LLM Basic Notes
Generative AI
Generative Model
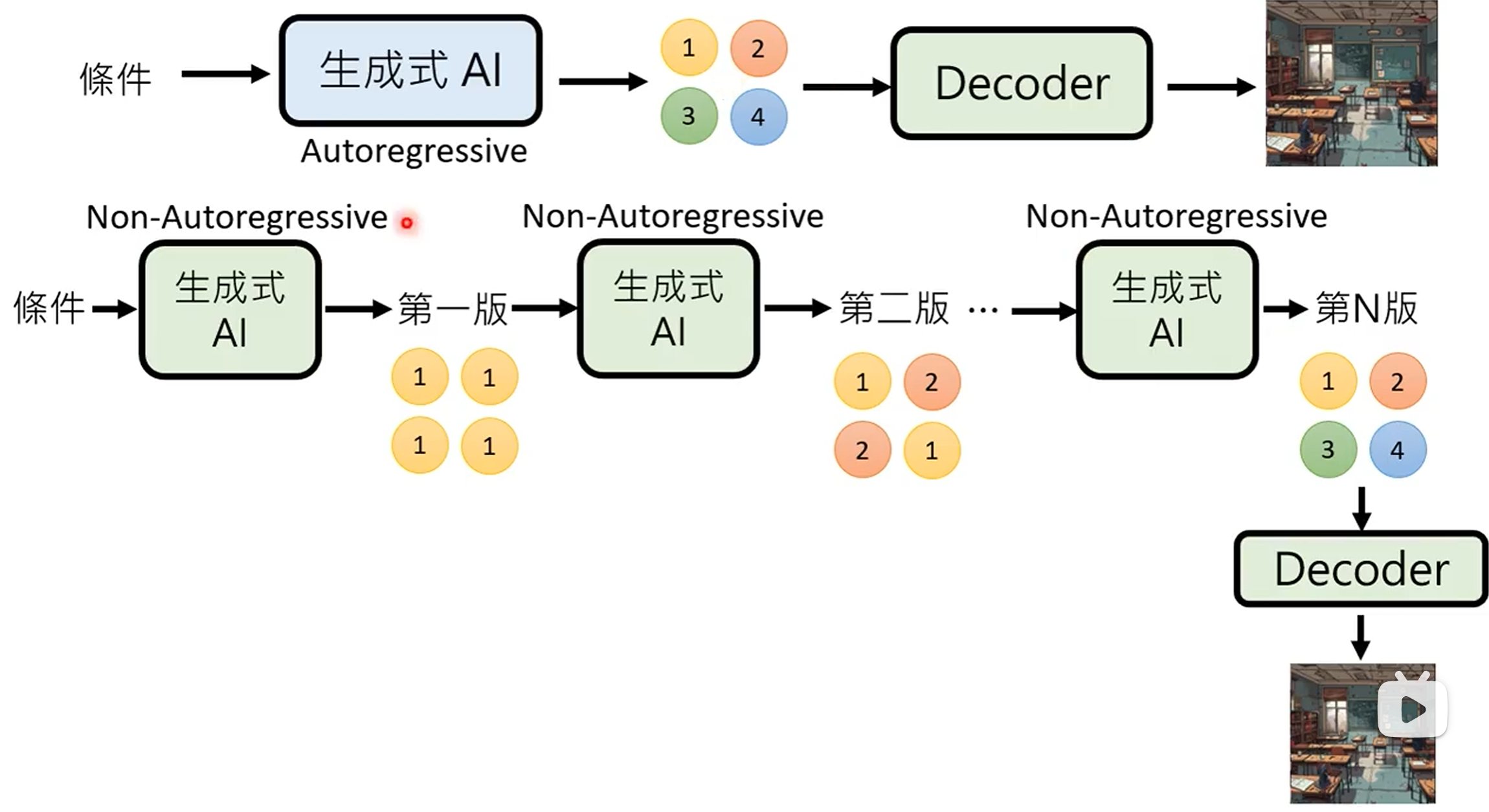
- Autoregressive (AR) model: generate output one token at a time, conditioned on previous tokens.
- Non-autoregressive (NAR) model: generate output all at once parallel, without conditioning on previous tokens.
| AR Model | NAR Model | |
|---|---|---|
| Parallelism | Low | High |
| Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Quality | High | Low |
结合上述两种方法 (Encoder + Decoder 架构):
- 用 AR model 生成中间向量, 用 NAR model 生成最终输出.
- 用 NAR model 多次生成, 逐步优化输出.
- Speculative decoding: 用 NAR model 快速生成若干个预测输出, 作为 AR model 的后续输入, 使得 AR model 可以同时输出多个结果.
Scaling Law
现有的预训练语言模型对于数据的需求量远高于扩展法则 (e.g. Chinchilla) 中所给出的估计规模. 很多更小的模型也能够通过使用超大规模的预训练数据获得较大的模型性能提升. 这种现象的一个重要原因是由于 Transformer 架构具有较好的数据扩展性. 目前为止, 还没有实验能够有效验证特定参数规模语言模型的饱和数据规模 (即随着数据规模的扩展, 模型性能不再提升).
Emergent Ability
大语言模型的涌现能力被非形式化定义为
在小型模型中不存在但在大模型中出现的能力:
- In-context learning.
- Instruction following.
- Step-by-step reasoning.
ChatGPT
Fine-tuned GPT model on conversational data:
- Pre-training: 学习文字接龙, 学习大规模资料 (self-supervised learning), 生成下一个单词.
- Instruction-tuning (IT): 人工文字接龙, 人工标注部分问题的答案 (supervised learning), 引导模型生成的方向.
- Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF): 训练一个 reward model, 负责评价模型生成的答案, 提供人类反馈. 以 reward model 的评价分数为 reward, 通过强化学习优化模型. 一般聚焦于三个方面: 有用性 (Helpfulness), 诚实性 (Honesty), 无害性 (Harmlessness).
Instruction-tuning (IT) with supervised learning on labelled data and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF).
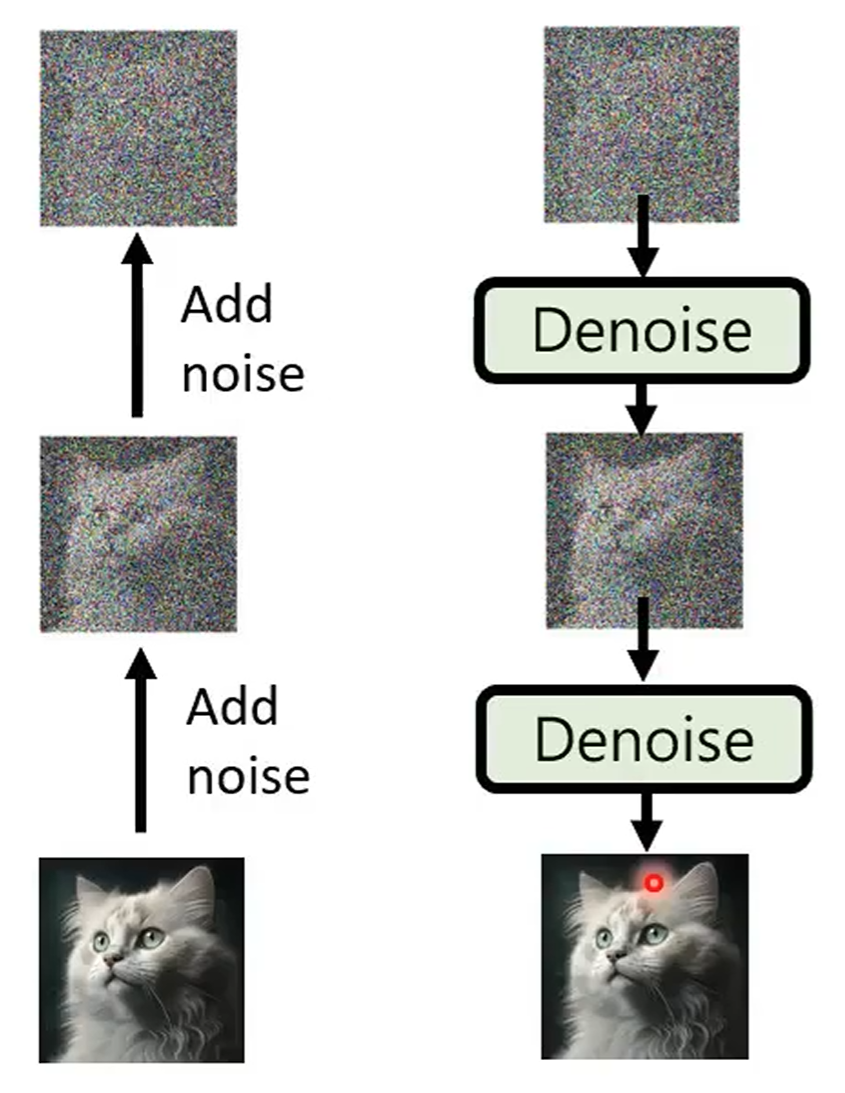
Diffusion Model
Forward process (diffusion) + reverse process (denoise):
Stable diffusion model:
Video Model
Generative videos as world models simulator.
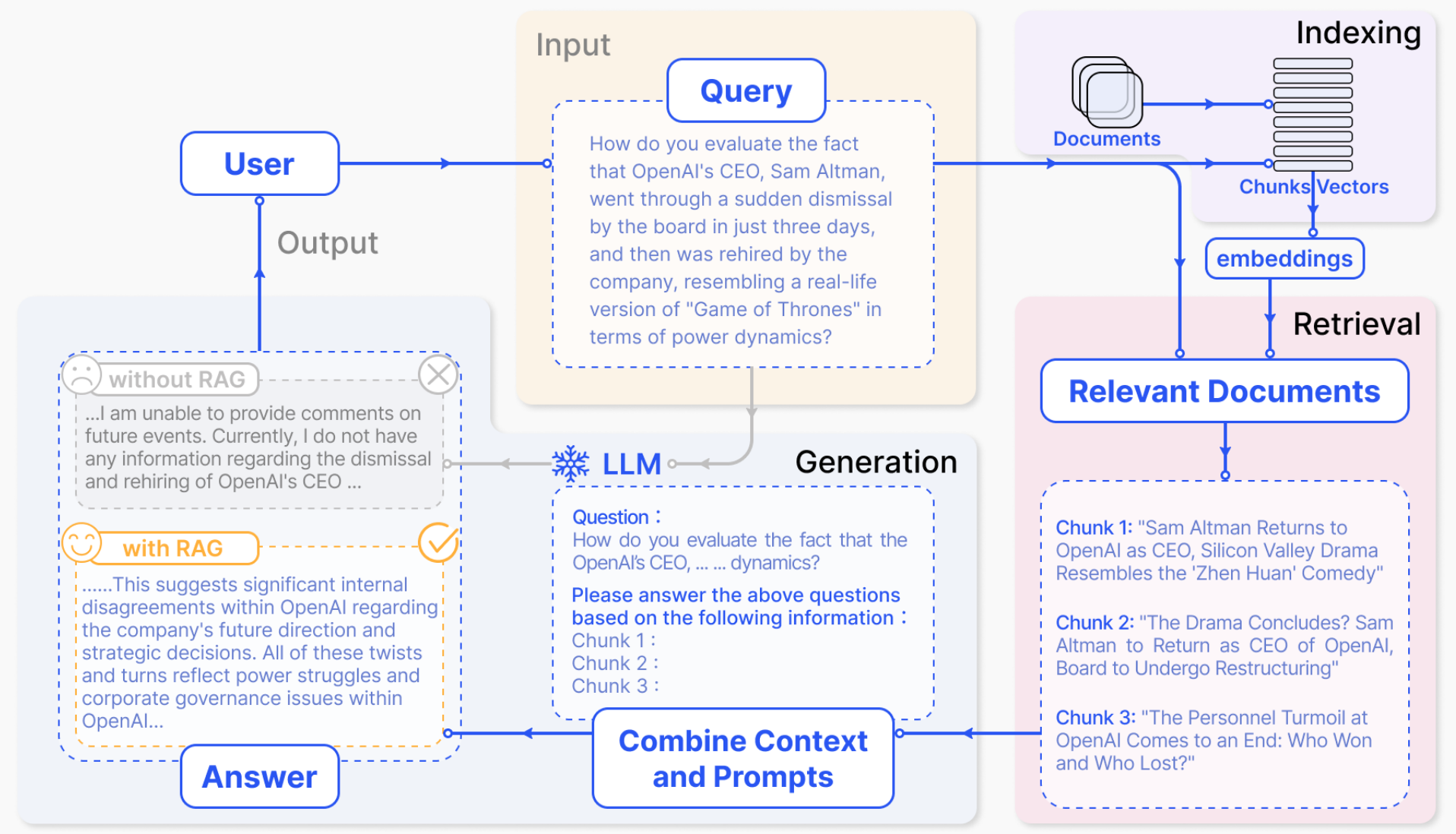
Retrieval-Augmented Generation
检索增强生成, 通常称为 RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), 是一种强大的聊天机器人的设计模式. 其中, 检索系统实时获取与查询相关的经过验证的源 / 文档, 并将其输入生成模型 (例如 GPT-4) 以生成响应.
Context is everything when it comes to getting the most out of an AI tool. To improve the relevance and quality of a generative AI output, you need to improve the relevance and quality of the input.
from langchain_community.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_community.embeddings import HuggingFaceBgeEmbeddings
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from google.colab import userdata
# Load document
document_url = "https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.10997.pdf"
loader = PyPDFLoader(document_url)
pages = loader.load()
# Split document into chunks
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=400,
chunk_overlap=40,
length_function=len,
is_separator_regex=False,
)
chunks = text_splitter.split_documents(pages)
# Create embeddings from chunks
model_name = "BAAI/bge-small-en"
model_kwargs = {"device": "cpu"}
encode_kwargs = {"normalize_embeddings": True}
bge_embeddings = HuggingFaceBgeEmbeddings(
model_name=model_name, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, encode_kwargs=encode_kwargs
)
chunk_texts = list(map(lambda d: d.page_content, chunks))
embeddings = bge_embeddings.embed_documents(chunk_texts)
# Store embeddings
text_embedding_pairs = zip(chunk_texts, embeddings)
db = FAISS.from_embeddings(text_embedding_pairs, bge_embeddings)
# Search database for similar contexts
query = "Which are the drawbacks of Naive RAG?"
contexts = db.similarity_search(query, k=5)
# Chat with model
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
"""You are an expert at answering questions
based on a context extracted from a document.
The context extracted from the document is: {context}""",
),
("human", "{question}"),
]
)
api_key = userdata.get("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY")
model = ChatAnthropic(model="claude-3-haiku-20240307", api_key=api_key)
chain = prompt | model
response = chain.invoke(
{
"context": "\n\n".join(list(map(lambda c: c.page_content, contexts))),
"question": query,
}
)
print(response.content)
LLM Toolchain
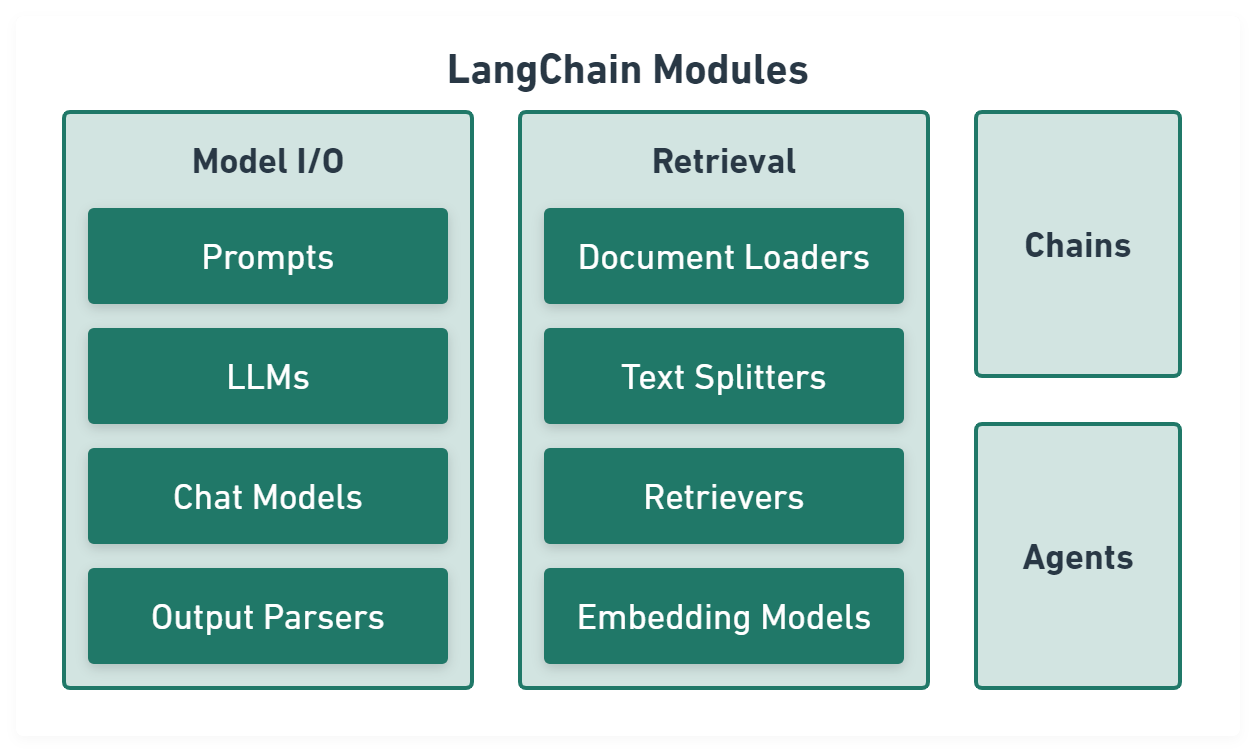
LangChain
LangChain aims to make programming with LLMs easier.
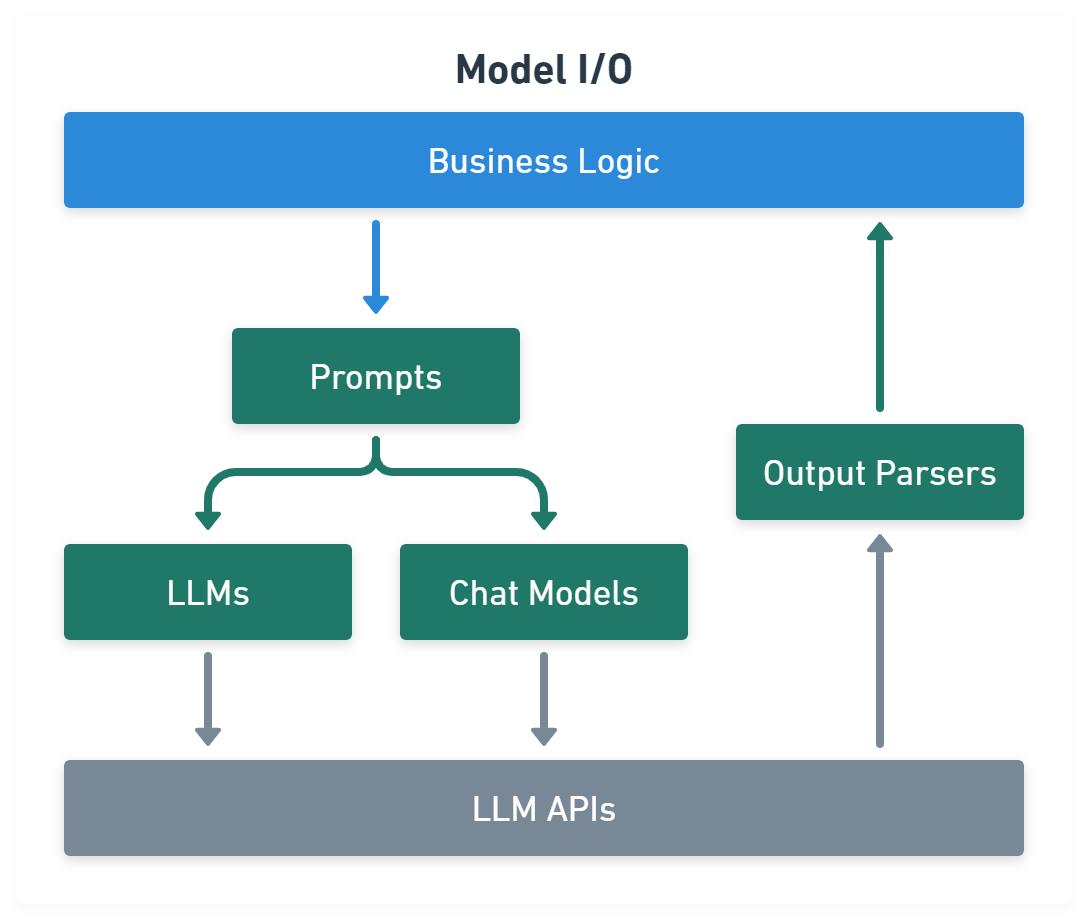
Model I/O module normalize LLM inputs (e.g. prompts), APIs, and outputs (e.g. completions):
import { CommaSeparatedListOutputParser } from '@langchain/core/output_parsers'
import { PromptTemplate } from '@langchain/core/prompts'
import { OpenAI } from '@langchain/openai'
const template = PromptTemplate.fromTemplate('List 10 {subject}.\n{format_instructions}')
const model = new OpenAI({ temperature: 0 })
const listParser = new CommaSeparatedListOutputParser()
const prompt = await template.format({
subject: 'countries',
format_instructions: listParser.getFormatInstructions(),
})
const result = await model.invoke(prompt)
const listResult = await listParser.parse(result)
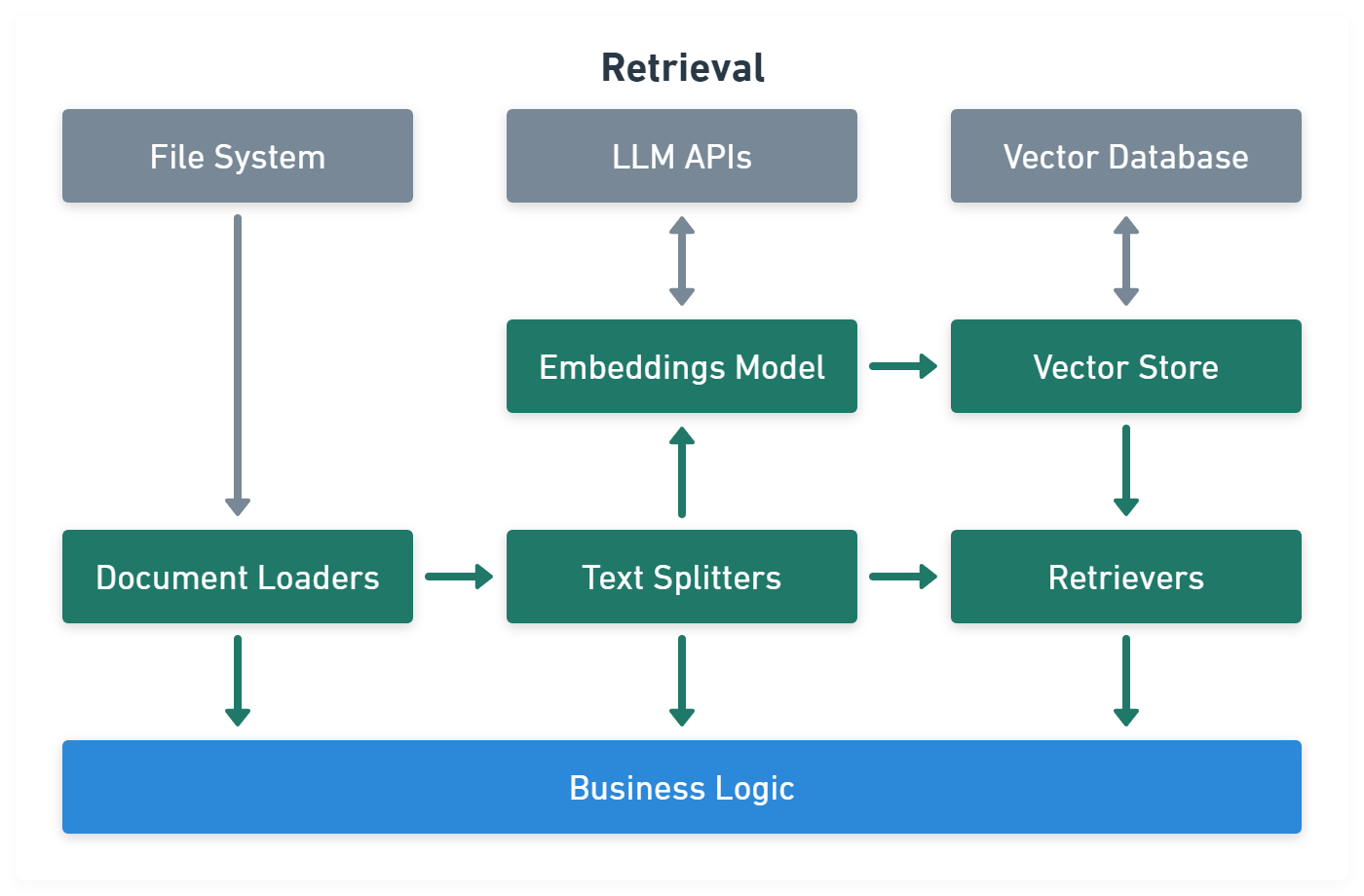
Retrieval module help to process data alongside the user inputs, making it easier to retrieve relevant information:
import { UpstashVectorStore } from '@langchain/community/vectorstores/upstash'
import { OpenAIEmbeddings } from '@langchain/openai'
import { CSVLoader } from 'langchain/document_loaders/fs/csv'
import { ScoreThresholdRetriever } from 'langchain/retrievers/score_threshold'
import { RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter } from 'langchain/text_splitter'
// CSV data.
const loader = new CSVLoader('path/to/example.csv')
const docs = await loader.load()
// Text splitter.
const splitter = new RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter({
chunkSize: 10,
chunkOverlap: 1,
})
const docs = await splitter.createDocuments(['...'])
// Embeddings and vector store.
const vectorStore = new UpstashVectorStore(new OpenAIEmbeddings())
await vectorStore.addDocuments(docs)
const retriever = ScoreThresholdRetriever.fromVectorStore(vectorStore, {
minSimilarityScore: 0.9,
})
const result = await retriever.getRelevantDocuments('...?')
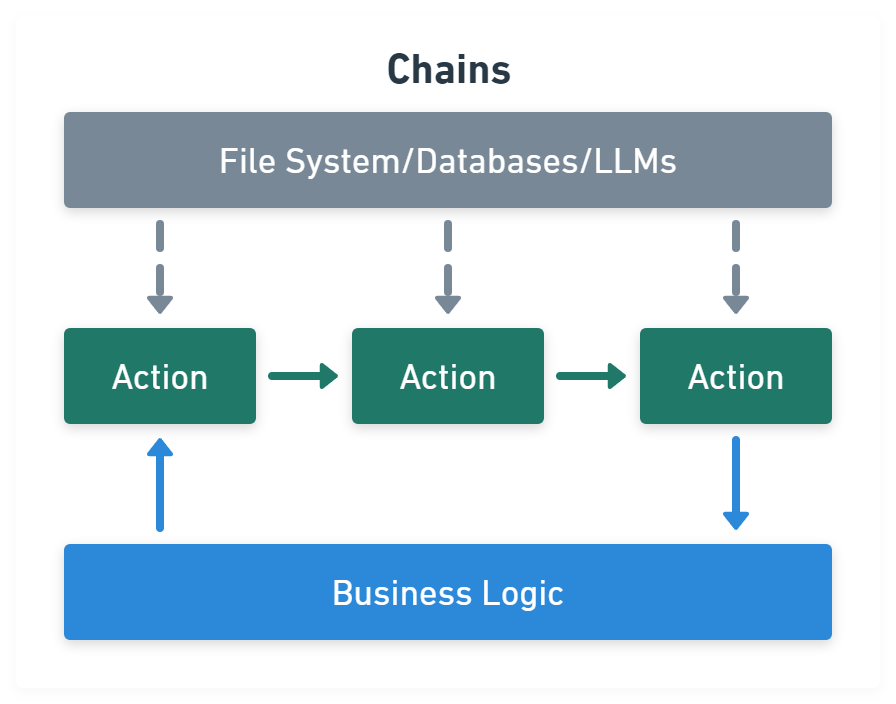
Chains module link tasks together:
import { CommaSeparatedListOutputParser } from '@langchain/core/output_parsers'
import { PromptTemplate } from '@langchain/core/prompts'
import { RunnableSequence } from '@langchain/core/runnables'
import { OpenAI } from '@langchain/openai'
const template = PromptTemplate.fromTemplate('List 10 {subject}.\n{format_instructions}')
const model = new OpenAI({ temperature: 0 })
const listParser = new CommaSeparatedListOutputParser()
const chain = RunnableSequence.from([template, model, listParser])
const result = await chain.invoke({
subject: 'countries',
format_instructions: listParser.getFormatInstructions(),
})
Agents module is chains with a list of functions (called tools) it can execute, while chains are hardcoded, agents choose their actions with the help of an LLM:
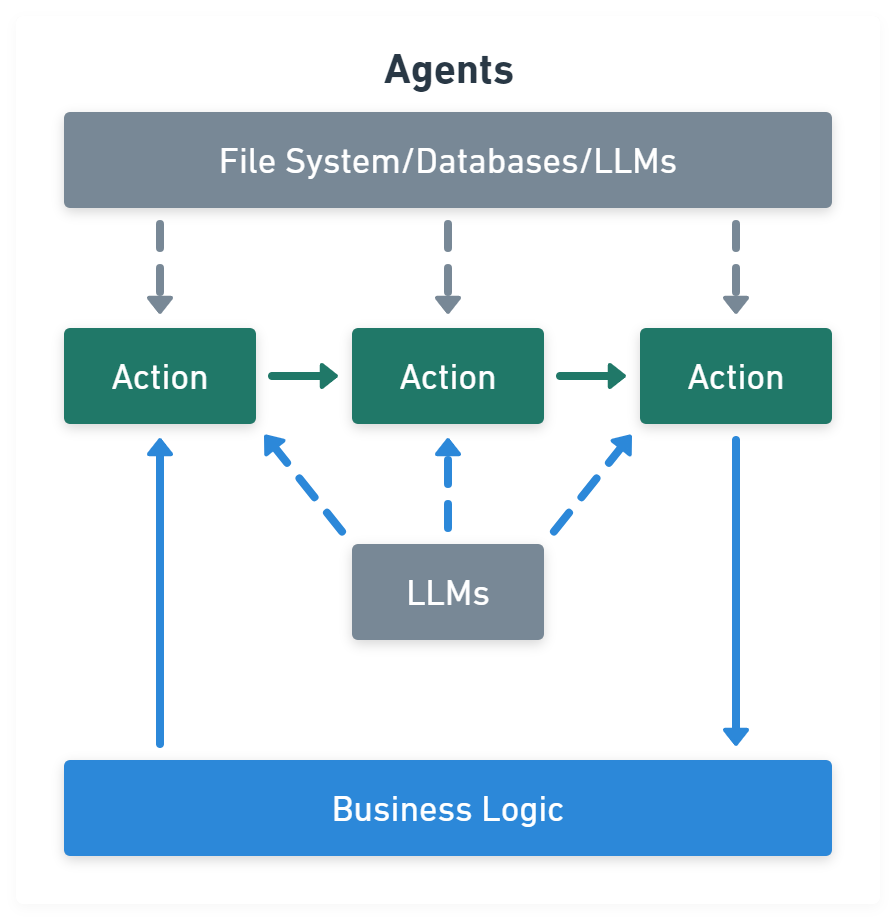
import { createVectorStoreAgent, VectorStoreToolkit } from 'langchain/agents'
const toolkit = new VectorStoreToolkit({ name: 'Demo Data', vectorStore }, model)
const agent = createVectorStoreAgent(model, toolkit)
const result = await agent.invoke({ input: '...' })
LLM Platform
LLM Reference
- LLM survey: 大语言模型.