Inheritance
Prototype Proxy
可用于所有继承模式中, 减少内存消耗:
const inherit = (function () {
// 减少继承过程中父类的实例化,减少资源消耗
// 实例化一个空类所需资源更少
const F = function () {}
return function (C, P) {
// c.__proto__ = C.prototype = f
// f.__proto__ = F.prototype
// F.prototype = P.prototype
// c.__proto__.__proto__ = f.__proto__ = P.prototype
F.prototype = P.prototype // f.__proto__ = F.prototype = P.prototype
C.prototype = new F() // C.prototype = f
C.prototype.constructor = C
C.super = P.prototype // 此句可提高代码的重用性
}
})()
Child.prototype.add = function () {
return Child.super.add.call(this)
}
Class Simulation
复制式地继承, 将会消耗大量内存单元:
function classSim(Parent, props) {
// 新的构造函数
const Child = function (...args) {
if (
Child.uber
&& Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(Child.uber, '_construct')
) {
Child.uber._construct.apply(this, args)
}
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(Child.prototype, '_construct'))
Child.prototype._construct.apply(this, args)
}
// 类式继承
Parent = Parent || Object
// 代理构造函数F
const F = function () {}
F.prototype = Parent.prototype
Child.prototype = new F()
Child.prototype.constructor = Child
// 添加属性与方法
for (const i in props) {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(props, i))
Child.prototype[i] = props[i]
}
// return the "class"
return Child
}
const SuperMan = classSim(Man, {
_construct(what) {
console.log('SuperMan\'s constructor')
},
getName() {
const name = SuperMan.uber.getName.call(this)
return `I am ${name}`
},
})
Composite
原型继承 (设置原型) 与类式继承 (借用构造函数) 组合继承模式:
child.prototype = new Parent(); Child.prototype.constructor = Child.Parent.apply(this, arguments): 借用构造函数可以防止引用类型被迫共享.- 此模式会调用两次父类构造函数, 使得子类属性继承两次, 存在一定的效率问题.
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name || 'Adam'
}
// Adding functionality to the prototype
Parent.prototype.say = function () {
return this.name
}
// Child constructor
function Child(...args) {
// 解决引用类型共享问题
Parent.apply(this, args)
this.childName = 'Child Name'
}
// Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
Child.prototype = new Parent() // 设置原型链,建立继承关系
Child.prototype.constructor = Child // 使得 Prototype 对象与 Constructor 对象形成闭环
Clone
Shallow
Object.assign:
- Enumerable: 可枚举属性扩展.
- Own: 自有属性扩展.
- Shallow: 浅拷贝扩展.
- Trigger
sourceObj.setand changesourceObj.
const dest = {}
const src = { a: {} }
Object.assign(dest, src)
// 浅复制意味着只会复制对象的引用
console.log(dest) // { a :{} }
console.log(dest.a === src.a) // true
... object spread syntax:
- Enumerable: 可枚举属性扩展.
- Own: 自有属性扩展.
- Shallow: 浅拷贝扩展.
- Not copy prototype (
__proto__). - Not copy getter and setter.
- Not trigger
sourceObj.setand not changesourceObj(create new properties).
// Shallow copy
const foo = { a: 1 }
const bar = { b: 2, c: { d: 3 } }
const foobar = { ...foo, ...bar }
console.log(foobar.c === bar.c) // true
// Not copy prototype (`__proto__`)
class MyClass {}
const original = new MyClass()
assert.equal(original instanceof MyClass, true)
const copy = { ...original }
assert.equal(copy instanceof MyClass, false)
Deep
Recursively copy all properties of an object:
function deepClone(original) {
if (Array.isArray(original)) {
return original.map(elem => deepClone(elem))
} else if (typeof original === 'object' && original !== null) {
return Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(original).map(([key, value]) => [key, deepClone(value)])
)
} else {
// Primitive value: atomic, no need to copy
return original
}
}
function deepUpdate(original, keys, value) {
if (keys.length === 0)
return value
const currentKey = keys[0]
if (Array.isArray(original)) {
return original.map((v, index) =>
index === currentKey ? deepUpdate(v, keys.slice(1), value) : v
)
} else if (typeof original === 'object' && original !== null) {
return Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(original).map(([k, v]) =>
k === currentKey ? [k, deepUpdate(v, keys.slice(1), value)] : [k, v]
)
)
} else {
// Primitive value
return original
}
}
Using JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj)):
- Not copy prototype (
__proto__). - Not copy getter and setter.
- Not copy non-enumerable properties.
- Not copy Symbol properties.
- Not copy circular references.
- Not copy
undefined,function,symbol.
const obj = { a: 1, b: { c: 2 } }
const clone = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(obj))
console.log(clone) // { a: 1, b: { c: 2 } }
Using window.structuredClone():
// Create an object with a value and a circular reference to itself.
const original = { name: 'MDN' }
original.itself = original
// Clone it
const clone = structuredClone(original)
console.assert(clone !== original) // the objects are not the same (not same identity)
console.assert(clone.name === 'MDN') // they do have the same values
console.assert(clone.itself === clone) // and the circular reference is preserved
const room1 = {
people: ['Alan', 'Bob'],
}
const room2 = structuredClone(room1)
room2.people.push('Charlie')
room1.people.pop()
console.log(room2.people) // ["Alan", "Bob", "Charlie"]
console.log(room1.people) // ["Alan"]
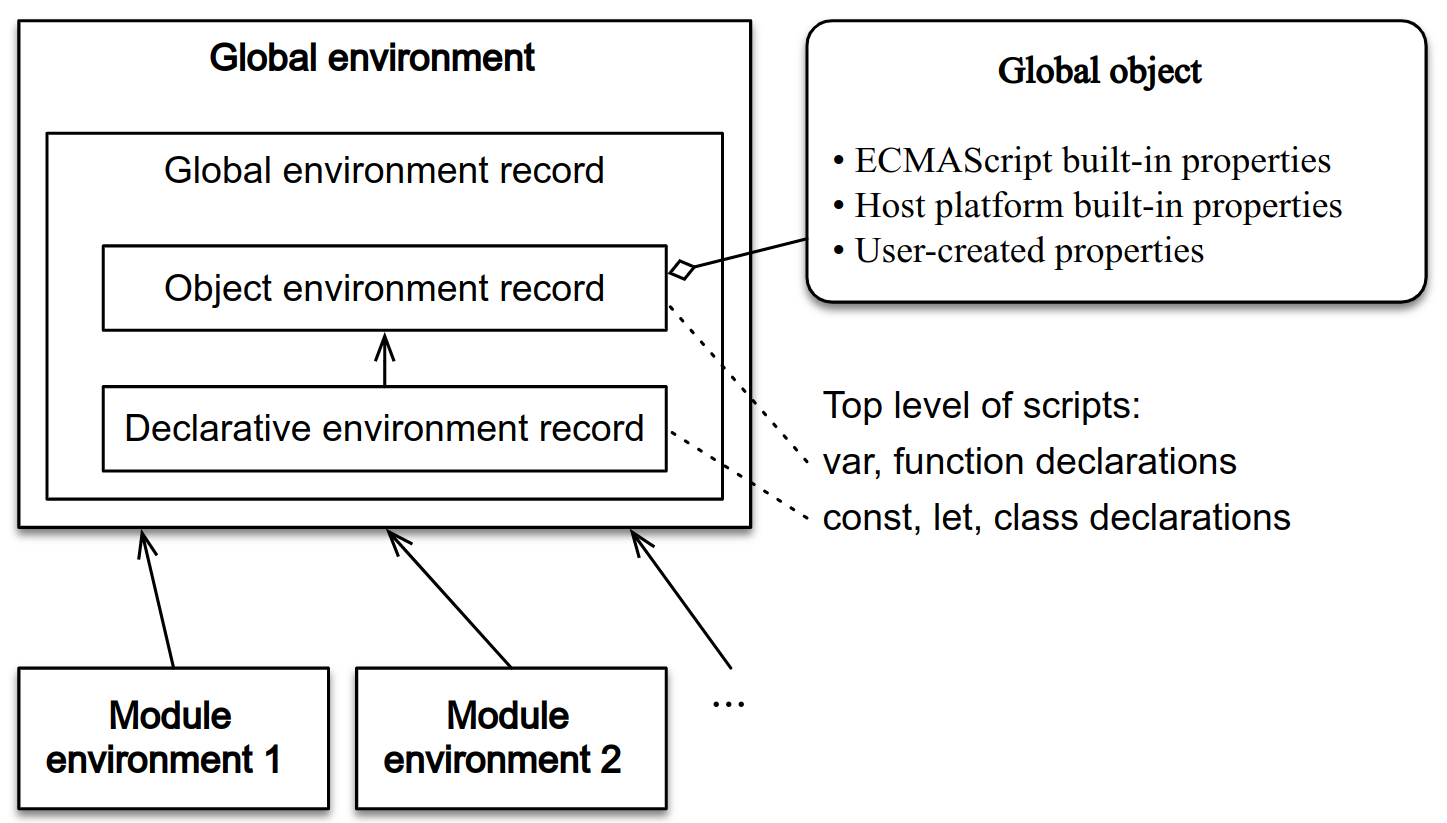
Global Object
// 立即函数模式:
// 此时返回值不是函数本身, 而是函数执行后的 return 语句返回值.
const global = (function () {
// 返回全局对象
return this
})()
Global Object 属性:
- undefined.
- NaN.
- Infinity.
- Object.
- Array.
- Function.
- Boolean.
- String.
- Number.
- Date.
- RegExp.
- Symbol.
- Error.
- EvalError.
- RangeError.
- ReferenceError.
- SyntaxError.
- TypeError.
- URIError.
- encodeURI.
- encodeURIComponent.
- decodeURI.
- decodeURIComponent.
- eval.
;(function () {
// Grab browser's default global variables.
const iframe = window.document.createElement('iframe')
iframe.src = 'about:blank'
window.document.body.appendChild(iframe)
const browserGlobals = Object.keys(iframe.contentWindow)
window.document.body.removeChild(iframe)
// Get the global variables added at runtime by filtering out the browser's
// default global variables from the current window object.
const runtimeGlobals = Object.keys(window).filter((key) => {
const isFromBrowser = browserGlobals.includes(key)
return !isFromBrowser
})
console.log('Runtime globals', runtimeGlobals)
})()