Cache
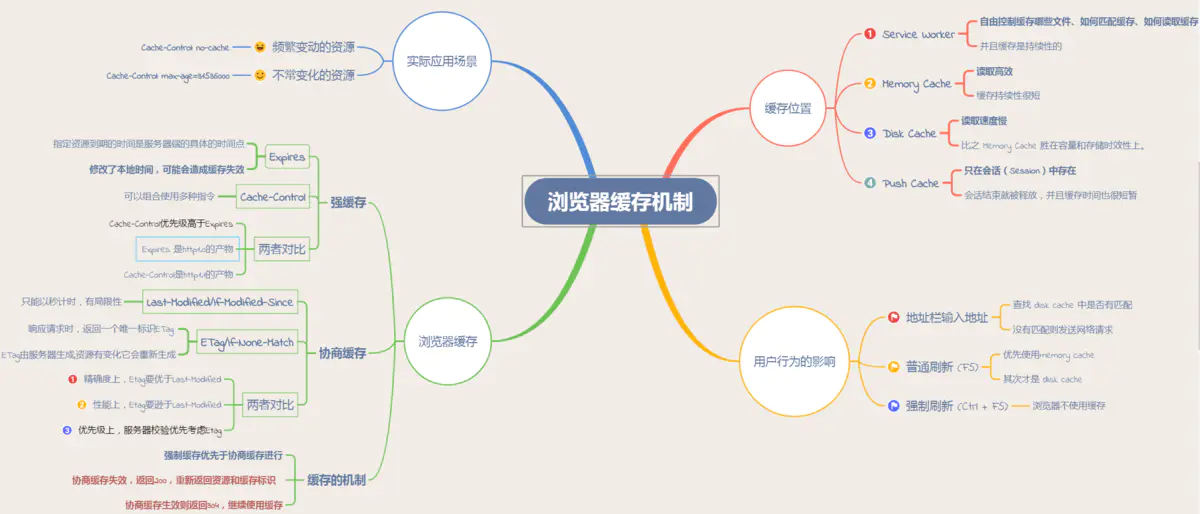
Browser caches 从缓存位置上来说分为四种, 并且各自有优先级, 当依次查找缓存且都没有命中的时候, 才会去请求网络:
- Service Worker: PWA.
- (In-) Memory Cache: reload Tab page.
- (On-) Disk Cache: big files.
- Push Cache: HTTP/2.
globalThis.addEventListener('install', (event) => {
async function buildCache() {
const cache = await caches.open(cacheName)
return cache.addAll(['/main.css', '/main.mjs', '/offline.html'])
}
event.waitUntil(buildCache())
})
globalThis.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
async function cachedFetch(event) {
const cache = await caches.open(cacheName)
let response = await cache.match(event.request)
if (response) {
return response
}
response = await fetch(event.request)
cache.put(event.request, response.clone())
return response
}
event.respondWith(cachedFetch(event))
})
HTTP
浏览器缓存, 也称 HTTP 缓存,
分为强缓存和协商缓存.
优先级较高的是强缓存,
在命中强缓存失败的情况下或者
Cache-Control: no-cache (no-cache allows caches but requires revalidate) 时,
才会走协商缓存.
Local
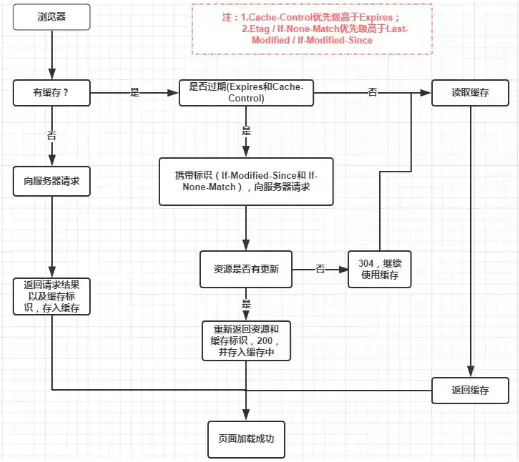
强缓存是利用 HTTP 头中的 Expires 和 Cache-Control 两个字段来控制的.
强缓存中, 当请求再次发出时, 浏览器会根据其中的 Expires 和 Cache-Control 判断目标资源是否 命中 强缓存,
若命中则直接从缓存中获取资源, 不会再与服务端发生通信.
Cache-Control 相对于 Expires 更加准确, 它的优先级也更高,
当 Cache-Control 与 Expires 同时出现时, 以 Cache-Control 为准.
Expires: Wed, 12 Sep 2019 06:12:18 GMT
Cache-Control: max-age=31536000
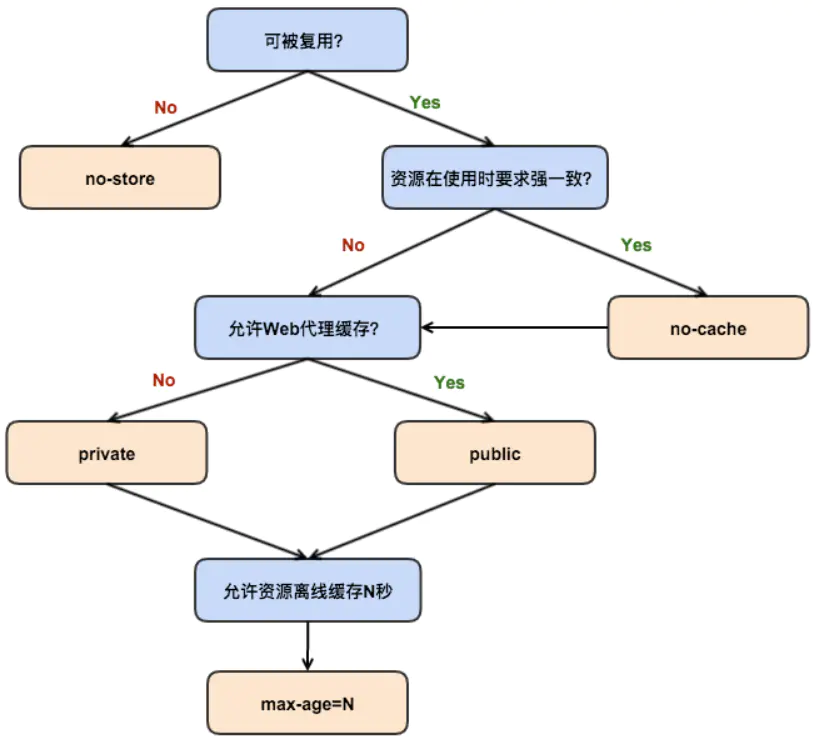
Cache-Control directives:
public: 允许代理服务器缓存资源.private: 不允许代理服务器缓存资源, 只有浏览器可以缓存.immutable: 就算过期了也不用协商, 资源就是不变的.max-age=<time>: 资源过期时间 (浏览器计算), 比Expires精准 (服务器计算).s-maxage=<time>: 代理服务器的资源过期时间.max-stale=<time>: 允许使用过期资源, 指定允许时间.stale-while-revalidate=<time>: 在验证 (协商) 期间, 返回过期的资源. If the cached page has expired, then it will send a stale version while it revalidate the page in the background. The page load is never blocked for the user, though it won't be perfectly fresh for everyone.stale-if-error=<time>: 验证 (协商) 出错的话, 返回过期的资源.must-revalidate: 强缓存过期后, 强制等待协商缓存, 不允许使用过期资源.no-store: 禁止强缓存和协商缓存.no-cache: 禁止强缓存, 允许协商缓存.
Cache the response of the API request, serve the cached version to any visitor, but automatically revalidate the cached object in the background:
export default async () => {
const resp = await fetch('https://hacker-news.firebaseio.com/v0/topstories.json')
const ids = await resp.json()
const stories = await Promise.all(
ids.slice(0, 100).map(async (id) => {
const story = await fetch(`https://hacker-news.firebaseio.com/v0/item/${id}.json`)
return story.json()
}),
)
return new Response(JSON.stringify(stories), {
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json',
'netlify-cdn-cache-control': 'public, max-age=0, stale-while-revalidate=86400',
},
})
}
Page is stale after 5 minutes, but tells the CDN to return the stale response and regenerate it in the background unless it’s over a week old. A popular page will always be fresh, but a rarely-visited one will not keep re-rendering:
// Tell the browser to always check the freshness of the cache
Astro.response.headers.set('Cache-Control', 'public, max-age=0, must-revalidate')
// Tell the CDN to treat it as fresh for 5 minutes,
// then return a stale version while it revalidate.
Astro.response.headers.set('Netlify-CDN-Cache-Control', 'public, s-maxage=604800, stale-while-revalidate=604800')
Server
协商缓存机制下,
浏览器需要向服务器去询问缓存的相关信息,
进而判断是重新发起请求/下载完整的响应,
还是从本地获取缓存的资源.
如果服务端提示缓存资源未改动 (Not Modified),
资源会被重定向到浏览器缓存,
这种情况下网络请求对应的状态码是 304.
Last-Modified 是一个时间戳,
如果启用了协商缓存,
它会在首次请求时随着 response headers 返回:
Last-Modified: Fri, 27 Oct 2017 06:35:57 GMT
随后每次请求时, 会带上一个叫 If-Modified-Since 的时间戳字段,
它的值正是上一次 response 返回给它的 Last-Modified 值:
If-Modified-Since: Fri, 27 Oct 2017 06:35:57 GMT
服务器可能无法正确感知文件的变化 (未实际改动或改动过快),
为了解决这样的问题, Etag 作为 Last-Modified 的补充出现了.
Etag 是由服务器为每个资源生成的唯一的标识字符串,
这个标识字符串可以是基于文件内容编码的,
因此 Etag 能够精准地感知文件的变化.
GET /i/example.gif HTTP 1.1
Host: image.example.com
------
HTTP 1.1 200 OK
Last-Modified: Tue, 12 Dec 2022 03:03:03 GMT
ETag: "10c24bc-4ab-457e1c1f"
Content-Length: 1195
GET /i/example.gif HTTP 1.1
Host: image.example.com
If-Modified-Since: Tue, 12 Dec 2022 03:03:03 GMT
If-None-Match: "10c24bc-4ab-457e1c1f"
------
HTTP 1.1 304 Not Modified
Code
- Cold run:
download -> compile -> store into on-disk cache - Warm run:
fetch from browser cache -> compile -> store metadata - Hot run:
fetch scripts and metadata from browser cache -> skip compile - Positive case: IIFE function heuristics
- Passive case: too small (
< 1KB) and inline scripts
BFCache
Cache-Control: no-store.unloadevent on page and iframes: reaplce it withpagehideevent.- Unclosed modern APIs:
IndexedDB,WebSocket,WebRTC, etc. - SPA soft navigation.