HTTP
Application layer protocol defines:
- Types of messages exchanged.
- Syntax of various message types(fields definition).
- Semantics of fields.
- Rules for when/how to send/respond to messages.
Protocol
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (RFC 2068):
- HTTP -> Socket Interface -> TCP.
- Stateless protocol.
- HTTP/1.0 默认不开启长连接: 客户端与服务端必须同时发送
Connection: Keep-Alive. - HTTP/1.1 默认开启长连接:
Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=100: 表示 TCP 通道保持 5 秒, 最多接收 100 次请求.Keep-Alive无法保证客户端和服务器之间的连接一定活跃.
- HTTP 为无状态协议: 每个请求相互独立.
Connections
- Non-persistent connections: 1 http request with 1 tcp connection.
- Persistent connections: multiple http request with 1 tcp connection.
Message Format
HTTP request format:
request line -> (method field, object url field, protocol version)
header lines -> Host/Connections(close -> non-persistent connection)/User-agent/Accept-language
\r\n
entity body
HTTP response format:
status line -> (protocol version, status code, corresponding status message)
header lines -> Connections/Date/Server/Last-Modified/Content-Length(bytes)/Content-Type
\r\n
entity body
Headers
HTTP;Colon help to learn and master HTTP headers.
Process
Port to Transport Layer
- Bandwidth-sensitive application: UDP.
- Reliable-sensitive application: TCP.
| Application | Application Layer | Transport Layer |
|---|---|---|
| SMTP | TCP | |
| Remote terminal access | Telnet | TCP |
| Web | HTTP/HTTPS | TCP |
| File transfer | FTP | TCP |
| Streaming multimedia | HTTP/HTTPS/RTP | TCP/UDP |
| Internet telephony | SIP/RTP | UDP |
Address
- IP (32 bits network layer): find specific host/end-system.
- Port (16 bits transport layer): find specific process.
Status Codes
RFC 2616 defines the following status codes:
- Informational responses: 100–199.
- Successful responses: 200–299.
- 200 OK.
- 201 Created.
- 202 Accepted.
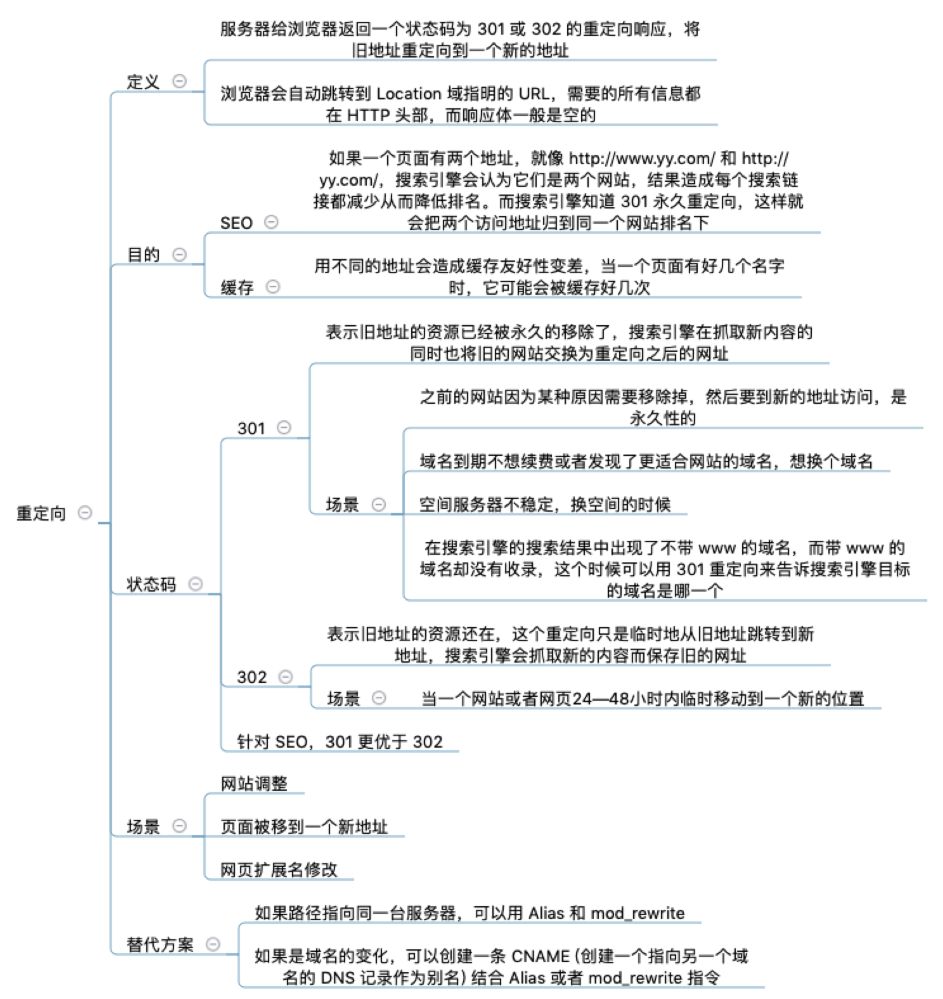
- Redirects: 300–399.
- 301 Moved Permanently.
- 302 Found.
- 304 Not Modified.
- 307 Temporary Redirect.
- 308 Permanent Redirect.
- Client errors: 400–499.
- 400 Bad Request.
- 401 Unauthorized.
- 403 Forbidden.
- 404 Not Found.
- 405 Method Not Allowed.
- 406 Not Acceptable.
- Server errors: 500–599.
- 500 Internal Server Error.
- 501 Not Implemented.
- 502 Bad Gateway.
- 503 Service Unavailable.
- 504 Gateway Timeout.
Use reasonable HTTP status codes:
- 200: general success.
- 201: successful creation.
- 301: moved permanently (SEO friendly).
- 302: moved temporarily.
- 304: not modified (HTTP cache).
- 400: bad requests from client.
- 401: unauthorized requests.
- 403: missing permissions.
- 404: missing resources.
- 429: too many requests.
- 5xx: internal errors (these should be avoided at all costs).
HTTP 402
HTTP 402 Payment Required
embeds payments directly into HTTP.
Based on x402,
agent payments protocol (AP2) designed to agentic commerce.
Performance
限制 Web 性能的主要因素是客户端与服务器之间的网络往返延迟 (RTT):
- 持久化连接以支持连接重用:
N次 HTTP 请求节省的总延迟时间为(N-1) * RTT. - 分块传输编码以支持流式响应.
- 请求管道以支持并行请求处理 (局限性较大):
- FIFO 管道, 队头请求会阻塞后续请求.
- 应用必须处理中断的连接并恢复.
- 应用必须处理中断请求的幂等问题.
- 应用必须保护自身不受出问题的代理的影响.
- 模拟多路复用: 并行使用多个 TCP 连接 (大多数现代浏览器支持每个主机打开 6 个连接).
- 利用多个 TCP 连接进行域名分区.
- Resources bundling and inlining (但一定程度上放弃缓存粒度).
- 改进的更好的缓存机制.