Engine
Variables Lifecycle
- Creation phase (Hoisting)
- Declaration phase: 在作用域中注册变量
- Initialization phase: 分配内存, 在作用域中绑定变量 (
undefined)
- Execution phase/Assignment phase
Execution Context
Global
- Create global object (
window). - Create
thisobject (refer towindow). - Declare and initialize variable/function (
undefined), setup memory space for them.
Function
- Create arguments object.
- Create
thisobject. - Declare and initialize variable(
undefined)/function, store them into memory.
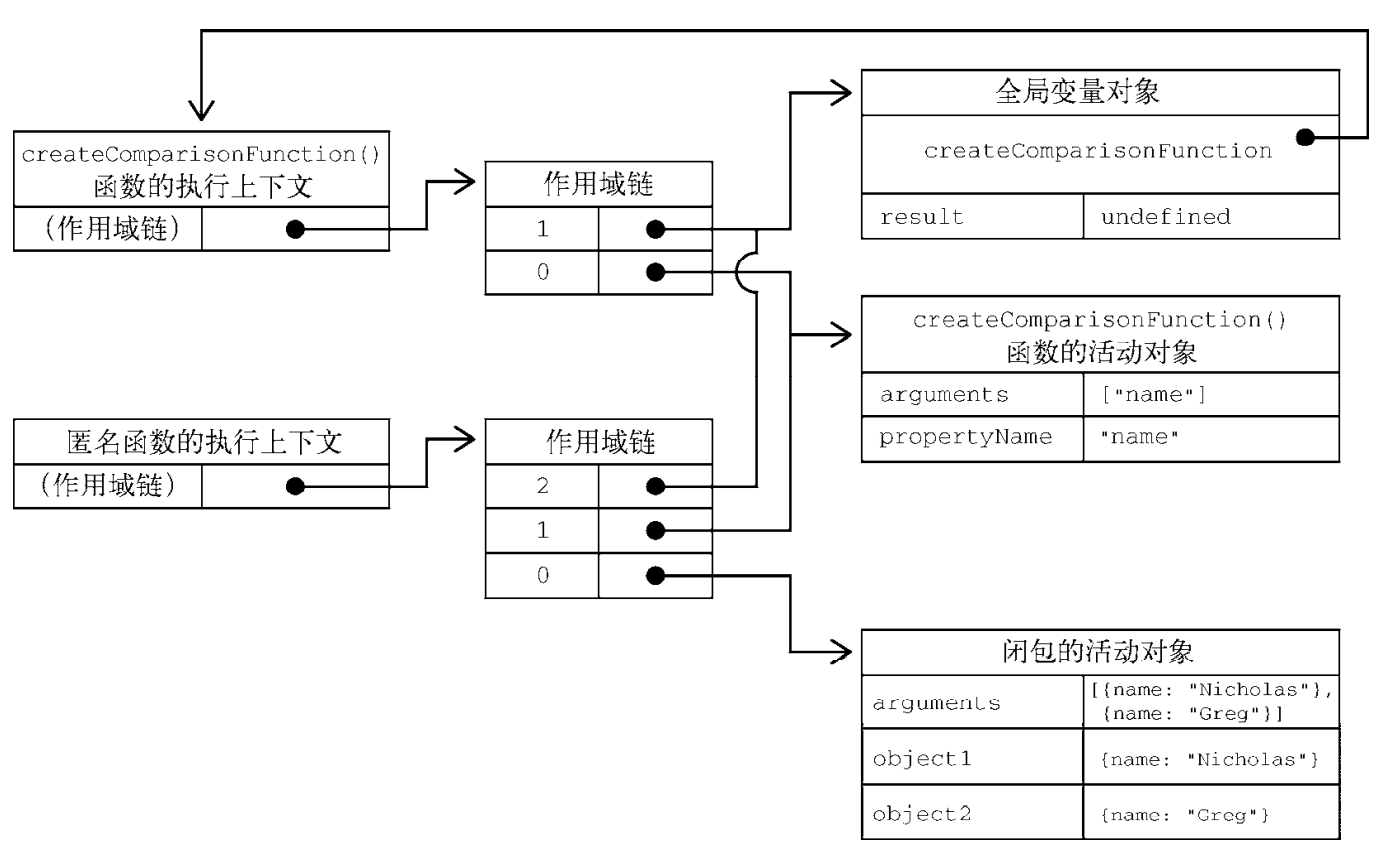
如果 JavaScript 引擎在函数执行上下文中找不到变量, 它会在最近的父级执行上下文中查找该变量. 这个查找链将会一直持续, 直到引擎查找到全局执行上下文. 这种情况下, 如果全局执行上下文也没有该变量, 那么将会抛出引用错误 (Reference Error). 子函数包含它父级函数的变量环境, 把这个概念称为闭包(Closure), 即使父级函数执行环境已经从执行栈弹出了, 子函数还是可以访问父级函数变量 x (通过作用域链).
Event Loop
Browser
The job of the event loop is to look into the call stack and determine if the call stack is empty or not. If the call stack is empty, it looks into the ES6 job queue and message queue to see if there’s any pending call back waiting to be executed:
- ES6 job queue: used by
Promises(higher priority). - Message queue: used by
setTimeout,DOM events. - 微任务 MicroTask (Jobs), 有特权, 可以插队:
process.nextTick.Promises.then(Promise 构造函数是同步函数).Object.observer,MutationObserver.catch finally.
- 宏任务 MacroTask (Tasks), 没有特权:
scripts: 整体脚本视作一个宏任务.MessageChannel,postMessage.setImmediate,I/O.setTimeout,setInterval.XHRcallback function.requestAnimationFrame.- UI interaction
eventscallback function. - UI rendering.
- MicroTask 优先于 MacroTask.
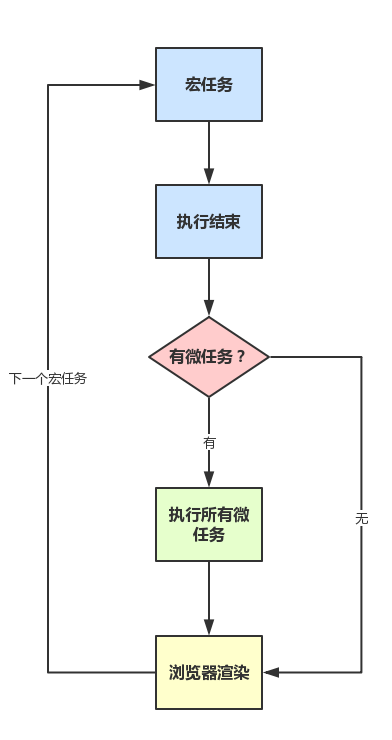
- 浏览器为了能够使得 JS 内部 (macro)task 与 DOM 任务能够有序的执行, 会在一个 (macro)task 执行结束后, 在下一个 (macro)task 执行开始前, 对页面进行重新渲染. 当 JS 引擎从任务队列中取出一个宏任务来执行, 如果执行过程中有遇到微任务, 那么执行完该宏任务就会去执行宏任务内的所有微任务, 然后更新 UI. 后面就是再从任务队列中取出下一个宏任务来继续执行, 以此类推.
Event Loop与Call Stack有且仅有一个,Task/Job/Message Queue可以有多个.
宏任务队列取宏任务 -> 执行 1 个宏任务 -> 检查微任务队列并执行所有微任务 -> requestAnimationFrame -> 浏览器重排/重绘 -> requestIdleCallback -> 宏任务队列取宏任务
Event Loop simple model:
for (const macroTask of macroTaskQueue) {
// 1. Handle current MacroTask.
runTask(macroTask)
// 2. Handle all MicroTasks.
for (const microTask of microTaskQueue)
runTask(microTask)
// 3. Handle Animation Frame.
if (shouldRepaint()) {
if (!animationFrameCallbackQueue.isEmpty()) {
const animationTasks = animationFrameCallbackQueue.copyTasks()
for (const animationTask of animationTasks)
runTask(animationTask)
}
repaint()
}
}
Using setTimeout with 0 seconds timer
helps to defer execution of Promise and bar until the stack is empty.
function bar() {
console.log('bar')
}
function baz() {
console.log('baz')
}
function foo() {
console.log('foo')
setTimeout(bar, 0)
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('Promise resolved')
})
.then(res => console.log(res))
.catch(err => console.log(err))
baz()
}
foo()
// foo
// baz
// Promised resolved
// bar
process.nextTick() run before Promise.then():
console.log('1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(2)
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log(3)
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log(4)
})
})
})
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log(5)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(6)
})
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log(7)
})
})
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log(8)
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log(9)
})
})
console.log('10')
// 1 10 8 9 5 7 2 3 4 6
Promise 构造函数本身是同步函数:
console.log('script start')
const promise1 = new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('promise1')
resolve()
console.log('promise1 end')
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise2')
})
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout')
})
console.log('script end')
// 输出顺序:
// script start
// promise1
// promise1 end
// script end
// promise2
// setTimeout.
await a(); b() 等价于 Promise(a()).then(b()),
a 是同步执行, b 是 MicroTask:
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start')
await async2()
console.log('async1 end')
}
async function async2() {
console.log('async2')
}
console.log('script start')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout')
}, 0)
async1()
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('promise1')
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise2')
})
console.log('script end')
// script start
// async1 start
// async2
// promise1
// script end
// async1 end
// promise2
// setTimeout
当调用栈没有同步函数时, 清空 MicroTask 任务队列里的函数, 再从 MacroTask 任务队列里取出一个函数执行 (第二次 Event Loop):
function test() {
console.log('start')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('children2')
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('children2-1')
})
}, 0)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('children3')
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('children3-1')
})
}, 0)
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('children1')
})
console.log('end')
}
test()
// start
// end
// children1
// children2
// children2-1
// children3
// children3-1
Node.js
Node.js can run I/O operations in a non-blocking way, meaning other code (and even other I/O operations) can be executed while an I/O operation is in progress.
Instead of having to wait for an I/O operation to complete (and essentially waste CPU cycles sitting idle), Node.js can use the time to execute other tasks.
When the I/O operation completes, event loop give back control to the piece of code that is waiting for the result of that I/O operation.
The Node.js execution model was designed to cater to the needs of most web servers, which tend to be I/O-intensive (due to non-blocking I/O).
console.log('glob1')
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('timeout1')
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log('timeout1_nextTick')
})
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('timeout1_promise')
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log('timeout1_then')
})
})
setImmediate(() => {
console.log('immediate1')
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log('immediate1_nextTick')
})
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('immediate1_promise')
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log('immediate1_then')
})
})
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log('glob1_nextTick')
})
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('glob1_promise')
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log('glob1_then')
})
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('timeout2')
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log('timeout2_nextTick')
})
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('timeout2_promise')
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log('timeout2_then')
})
})
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log('glob2_nextTick')
})
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('glob2_promise')
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log('glob2_then')
})
setImmediate(() => {
console.log('immediate2')
process.nextTick(() => {
console.log('immediate2_nextTick')
})
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('immediate2_promise')
resolve()
}).then(() => {
console.log('immediate2_then')
})
})
console.log('glob2')
// glob1
// glob1_promise
// glob2_promise
// glob2
// glob1_nextTick
// glob2_nextTick
// glob1_then
// glob2_then
// timeout1
// timeout1_promise
// timeout1_nextTick
// timeout1_then
// timeout2
// timeout2_promise
// timeout2_nextTick
// timeout2_then
// immediate1
// immediate1_promise
// immediate1_nextTick
// immediate1_then
// immediate2
// immediate2_promise
// immediate2_nextTick
// immediate2_then
V8
- source code (parser) AST (interpreter) bytecode
- send profiling data from bytecode to optimizing compiler, generate optimized code
- Ignition interpreter
- TurboFan optimizing compiler (2 for SpiderMonkey/Edge, 3 for Safari)
- JavaScript implementation list.
Object Shape
V8 object shapes:
// o1 and o2 have the same shape
// JSObject(1, 2) => Shape('x', 'y')
// JSObject(3, 4) => Shape('x', 'y')
// 'x' => 0 Offset, Writable, Enumerable, Configurable
// 'y' => 1 Offset, Writable, Enumerable, Configurable
const o1 = { x: 1, y: 2 }
const o2 = { x: 3, y: 4 }
Shape transform:
// Shape chain: Shape(empty) => Shape(x) => Shape(x, y)
const o = {}
o.x = 1
o.y = 2
// Shape chain: Shape(empty) => Shape(y) => Shape(y, x)
const o = {}
o.y = 2
o.x = 1
// Shape chain: Shape(x)
const o = { x: 1 }
Array shape: Shape('length'), 'length' => 0 Offset, Writable.
Inline Cache
V8 use ICs to memorize information (same shape) where to find properties on objects:
- always initialize objects in the same way (generate the same shape)
- don't add property to objects dynamically (invalid inline cache)
- don't mess with property attributes of array elements
V8 为了提高对象属性的访问效率, 将属性分为多种类型:
- 排序属性 (elements): 符合数组索引类型的属性 (正整数), 存储为线性结构, 可快速访问.
- 常规属性 (properties): 字符串类型的属性 (包括负数/浮点数/Symbol), 存储为线性结构, 可快速访问.
- 慢属性: 属性需要反复增删时, 会将属性存储类型从线性结构 (快属性) 改为字典结构 (慢属性).
Object Structure
Basic object structure:
- Every object in JavaScript has its main internal class and a hidden class that describes its shape.
- Hidden classes
inherit from each other and are organized into class trees.
The shape of an object
{ a: 1 }will be the parent for the shape of an object{ a: 1, b: 2 }. - The order of properties matters.
Objects
{ a: 1, b: 2 }and{ b: 2, a: 1 }will have two different shapes. - A subclass holds a reference to the superclass and information about what has changed (transition).
- In the class tree of each object, the number of levels is not less than the number of properties in the object.
- The fastest properties of an object will be those declared at initialization, in-object property faster than external property.
- Atypical changes in the object's structure, such as property removal (
delete), can lead to a change in the storage type of properties to a slower one.
const obj1 = { a: undefined }
obj1.a = 1 // <- "a" - in-object property.
const obj2 = {}
obj2.a = 1 // <- "a" - external property.
// Change storage type to NameDictionary.
const obj1 = { a: 1, b: 2 }
delete obj1.a
// Storage type is not changed.
const obj2 = { a: 1, b: 2 }
obj2.a = undefined
An array is a regular class whose structure looks like { length: [W__] }.
The elements of the array are stored in special structures,
and references to these structures are placed inside the object:
- Adding or removing elements from the array does not lead to an increase in the class tree.
- The use of atypical keys in an array,
such as non-numeric keys or keys outside the range
[0 .. 2**32 - 2], leads to the creation of new shapes in the class tree. - Attempting to modify an array element's attribute will result in a switch to a slower storage type.
// 1. New element of the array doesn't extends the shapes tree.
const arr = []
arr[0] = 1
// 2. Leads to the shapes tree generation:
// { length } => { length, [-1] } => { length, [-1], [2**32 - 1] }.
const arr = []
arr[-1] = 1
arr[2 ** 32 - 1] = 2
// 3. Modify element's attribute result in switch to slower storage type.
const arr = [1, 2, 3]
// { elements: {
// #0: 1,
// #1: 2,
// #2: 3
// }}
Object.defineProperty(arr, '0', { writable: false })
// { elements: {
// #0: { value: 1, attrs: [_EC] },
// #1: { value: 2, attrs: [WEC] },
// #2: { value: 3, attrs: [WEC] }
// }}
Garbage Collection
V8 garbage collection 分代垃圾回收算法, 将堆分为两个空间:
- 新生代: 存放短周期对象, 空间小, 使用
Scavenge回收算法, 副垃圾回收器. - 老生代: 存放长周期对象, 空间大, 使用
Mark-Sweep-Compact回收算法, 主垃圾回收器.
Scavenge
- 空间换时间算法 (复制算法).
- 标记活动对象和非活动对象.
- 复制 from-space 中的活动对象到 to-space 中并进行排序.
- 清除 from-space 中的所有对象.
- 将 from-space 和 to-space 进行角色互换, 等待下一次 GC.
- 新生代对象晋升 (计算存活周期, 初始为 nursery 子代): allocation -> nursery 子代 -> intermediate 子代 -> 老生代.
Mark-Sweep-Compact
- 老生代空间大, 无法使用空间换时间 (复制) 算法.
- 标记阶段: 对老生代对象进行第一次扫描, 对活动对象进行标记.
- 清理阶段: 对老生代对象进行第二次扫描, 清除未标记的对象.
- 压缩阶段: 每次清理完非活动对象, 把剩下活动对象整理到内存的一侧, 回收掉边界上的内存 (以备后续大对象老生代).
Stop-The-World
垃圾回收优先于代码执行, 会先停止代码的执行, 等到垃圾回收完毕, 再执行 JS 代码, 成为全停顿.
Orinoco 优化 (优化全停顿现象):
- Incremental marking (time slice):
JS + Mark + JS + Mark .... - Lazy sweeping.
- Concurrent GC.
- Parallel GC.
Performance
Browser Engine
- Chrome: Blink (fork of
WebCorecomponent fromWebKit) + V8. - Edge: Trident/EdgeHTML + Chakra -> Chromium.
- Firefox: Gecko + SpiderMonkey.
- Safari: Webkit (fork of
KHTMLandKJSfromKDE) + JavaScriptCore (Nitro).
Browser process architecture:
- 浏览器进程:
- Singleton.
- 浏览器界面显示, 提供用户交互, e.g. 前进/后退.
- 子进程管理.
- 网络资源管理.
- 存储管理.
- 网络进程:
- Singleton.
- 主要负责页面的网络资源加载.
Vizprocess:- Singleton.
- 实现 3D CSS, 绘制 UI 界面.
- GPU main thread: rasters display lists and video frames into GPU texture tiles, draws compositor frames to screen using GPU, Out-of-Process display compositor, raster and iframes (OOP-D, OOP-R, OOPIFs).
- Display compositor thread: aggregates and optimizes compositing from render processes and browser process.
- 渲染进程:
- 核心任务是将 HTML/CSS 和 JavaScript 转换为用户可以与之交互的网页 (页面渲染, 脚本执行, 事件处理).
- 排版引擎 Blink 和 JavaScript 引擎 V8 都是运行在该进程中.
- 默认情况下, Chrome 会为每个 Tab 标签创建一个渲染进程.
- Within a single browser tab,
frames (
<iframe>) from different sites are always in different render processes (OOPIFs, Out-of-Process iframes), but frames (<iframe>) from same site are always in same render process. - 出于安全考虑, 渲染进程都是运行在沙箱模式下.
- 插件进程: 主要是负责插件的运行, 因插件易崩溃, 所以需要通过隔离以保证插件进程崩溃不会对浏览器和页面造成影响.
RenderingNG
Chromium rendering engine.
Architecture
RenderingNG key goals:
RenderingNG key changes:
- Uniform point of entry: always enter the pipeline at the beginning (no longer possible to enter the pipeline starting at an intermediate phase).
- Functional stages: each stage should have well-defined inputs and outputs, and its behavior should be functional.
- Constant inputs: inputs should be effectively constant while the stage is running.
- Immutable outputs: outputs should be immutable for the remainder of the rendering update.
- Checkpoint consistency: rendering data produced thus far should be in a self-consistent state at the end of each stage.
- De-duplication of work: only compute each thing once.
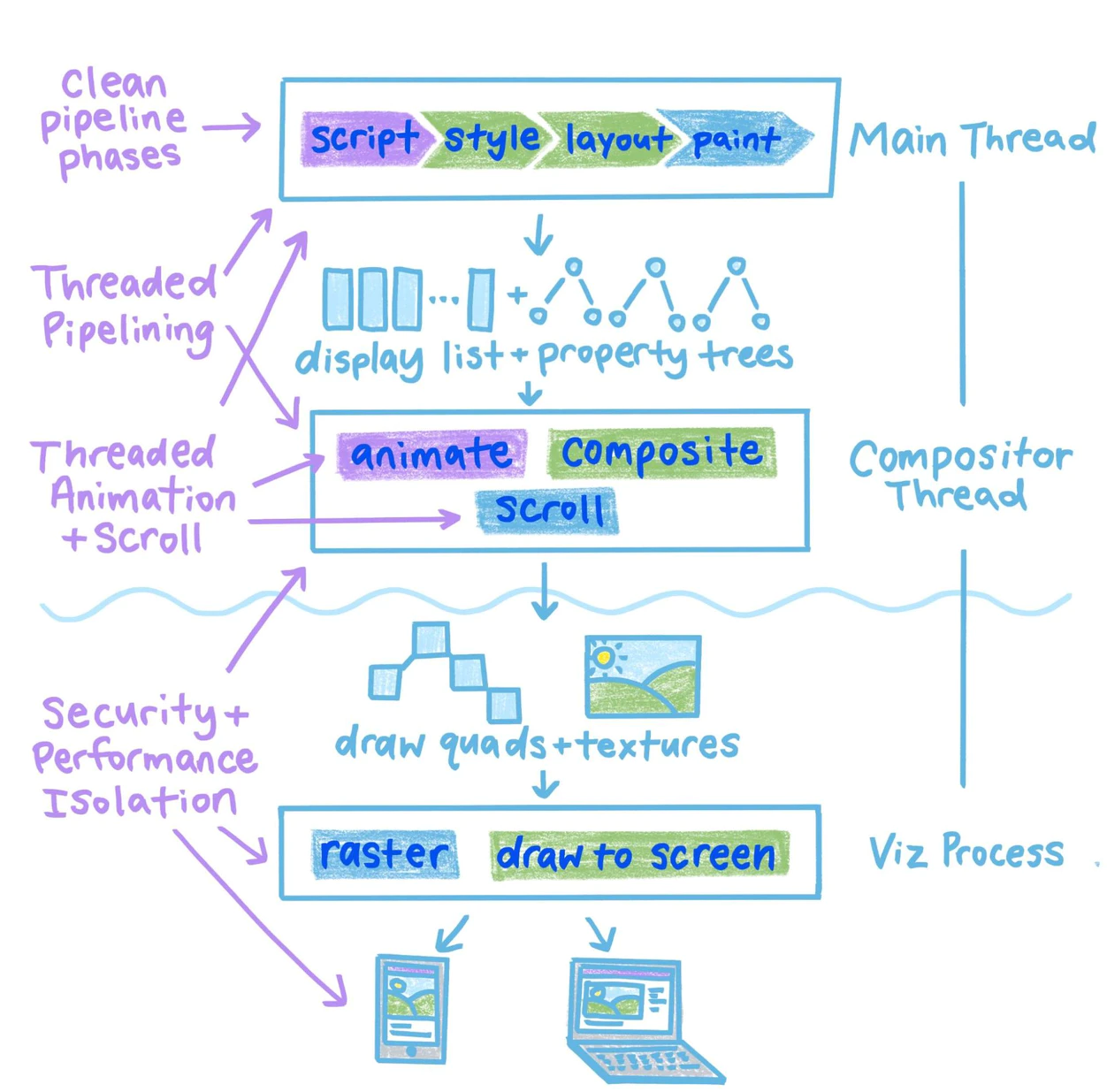
Pipeline
RenderingNG
pipeline
(green main thread -> yellow compositor thread -> orange Viz process):
- Animate.
- Style.
- Layout.
- Pre-paint.
- Scroll.
- Paint.
- Commit.
- Layerize.
- Raster, decode and paint worklet (GPU hardware acceleration).
- Activate.
- Aggregate (GPU hardware acceleration).
- Draw (GPU hardware acceleration).
Stages of the rendering pipeline can be skipped if they aren't needed:
Scrolling and visual effects animation can skip layout, pre-paint and paint.
If layout, pre-paint, and paint can be skipped for visual effects,
they can be run entirely on compositor thread and skip main thread.
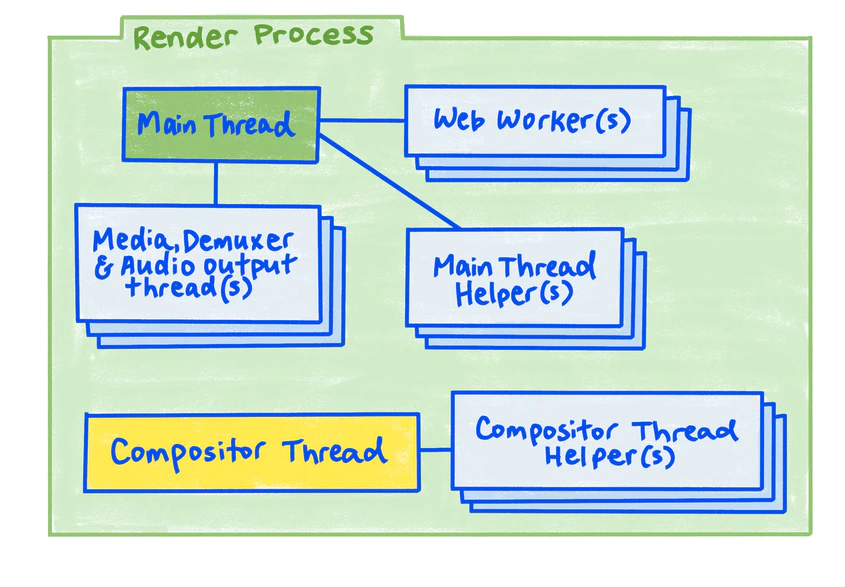
Render Process
- Download HTML.
- Parser/Script.
- DOM and CSSOM Construction.
- Render Tree = DOM Tree + Styled Tree.
- Layout.
- Paint.
- Composite.
- GUI 渲染线程 (
mainthread):- Parse
HTML/CSS. - Construct
DOMtree,CSSOMtree andRenderObjecttree. - Layout render tree.
- Paint render tree.
- Send information to GPU (Composite render tree):
separating
mainandcompositorthreads is critically important forperformance isolationof animation and scrolling from main thread work.
- Parse
- JS 引擎线程:
- JS 内核运行线程, 负责解析
JavaScript脚本, 运行代码. - 一个 Tab 页 (渲染进程) 中只有一个 JS 引擎线程在运行 JS 程序.
- JS 引擎一直等待着任务队列中任务的到来, 然后加以处理.
- JS 内核运行线程, 负责解析
- 事件触发线程:
- 负责控制事件循环.
- JS 引擎线程触发 MacroTask/MicroTask, 事件线程将任务添加到任务队列, 等待 JS 引擎线程执行.
- 定时触发器线程:
setInterval与setTimeout执行线程.- 此线程计时并触发定时器任务, 计时完毕后, 事件线程将定时器任务添加到任务队列, 等待 JS 引擎线程执行.
- 异步 HTTP 请求线程:
XMLHttpRequest连接后, 通过浏览器产生一个新的异步 HTTP 请求线程.- 当检测到 HTTP 请求状态变更时, 此线程产生状态变更事件, 并将 HTTP 响应处理函数 (用户回调函数) 添加到任务队列, 等待 JS 引擎线程执行.
GUI 渲染线程与 JS 引擎线程互斥.
Threads help achieve:
- Performance isolation and responsiveness in spite of slow tasks.
- Helper threads: sending long-running subtasks off to additional threads, to keep parent thread responsive to other requests happening simultaneously.
- Multiple buffering: showing previously rendered content while rendering new content, to hide latency of rendering.
- Pipeline parallelization: running rendering pipeline in multiple places simultaneously (fast scrolling and animation).
HTML Parser
DTD is context-sensitive grammar. Use State Machine pattern to implement a tokenizer:
Data -> Tag Open -> Tag Name -> Tag Close -> Data.
tokenizer send tokens to constructor, constructing DOM tree:
initial -> before HTML -> before head -> in head -> after head -> in body -> after body -> after after body -> EOF token.
HTML parser performance:
<= 1500DOM nodes.<= 60children nodes.<= 32levels.
CSS Parser
CSS is context-free grammar. Webkit use flex/bison (bottom-to-up), Gecko use up-to-bottom.
ruleSet
: selector [ ',' S* selector ]*
'{' S* declaration [ ';' S* declaration ]* '}' S*
;
selector
: simple_selector [ combinator selector | S+ [ combinator? selector ]? ]?
;
simple_selector
: element_name [ HASH | class | attrib | pseudo ]*
| [ HASH | class | attrib | pseudo ]+
;
class
: '.' IDENT
;
element_name
: IDENT | '*'
;
attrib
: '[' S* IDENT S* [ [ '=' | INCLUDES | DASHMATCH ] S*
[ IDENT | STRING ] S* ] ']'
;
pseudo
: ':' [ IDENT | FUNCTION S* [IDENT S*] ')' ]
;
Layout Engine
为避免对所有细小更改都进行整体布局, 浏览器采用了一种 dirty bit 系统.
如果某个呈现器发生了更改, 或者将自身及其子代标注为 dirty, 则需要进行布局:
- 父呈现器确定自己的宽度.
- 父呈现器依次处理子呈现器, 并且:
- 放置子呈现器 (设置
(x, y)坐标). - 如果有必要, 调用子呈现器的布局 (如果子呈现器是 dirty 的, 或者这是全局布局, 或出于其他某些原因), 这会计算子呈现器的高度.
- 放置子呈现器 (设置
- 父呈现器根据子呈现器的累加高度以及边距和补白的高度来设置自身高度, 此值也可供父呈现器的父呈现器使用.
- 将其
dirty 位设置为false.
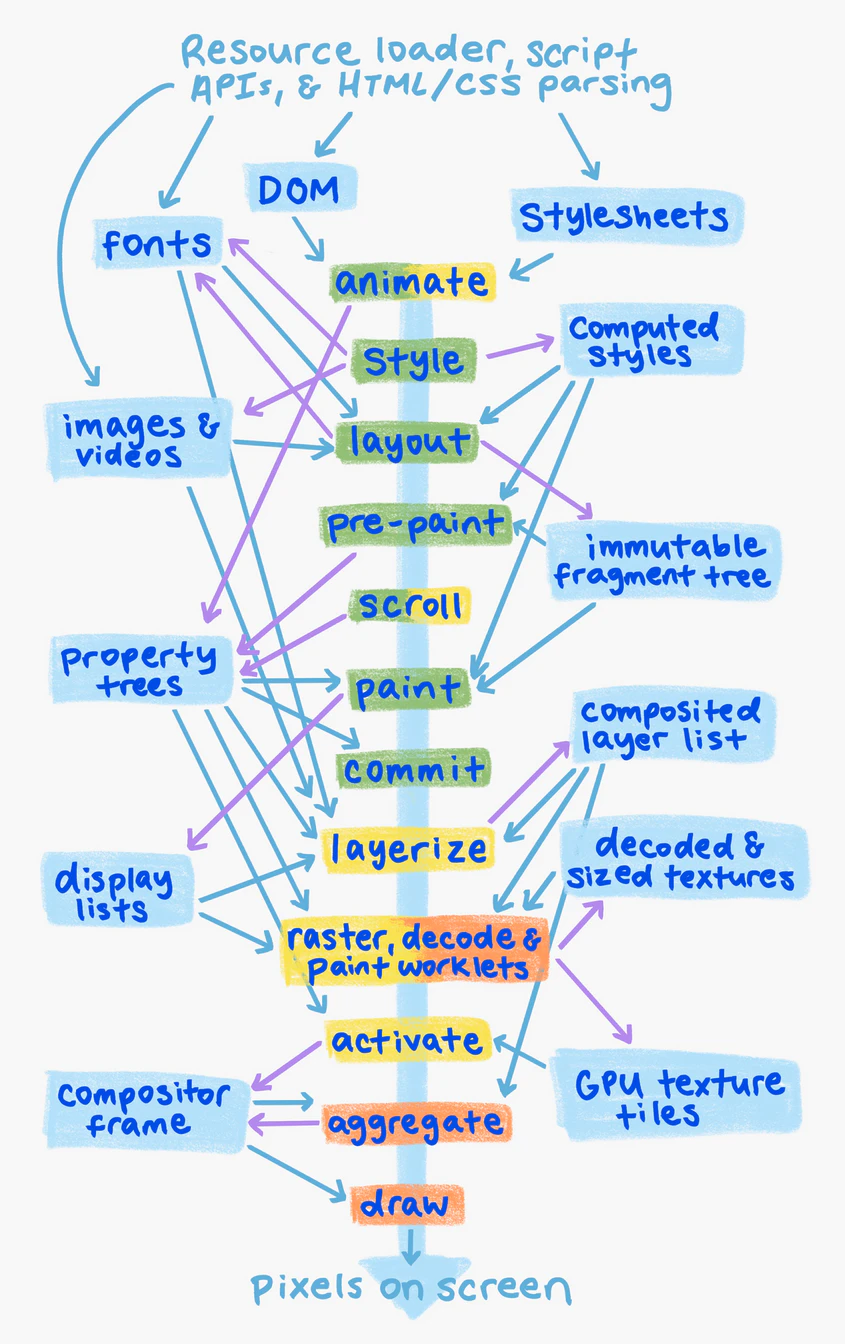
RenderingNG layout engine
generate
immutable fragment tree
and
immutable flat list.
It helps mitigate layout bugs including:
Paint Engine
Paint order:
- 背景颜色.
- 背景图片.
- 边框.
- 子代.
- 轮廓.
Property trees are data structures that explain how visual and scrolling effects apply to DOM elements. Every web document has four separate property trees:
- Transform tree represents CSS transforms and scrolling.
- Clip tree represents overflow clips.
- Effect tree represents all other visual effects: opacity, filters, masks, blend modes, and other kinds of clips such as clip-path.
- Scroll tree represents information about scrolling,. such as how scrolls chain together
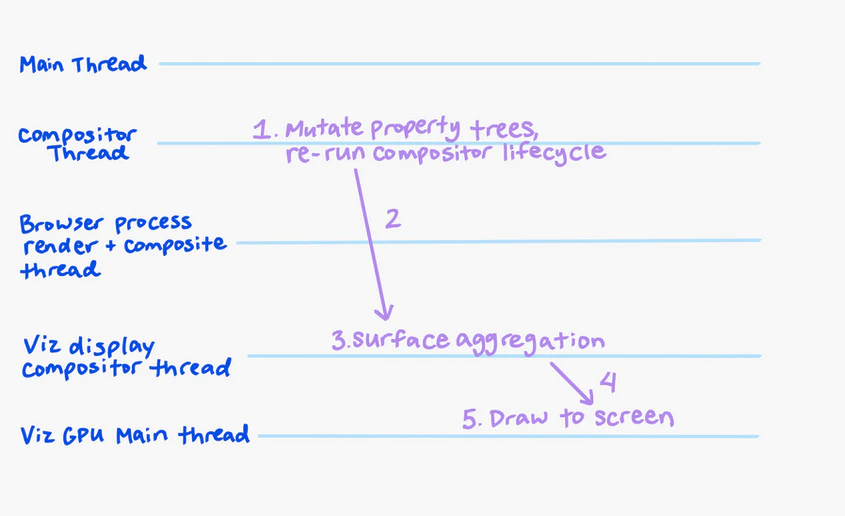
JavaScript 阻塞渲染:
- 渲染进程 (
Renderprocess) 中主线程 (mainthread)Layout阶段与Paint阶段不负责实际的绘制操作:Layout阶段执行Update Layer Tree, 更新每层信息,Paint阶段整理每层页面的绘制信息, 构建绘制列表. - 以上阶段的数据最终会交给
渲染进程 (
Renderprocess) 中合成线程 (compositorthread) 与Vizprocess 执行实际的绘制操作. - JavaScript 阻塞了同在主线程的
Layout阶段与Paint阶段, 间接阻塞了compositorthread 与Vizprocess 的绘制操作.
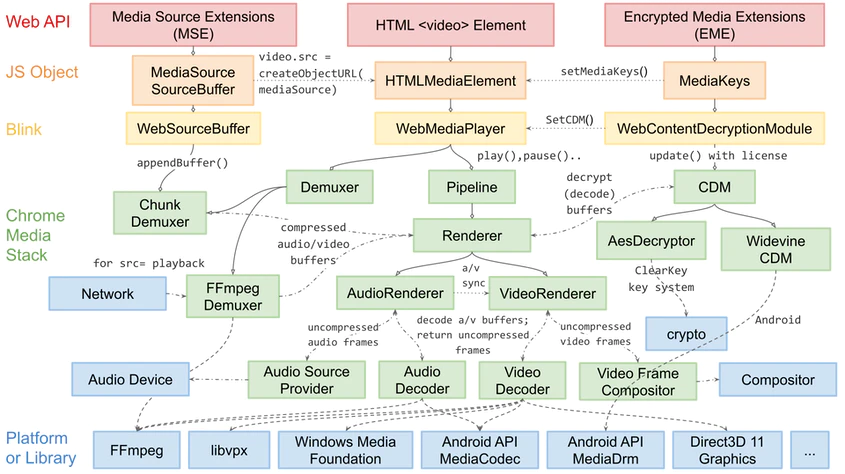
Video Engine
- Each video talks directly to
Vizprocess: video rendering is largely decoupled fromRenderingNGmain rendering pipeline.
Scrolling Performance
- Cached GPU textures and display lists: help battery life and animation frame rate for scrolling.
- Every possible scroll is threaded: don't have to depend on the JavaScript and layout thread.
Animation Performance
CSS transform animation only runs on compositor thread and Viz process.
References
- Chromium rendering engine: RenderingNG.
- Chromium
RenderingNGarchitecture. - Chromium
RenderingNGkey data structures. - Chromium video engine architecture.
- Chromium layout engine architecture.
- Chromium
Blinkarchitecture. - Web platform tests.
- Google Chrome platform feature status.
- Mozilla Firefox platform feature status.
- Thin wrappers around native APIs.
- JavaScript runtimes.