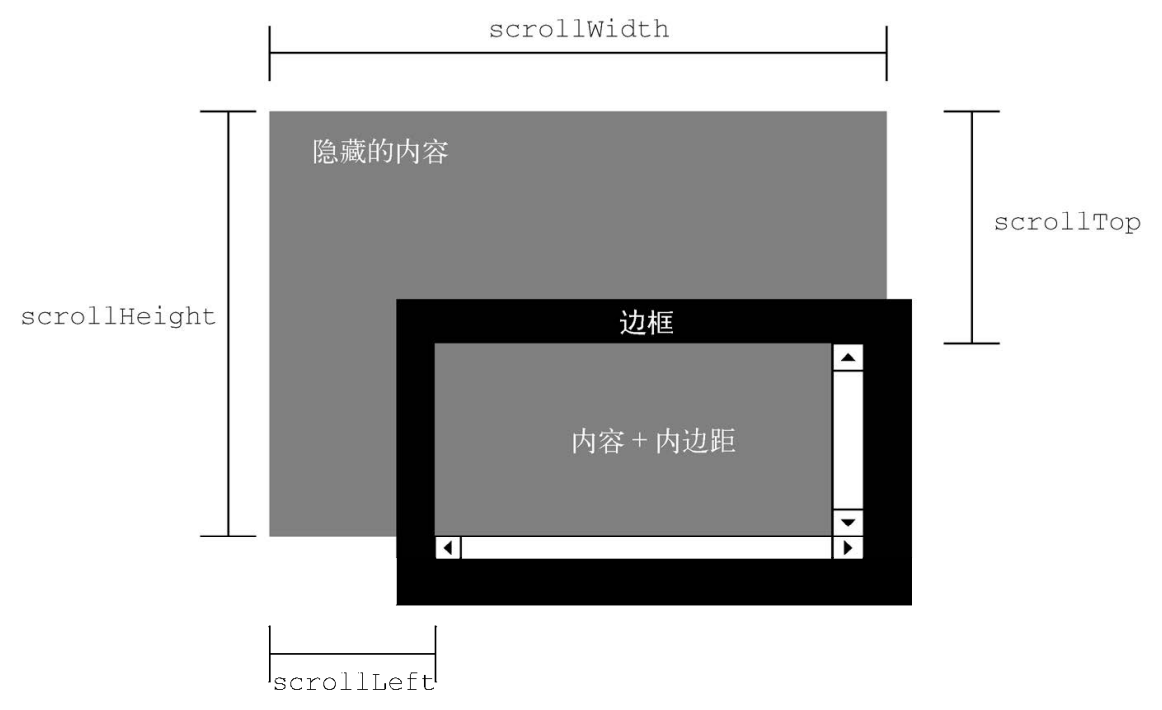
.getComputedStyle()返回的border-left-width/border-top-width. - scrollLeft/scrollTop: 元素滚动条位置, 被隐藏的内容区域左侧/上方的像素位置.
function getElementLeft(element) {
let actualLeft = element.offsetLeft
let current = element.offsetParent
while (current !== null) {
actualLeft += current.offsetLeft
current = current.offsetParent
}
return actualLeft
}
function getElementTop(element) {
let actualTop = element.offsetTop
let current = element.offsetParent
while (current !== null) {
actualTop += current.offsetTop
current = current.offsetParent
}
return actualTop
}
// 把窗口移动到左上角
window.moveTo(0, 0)
// 把窗口向下移动 100 像素
window.moveBy(0, 100)
// 把窗口移动到坐标位置 (200, 300)
window.moveTo(200, 300)
// 把窗口向左移动 50 像素
window.moveBy(-50, 0)
Scrolling
- scrollLeft/scrollX/PageXOffset: 元素内容向右滚动了多少像素, 如果没有滚动则为 0.
- scrollTop/scrollY/pageYOffset: 元素内容向上滚动了多少像素, 如果没有滚动则为 0.
// const supportPageOffset = window.pageXOffset !== undefined;
// const isCSS1Compat = (document.compatMode || '') === 'CSS1Compat';
const x
= window.pageXOffset
|| document.documentElement.scrollLeft
|| document.body.scrollLeft
const y
= window.pageYOffset
|| document.documentElement.scrollTop
|| document.body.scrollTop
if (window.innerHeight + window.pageYOffset === document.body.scrollHeight)
console.log('Scrolled to Bottom!')
// 相对于当前视口向下滚动 100 像素
window.scrollBy(0, 100)
// 相对于当前视口向右滚动 40 像素
window.scrollBy(40, 0)
// 滚动到页面左上角
window.scrollTo(0, 0)
// 滚动到距离屏幕左边及顶边各 100 像素的位置
window.scrollTo(100, 100)
// 正常滚动
window.scrollTo({
left: 100,
top: 100,
behavior: 'auto',
})
// 平滑滚动
window.scrollTo({
left: 100,
top: 100,
behavior: 'smooth',
})
document.forms[0].scrollIntoView() // 窗口滚动后, 元素底部与视口底部对齐.
document.forms[0].scrollIntoView(true) // 窗口滚动后, 元素顶部与视口顶部对齐.
document.forms[0].scrollIntoView({ block: 'start' })
document.forms[0].scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth', block: 'start' })
Loading
Dynamic Scripts
function loadScript(url) {
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.src = url
script.async = true
document.body.appendChild(script)
}
function loadScriptString(code) {
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.async = true
script.type = 'text/javascript'
try {
script.appendChild(document.createTextNode(code))
} catch (ex) {
script.text = code
}
document.body.appendChild(script)
}
所有现代浏览器中, 通过 innerHTML 属性创建的 <script> 元素永远不会执行.
Dynamic Styles
function loadStyles(url) {
const link = document.createElement('link')
link.rel = 'stylesheet'
link.type = 'text/css'
link.href = url
const head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0]
head.appendChild(link)
}
function loadStyleString(css) {
const style = document.createElement('style')
style.type = 'text/css'
try {
style.appendChild(document.createTextNode(css))
} catch (ex) {
style.styleSheet.cssText = css
}
const head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0]
head.appendChild(style)
}
- 若重用同一个
<style>元素并设置该属性超过一次, 则可能导致浏览器崩溃. - 将
cssText设置为空字符串也可能导致浏览器崩溃.
XML Namespace
XML 命名空间可以实现在一个格式规范的文档中混用不同的 XML 语言,
避免元素命名冲突 (tagName/localName/namespaceURI):
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>Example XHTML page</title>
</head>
<body>
<s:svg xmlns:s="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1" viewBox="0 0 100 100" style="width: 100%; height: 100%">
<s:rect x="0" y="0" width="100" height="100" style="fill: red" />
</s:svg>
</body>
</html>
console.log(document.body.isDefaultNamespace('http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml'))
console.log(svg.lookupPrefix('http://www.w3.org/2000/svg')) // "s"
console.log(svg.lookupNamespaceURI('s')) // "http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
const newSvg = document.createElementNS('http://www.w3.org/2000/svg', 'svg')
const newAttr = document.createAttributeNS('http://www.somewhere.com', 'random')
const elems = document.getElementsByTagNameNS(
'http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml',
'*'
)