JavaScript DevOps Notes
PWA
Progressive Web Apps:
- Served over
HTTPS. - Provide a manifest.
- Register a
ServiceWorker(web cache for offline and performance). - Consists of website, web app manifest, service worker, expanded capabilities and OS integration.
Service Worker Pros
- Cache.
- Offline.
- Background.
- Custom request to minimize network.
- Notification API.
Service Worker Costs
- Need startup time.
// 20~100 ms for desktop
// 100 ms for mobile
const entry = performance.getEntriesByName(url)[0]
const swStartupTime = entry.requestStart - entry.workerStart
- cache reads aren't always instant:
- cache hit time = read time (only this case better than
NO SW), - cache miss time = read time + network latency,
- cache slow time = slow read time + network latency,
- SW asleep = SW boot latency + read time ( + network latency),
- NO SW = network latency.
- cache hit time = read time (only this case better than
const entry = performance.getEntriesByName(url)[0]
// no remote request means this was handled by the cache
if (entry.transferSize === 0) {
const cacheTime = entry.responseStart - entry.requestStart
}
async function handleRequest(event) {
const cacheStart = performance.now()
const response = await caches.match(event.request)
const cacheEnd = performance.now()
}
- 服务工作者线程缓存不自动缓存任何请求, 所有缓存都必须明确指定.
- 服务工作者线程缓存没有到期失效的概念.
- 服务工作者线程缓存必须手动更新和删除.
- 缓存版本必须手动管理: 每次服务工作者线程更新, 新服务工作者线程负责提供新的缓存键以保存新缓存.
- 唯一的浏览器强制逐出策略基于服务工作者线程缓存占用的空间. 缓存超过浏览器限制时, 浏览器会基于 LRU 原则为新缓存腾出空间.
Service Worker Caching Strategy
5 caching strategy in workbox.
Stale-While-Revalidate:
globalThis.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
event.respondWith(
caches.open(cacheName).then((cache) => {
cache.match(event.request).then((cacheResponse) => {
fetch(event.request).then((networkResponse) => {
cache.put(event.request, networkResponse)
})
return cacheResponse || networkResponse
})
})
)
})
Cache first, then Network:
globalThis.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
event.respondWith(
caches.open(cacheName).then((cache) => {
cache.match(event.request).then((cacheResponse) => {
if (cacheResponse)
return cacheResponse
return fetch(event.request).then((networkResponse) => {
cache.put(event.request, networkResponse.clone())
return networkResponse
})
})
})
)
})
Network first, then Cache:
globalThis.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
event.respondWith(
fetch(event.request).catch(() => {
return caches.match(event.request)
})
)
})
Cache only:
globalThis.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
event.respondWith(
caches.open(cacheName).then((cache) => {
cache.match(event.request).then((cacheResponse) => {
return cacheResponse
})
})
)
})
Network only:
globalThis.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
event.respondWith(
fetch(event.request).then((networkResponse) => {
return networkResponse
})
)
})
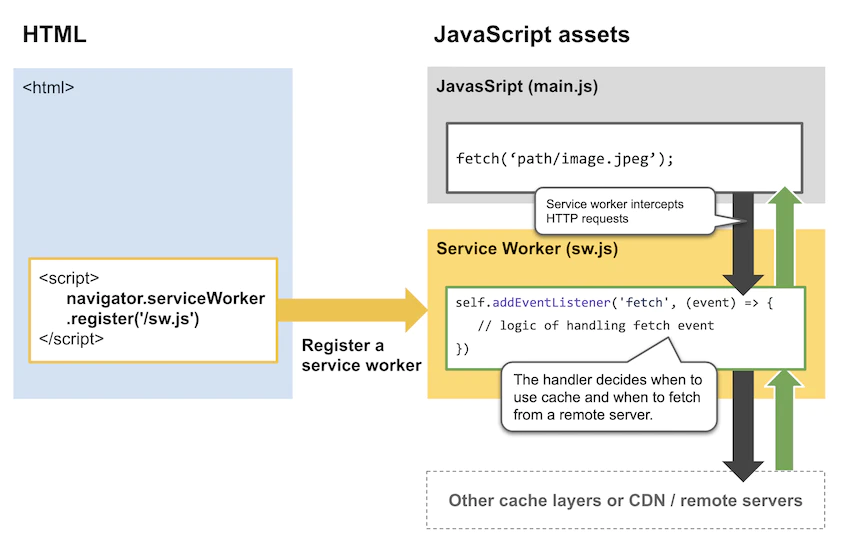
Service Worker Usage
Register Service Worker
// Check that service workers are registered
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
// Use the window load event to keep the page load performance
window.addEventListener('load', () => {
navigator.serviceWorker.register('/sw.js')
})
}
Broken Images Service Worker
function isImage(fetchRequest) {
return fetchRequest.method === 'GET' && fetchRequest.destination === 'image'
}
globalThis.addEventListener('fetch', (e) => {
e.respondWith(
fetch(e.request)
.then((response) => {
if (response.ok)
return response
// User is online, but response was not ok
if (isImage(e.request)) {
// Get broken image placeholder from cache
return caches.match('/broken.png')
}
})
.catch((err) => {
// User is probably offline
if (isImage(e.request)) {
// Get broken image placeholder from cache
return caches.match('/broken.png')
}
process(err)
})
)
})
globalThis.addEventListener('install', (e) => {
globalThis.skipWaiting()
e.waitUntil(
caches.open('precache').then((cache) => {
// Add /broken.png to "precache"
cache.add('/broken.png')
})
)
})
Caches Version Service Worker
globalThis.addEventListener('activate', (event) => {
const cacheWhitelist = ['v2']
event.waitUntil(
caches.keys().then((keyList) => {
return Promise.all([
keyList.map((key) => {
return cacheWhitelist.includes(key) ? caches.delete(key) : null
}),
globalThis.clients.claim(),
])
})
)
})
PWA Reference
- Service worker overview.
- Workbox library.
- Offline cookbook guide.
- PWA extensive guide.
- Network reliable web app definitive guide:
JamStack
JamStack 指的是一套用于构建现代网站的技术栈:
- JavaScript: enhancing with JavaScript.
- APIs: supercharging with services.
- Markup: pre-rendering.
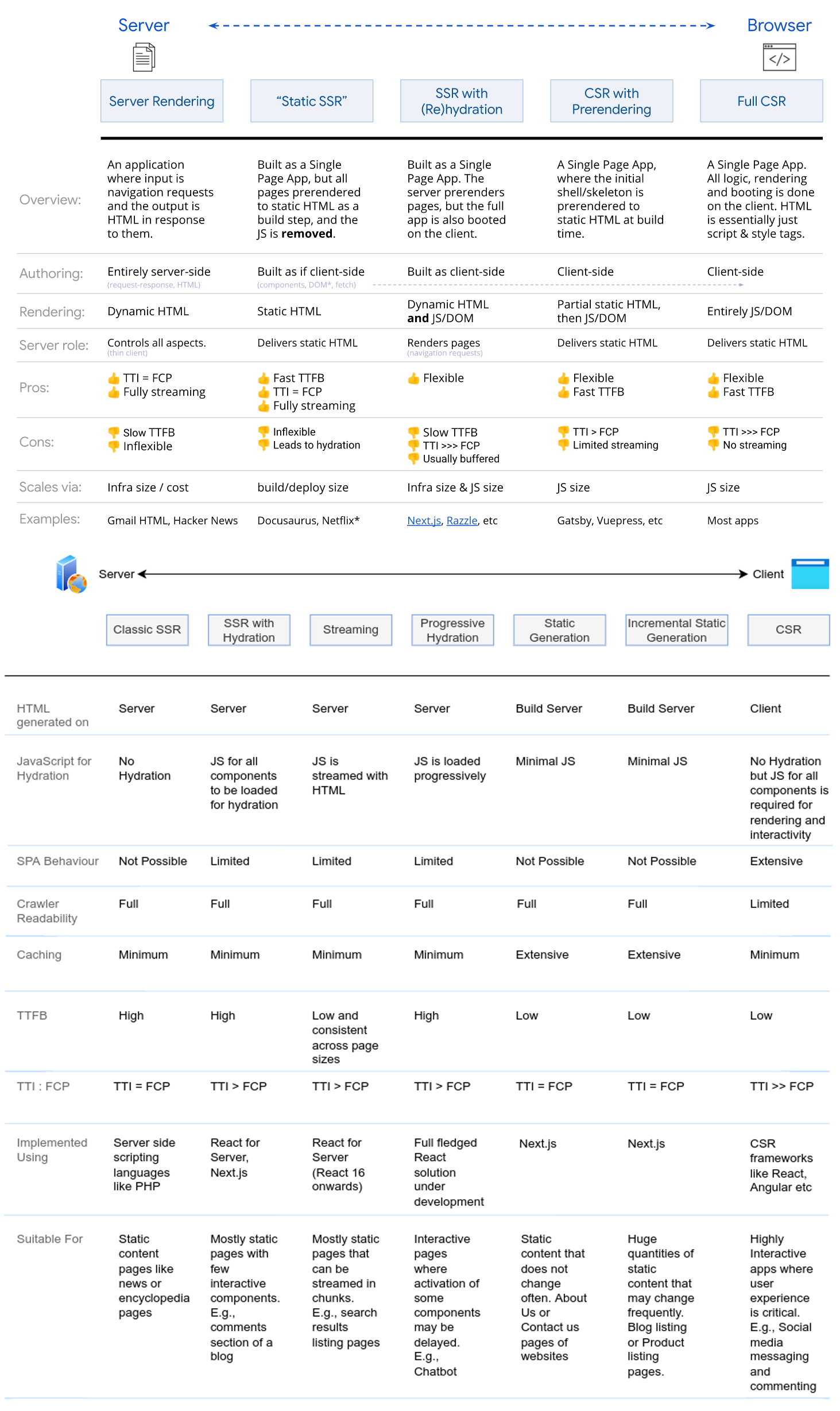
Rendering Patterns
- CSR (Client Side Rendering): SPA.
- SSR (Server Side Rendering): SPA with SEO.
- SSG (Static Site Generation): SPA with pre-rendering.
- ISR (Incremental Static Regeneration): SSG + SSR.
- SSR + CSR: HomePage with SSR, dynamic with CSR.
- SSG + CSR: HomePage with SSG, dynamic with CSR.
- SSG + SSR: static with SSG, dynamic with SSR.
CSR
- CSR hit API after the page loads (LOADING indicator).
- Data is fetched on every page request.
import { TimeSection } from '@components'
export default function CSRPage() {
const [dateTime, setDateTime] = React.useState<string>()
React.useEffect(() => {
axios
.get('https://worldtimeapi.org/api/ip')
.then((res) => {
setDateTime(res.data.datetime)
})
.catch(error => console.error(error))
}, [])
return (
<main>
<TimeSection dateTime={dateTime} />
</main>
)
}
SSR
Application code is written in a way that it can be executed both on the server and on the client. The browser displays the initial HTML (fetch from server), simultaneously downloads the single-page app (SPA) in the background. Once the client-side code is ready, the client takes over and the website becomes a SPA.
前后端分离是一种进步,但彻底的分离,也不尽善尽美, 比如会有首屏加载速度和 SEO 方面的困扰。 前后端分离+服务端首屏渲染看起来是个更优的方案, 它结合了前后端分离和服务端渲染两者的优点, 既做到了前后端分离,又能保证首页渲染速度,还有利于 SEO。
if (isBotAgent) {
// return pre-rendering static html to search engine crawler
// like Gatsby
} else {
// server side rendering at runtime for real interactive users
// ReactDOMServer.renderToString()
}
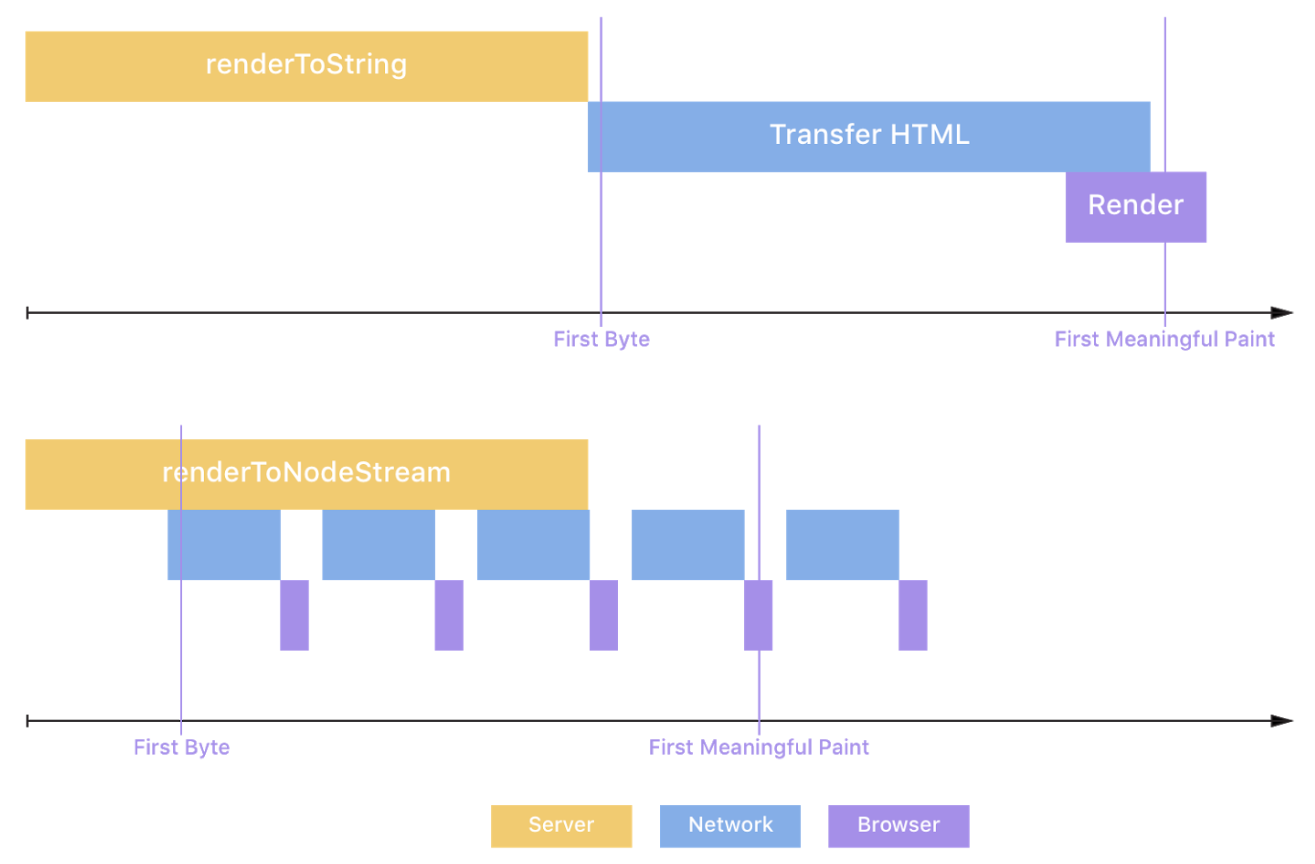
SSR Upside
- Smaller first meaningful paint time.
- HTML's strengths: progressive rendering.
- Browsers are incredibly good at rendering partial content.
- Search engine crawlers used to not execute scripts (or initial scripts).
- Search engine usually stop after a while (roughly 10 seconds).
- SPAs can't set meaningful HTTP status codes.
SSR Usage
Webpack configuration:
const baseConfig = require('./baseConfig')
const webConfig = {
...baseConfig,
target: 'web',
}
const nodeConfig = {
...baseConfig,
target: 'node',
output: {
...baseConfig.output,
libraryTarget: 'commonjs2',
},
externals: [require('webpack-node-externals')()],
}
module.exports = { webConfig, nodeConfig }
React server side rendering start.server.js
(compile to dist/server.js):
import Koa from 'koa'
import koaStatic from 'koa-static'
import { renderToString } from 'react-dom/server'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import { renderRoutes } from 'react-router-config'
import { StaticRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home, exact: true },
{
path: '/about',
component: About,
exact: true,
},
]
function getStore() {
return createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))
}
const app = new Koa()
app.use(koaStatic('public'))
app.use(async (ctx) => {
const store = getStore()
const matchedRoutes = matchRoutes(routes, ctx.request.path)
const loaders = []
matchedRoutes.forEach((item) => {
if (item.route.loadData) {
// item.route.loadData() 返回的是一个 promise.
loaders.push(item.route.loadData(store))
}
})
// 等待异步完成, store 已完成更新.
await Promise.all(loaders)
const content = renderToString(
<Provider store={store}>
<StaticRouter location={ctx.request.path}>
<div>{renderRoutes(routes)}</div>
</StaticRouter>
</Provider>
)
ctx.body = `
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">${content}</div>
<script>
window.context = {
state: ${JSON.stringify(store.getState())}
};
</script>
<script src="/public/client.js"></script>
</body>
</html>`
})
app.listen(3003, () => {
console.log('listen:3003')
})
React client side hydration start.client.js
(compile to public/client.js):
- 建立 Real DOM 与 Virtual DOM 的联系:
fiber.el = node. - 绑定事件处理器.
- 执行服务端未执行的 lifecycle hooks:
beforeMount()/onMounted().
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import { renderRoutes } from 'react-router-config'
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom'
const Routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home, exact: true },
{
path: '/about',
component: About,
exact: true,
},
]
function getStore() {
const defaultState = window.context ? window.context.state : {}
return createStore(reducer, defaultState, applyMiddleware(thunk))
}
export default function App() {
return (
<Provider store={getStore()}>
<BrowserRouter>
<div>{renderRoutes(Routes)}</div>
</BrowserRouter>
</Provider>
)
}
ReactDOM.hydrateRoot(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
Isomorphic data fetch
(getStaticProps/getServerSideProps in Next.js,
loader in Remix):
const data = await App.fetchData()
const app = <App {...data} />
return {
html: ReactDOMServer.renderToString(app),
state: { data },
}
Next.js SSR:
- SSR hit API before the page loads (DELAY before render, and no LOADING indicator).
- Data is fetched on every page request.
import { TimeSection } from '@components'
export default function SSRPage({ dateTime }: SSRPageProps) {
return (
<main>
<TimeSection dateTime={dateTime} />
</main>
)
}
export const getServerSideProps: GetServerSideProps = async () => {
const res = await axios.get('https://worldtimeapi.org/api/ip')
return {
props: { dateTime: res.data.datetime },
}
}
服务端返回的 HTML 与客户端渲染结果不一致时会产生
SSR Hydration Warning,
必须重视 SSR Hydration Warning,
要当 Error 逐个解决:
- 出于性能考虑,
hydrate可以弥补文本内容的差异, 但并不能保证修补属性的差异, 只在development模式下对这些不一致的问题报Warning. - 前后端不一致时,
hydrate时会导致页面抖动: 后端渲染的部分节点被修改, 用户会看到页面突然更改的现象, 带来不好的用户体验.
编写 SSR 组件时:
- 需要使用前后端同构的 API: 对于前端或后端独有的 API (e.g BOM, DOM, Node API), 需要进行封装与填充 (adapter/mock/polyfill).
- 注意并发与时序: 浏览器环境一般只有一个用户, 单例模式容易实现; 但 Node.js 环境可能存在多条连接, 导致全局变量相互污染.
- 部分代码只在某一端执行:
在
onCreated()创建定时器, 在onUnmounted()清除定时器, 由于onUnmounted()hooks 只在客户端执行, 会造成服务端渲染时产生内存泄漏.
SSR Reference
- Universal JavaScript presentation.
- React SSR complete guide:
- SSR and hydration.
- Isomorphic router.
- Isomorphic store.
- Isomorphic CSS.
- Vue SSR guide:
- Vite.
- Router.
- Pinia.
- Next.js for isomorphic rendering.
- Server side rendering with Puppeteer.
- Web rendering guide.
SSG
- Reloading did not change anything.
- Hit API when running
npm run build. - Data will not change because no further fetch.
import { TimeSection } from '@components'
export default function SSGPage({ dateTime }: SSGPageProps) {
return (
<main>
<TimeSection dateTime={dateTime} />
</main>
)
}
export const getStaticProps: GetStaticProps = async () => {
const res = await axios.get('https://worldtimeapi.org/api/ip')
return {
props: { dateTime: res.data.datetime },
}
}
ISR
- Based on SSG, with revalidate limit.
- Cooldown state: reloading doesn't trigger changes and pages rebuilds.
- First person that visits when cooldown state is off, is going to trigger a rebuild. That person won't be seeing changes. But, the changes will be served for the next full reload.
import { TimeSection } from '@components'
export default function ISR20Page({ dateTime }: ISR20PageProps) {
return (
<main>
<TimeSection dateTime={dateTime} />
</main>
)
}
export const getStaticProps: GetStaticProps = async () => {
const res = await axios.get('https://worldtimeapi.org/api/ip')
return {
props: { dateTime: res.data.datetime },
revalidate: 20,
}
}
Islands Architecture
- Script resources for these "islands" of interactivity (islands of dynamic components) can be delivered and hydrated independently, allowing the rest of the page to be just static HTML.
- Islands architecture combines ideas from different rendering techniques:
- Simple islands architecture implementation.
JamStack Reference
- Build your own RSC framework.
- Build your own Next.js.
- Build your own web framework.
- Modern websites building patterns.
- Modern rendering patterns.
SEO
SEO Metadata
import { Helmet } from 'react-helmet'
export default function App() {
const seo = {
title: 'About',
description:
'This is an awesome site that you definitely should check out.',
url: 'https://www.mydomain.com/about',
image: 'https://mydomain.com/images/home/logo.png',
}
return (
<Helmet
title={`${seo.title} | Code Mochi`}
meta={[
{
name: 'description',
property: 'og:description',
content: seo.description,
},
{ property: 'og:title', content: `${seo.title} | Code Mochi` },
{ property: 'og:url', content: seo.url },
{ property: 'og:image', content: seo.image },
{ property: 'og:image:type', content: 'image/jpeg' },
{ property: 'twitter:image:src', content: seo.image },
{ property: 'twitter:title', content: `${seo.title} | Code Mochi` },
{ property: 'twitter:description', content: seo.description },
]}
/>
)
}
SEO Best Practice
- Server side rendering (e.g Next.js).
- Pre-Rendering
- Mobile performance optimization (e.g minify resources, code splitting, CDN, lazy loading, minimize reflows).
- SEO-friendly routing and URL management.
- Google webmaster tools
<title>and<meta>in<head>(with tool likereact-helmet).- Includes a
robots.txtfile.
SEO Reference
Web Authentication
Cookie
- First request header -> without cookie.
- First response header ->
Set-Cookie: numberto client. - Client store identification number for specific site into cookies files.
- Second request header ->
Cookie: number. (extract identification number for specific site from cookies files). - Function: create User Session Layer on top of stateless HTTP.
用户能够更改自己的 Cookie 值 (client side), 因此不可将超过权限的数据保存在 Cookie 中 (如权限信息), 防止用户越权.
HTTP Basic Authentication
HTTP basic authentication is 401 authentication:
- 客户端向服务器请求数据:
Get /index.html HTTP/1.0
Host:www.google.com
- 服务器向客户端发送验证请求代码
401WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm="google.com"
HTTP/1.0 401 Unauthorized
Server: SokEvo/1.0
WWW-Authenticate: Basic realm="google.com"
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: xxx
- 当符合 HTTP/1.0 或 HTTP/1.1 的客户端收到 401 返回值时, 将自动弹出一个登录窗口, 要求用户输入用户名和密码.
- 用户输入用户名和密码后, 将用户名及密码以 BASE64 加密方式加密, 并将密文放入前一条请求信息中
- 服务器收到上述请求信息后, 将 Authorization 字段后的用户信息取出/解密, 将解密后的用户名及密码与用户数据库进行比较验证
Get /index.html HTTP/1.0
Host: www.google.com
Authorization: Basic d2FuZzp3YW5n==
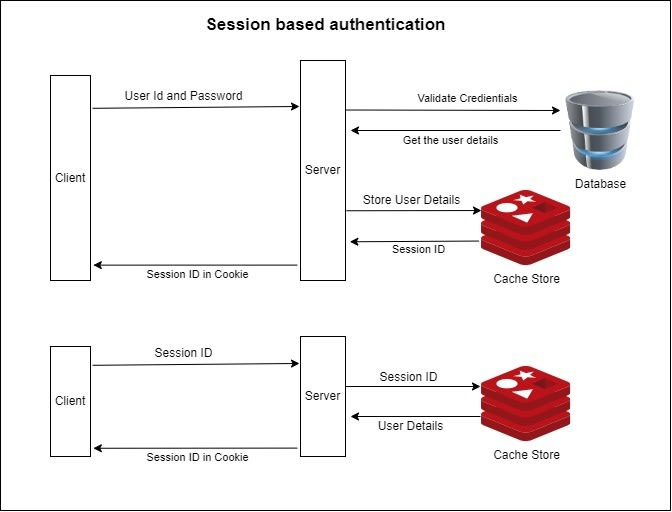
Session Cookie
Session Cookie Basis
HTTP 协议是一个无状态的协议,
服务器不会知道到底是哪一台浏览器访问了它,
因此需要一个标识用来让服务器区分不同的浏览器.
Cookie 就是这个管理服务器与客户端之间状态的标识.
Response header with Set-Cookie, Request header with Cookie.
浏览器第一次访问服务端, 服务端就会创建一次 Session, 在会话中保存标识该浏览器的信息. Session 缓存在服务端, Cookie 缓存在客户端, 他们都由服务端生成, 实现 HTTP 协议的状态.
- 客户端发送登录信息 (ID, Password).
- 服务器收到客户端首次请求并验证成功后,
会在服务器端创建 Session 并保存唯一的标识字符串 Session ID (Key-Value Store),
在 Response Header 中设置
Set-Cookie: <Session ID>. - 客户端后续发送请求都需在 Request Header 中设置:
Cookie: <Session ID>. - 服务器根据
<Session ID>进行用户验证, 利用 Session Cookie 机制可以简单地实现用户登录状态验证, 保护需要登录权限才能访问的路由服务. Max-Agepriority higher thanExpires. When both tonull, cookie become session cookie.
Set-Cookie: username=tazimi; domain=tazimi.dev; Expires=Wed, 21 Oct 2022 08:00:00
Set-Cookie: username=tazimi; domain=tazimi.dev; path=/blog
Set-Cookie: username=tazimi; domain=tazimi.dev; path=/blog; Secure; HttpOnly
Set-Cookie: username=tazimi; domain=github.com
Set-Cookie: height=100; domain=me.github.com
Set-Cookie: weight=100; domain=me.github.com
Session Cookie Cons
- 认证方式局限于在浏览器 (Cookie).
- 非 HTTPS 协议下使用 Cookie, 容易受到 CSRF 跨站点请求伪造攻击.
- Session ID 不包含具体用户信息, 需要 Key-Value Store (e.g Redis) 持久化, 在分布式环境下需要在每个服务器上都备份, 占用了大量的存储空间.
Session Cookie Usage
Session authentication with Lucia in Next.js:
signUpfunction.signInfunction.getAuthfunction.signOutfunction.- Protected routes
AuthenticatedLayout. - Authorization in UI
RootLayout.
SingUp React Server Component:
// src/features/auth/actions/sign-up.ts
'use server'
import { generateId } from 'lucia'
import { cookies } from 'next/headers'
import { redirect } from 'next/navigation'
import { Argon2id } from 'oslo/password'
import { lucia } from '@/lib/lucia'
import { prisma } from '@/lib/prisma'
async function signUp(formData: FormData) {
const formDataRaw = {
firstName: formData.get('firstName') as string,
lastName: formData.get('lastName') as string,
email: formData.get('email') as string,
password: formData.get('password') as string,
confirmPassword: formData.get('confirmPassword') as string,
}
if (formDataRaw.password !== formDataRaw.confirmPassword)
throw new Error('Passwords do not match')
// TODO: add validation yourself
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
try {
const hashedPassword = await new Argon2id().hash(
formDataRaw.password
)
const userId = generateId(15)
await prisma.user.create({
data: {
id: userId,
firstName: formDataRaw.firstName,
lastName: formDataRaw.lastName,
email: formDataRaw.email,
hashedPassword,
},
})
const session = await lucia.createSession(userId, {})
const sessionCookie = lucia.createSessionCookie(session.id)
cookies().set(
sessionCookie.name,
sessionCookie.value,
sessionCookie.attributes
)
} catch (error) {
// TODO: add error feedback yourself
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
// TODO: add error handling if user email is already taken
// The Road to Next
}
redirect('/dashboard')
}
export { signUp }
SingIn React Server Component:
// src/features/auth/actions/sign-in.ts
'use server'
import { cookies } from 'next/headers'
import { redirect } from 'next/navigation'
import { Argon2id } from 'oslo/password'
import { lucia } from '@/lib/lucia'
import { prisma } from '@/lib/prisma'
async function signIn(formData: FormData) {
const formDataRaw = {
email: formData.get('email') as string,
password: formData.get('password') as string,
}
// TODO: add validation yourself
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
try {
const user = await prisma.user.findUnique({
where: { email: formDataRaw.email },
})
if (!user) {
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
throw new Error('Incorrect email or password')
}
const validPassword = await new Argon2id().verify(
user.hashedPassword,
formDataRaw.password
)
if (!validPassword) {
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
throw new Error('Incorrect email or password')
}
const session = await lucia.createSession(user.id, {})
const sessionCookie = lucia.createSessionCookie(session.id)
cookies().set(
sessionCookie.name,
sessionCookie.value,
sessionCookie.attributes
)
} catch (error) {
// TODO: add error feedback yourself
// https://www.robinwieruch.de/next-forms/
}
redirect('/dashboard')
}
export { signIn }
getAuth function:
// src/features/auth/queries/get-auth.ts
import type { Session, User } from 'lucia'
import { cookies } from 'next/headers'
import { cache } from 'react'
import { lucia } from '@/lib/lucia'
export const getAuth = cache(
async (): Promise<
{ user: User, session: Session } | { user: null, session: null }
> => {
const sessionId
= cookies().get(lucia.sessionCookieName)?.value ?? null
if (!sessionId) {
return {
user: null,
session: null,
}
}
const result = await lucia.validateSession(sessionId)
try {
if (result.session && result.session.fresh) {
const sessionCookie = lucia.createSessionCookie(
result.session.id
)
cookies().set(
sessionCookie.name,
sessionCookie.value,
sessionCookie.attributes
)
}
if (!result.session) {
const sessionCookie = lucia.createBlankSessionCookie()
cookies().set(
sessionCookie.name,
sessionCookie.value,
sessionCookie.attributes
)
}
} catch {}
return result
}
)
SingOut React Server Component:
// src/features/auth/actions/sign-out.ts
'use server'
import { cookies } from 'next/headers'
import { redirect } from 'next/navigation'
import { lucia } from '@/lib/lucia'
import { getAuth } from '../queries/get-auth'
export async function signOut(_formData: FormData) {
const { session } = await getAuth()
if (!session)
redirect('/sign-in')
await lucia.invalidateSession(session.id)
const sessionCookie = lucia.createBlankSessionCookie()
cookies().set(
sessionCookie.name,
sessionCookie.value,
sessionCookie.attributes
)
redirect('/sign-in')
}
Protected routes:
// src/app/(authenticated)/layout.tsx
// - src/app/(authenticated)/dashboard/page.tsx
// - src/app/(authenticated)/account/page.tsx
// - and more ...
import { redirect } from 'next/navigation'
import { getAuth } from '@/features/auth/queries/get-auth'
export default async function AuthenticatedLayout({
children,
}: Readonly<{
children: React.ReactNode
}>) {
const { user } = await getAuth()
if (!user)
redirect('/sign-in')
return <>{children}</>
}
Authorization UI:
// src/app/layout.tsx
import Link from 'next/link'
import { getAuth } from '@/features/auth/queries/get-auth'
export default function RootLayout() {
const { user } = await getAuth()
const appNav = (
<>
<li>
<Link href="/">LOGO</Link>
</li>
{user && (
<li>
<Link href="/dashboard">Dashboard</Link>
</li>
)}
</>
)
const authNav = user
? (
<li>
<form action={signOut}>
<button type="submit">Sign Out</button>
</form>
</li>
)
: (
<>
<li>
<Link href="/sign-up">Sign Up</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link href="/sign-in">Sign In</Link>
</li>
</>
)
}
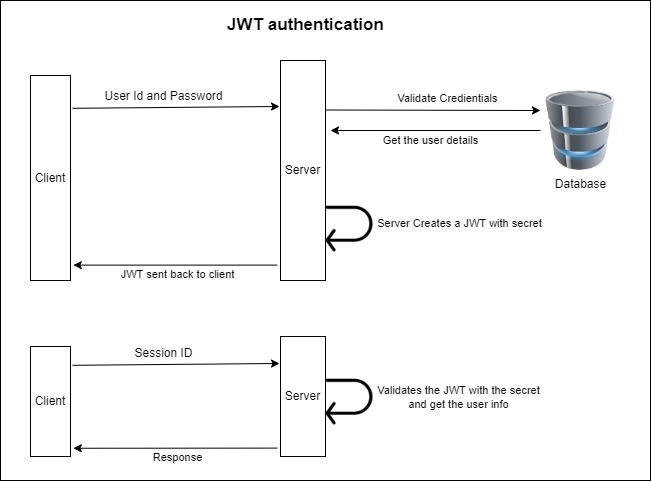
Token Authentication
Token Authentication Basis
- 客户端发送登录信息 (ID, Password).
- 服务端收到请求验证成功后, 服务端会签发一个 Token (包含用户信息) 并发送给客户端.
- 客户端收到 Token 后存储到 Cookie 或 Local Storage,
客户端每次向服务端请求都需在 Request Header 中设置:
Authorization: <Token>. - 服务端收到请求并验证 Token, 成功发送资源 (鉴权成功), 不成功发送 401 错误代码 (鉴权失败).
Token Authentication Pros
- 多端兼容性: Token 认证不局限于浏览器 (Cookie).
- 安全性: 不使用 Cookie 可以规避 CSRF 攻击.
- 灵活性: Token 中包含了用户信息, 不需要 Key-Value Store 持久化, 分布式友好. 服务器端变成无状态, 服务器端只需要根据定义的规则校验 Token 合法性. 上述两点使得 Token Authentication 具有更好的扩展性.
Token Authentication Cons
- Token 认证 (加密解密过程) 比 Session Cookie 更消耗性能.
- Token (包含用户信息) 比 Session ID 大, 更占带宽.
- 不保存 Session 状态, 无法中止或更改 Token 权限, Token 到期前会始终有效, 存在盗用风险:
- Token 有效期应短.
- Token 应使用 HTTPS 协议.
- 对于重要权限, 需使用二次验证 (Two Factor Authentication).
JSON Web Token
JSON Web Tokens is small, object-friendly (compared to SAML, Security Assertion Markup Language Tokens) and security for public/private key pair (compared to SWT, Simple Web Tokens).
JSON Web Token Basis
- 基于 Token 的解决方案中最常用的是 JWT.
- 服务器认证用户密码以后, 生成一个 JSON 对象并签名加密后作为 Token 返回给用户.
- JSON 对象包含用户信息, 用户身份, 令牌过期时间等:
- Header: 明文 Base64 编码 JSON 对象, 描述 JWT 的元数据.
一般为 Token 的加密算法和 Token 的类型, 如
{"alg": "HS256","typ": "JWT"}. - Payload: 明文 Base64 编码 JSOn 对象, 存放实际数据. 有 7 个官方字段和部分定义私有字段, 一般存放用户名, 用户身份, JWT 描述字段.
- Signature: 对 Header 和 Payload 的签名, 利用签名验证信息的正确性, 防止数据篡改. 签名需要服务端保存的密钥.
- Header: 明文 Base64 编码 JSON 对象, 描述 JWT 的元数据.
一般为 Token 的加密算法和 Token 的类型, 如
- 把三个部分拼成一个字符串, 每个部分之间用
.分隔:HeaderBase64.PayloadBase64.Signature. - 业务接口用来鉴权的 token 为
access token. 越是权限敏感的业务,access token有效期足够短, 以避免被盗用. - 一个专门生成
access token的 token, 称为refresh token.refresh token用来获取access token, 有效期更长, 通过独立服务和严格的请求方式增加安全性.
JSON Web TOken Pros
- JWT 默认是不加密.
- JWT 不加密的情况下, 不能将秘密数据写入 JWT.
- JWT 可以加密, 生成原始 Token 以后, 可以用密钥再加密一次.
- JWT 不仅可用于认证, 也可用于交换信息. 有效使用 JWT, 可以降低服务器查询数据库的次数.
JSON Web Token Cons
- 不保存 Session 状态, 无法中止或更改 Token 权限, Token 到期前会始终有效, 存在盗用风险:
- JWT 有效期应短.
- JWT 应使用 HTTPS 协议.
- 对于重要权限, 需使用二次验证 (Two Factor Authentication).
JWT Client
- HTTP request with credential data (email/password) for first request, get token data or error code from first response.
- Intercept token to
fetch/axiosrequest headers for rest requests- Sent requests with token data.
- Logout whenever token data inspire or deleted.
- Store token in
Redux/Vuexglobal state. - Store token in
localStorage/sessionStorage.
OAuth Authentication
OAuth (Open Authorization) 是一个开放标准, 作用于第三方授权和第三方访问. 用户数据的所有者告诉系统, 同意授权第三方应用进入系统, 获取这些数据. 系统从而产生一个短期进入令牌 (Token), 用来代替密码供第三方应用使用.
第三方应用申请令牌之前, 都必须先到系统备案, 说明自己的身份, 然后会拿到两个身份识别码: Client ID 和 Client Secret. 这是为了防止令牌被滥用, 没有备案过的第三方应用拿不到令牌 (Token).
OAuth Token 特征:
- 授权短 (Short Expire Time).
- 可撤销 (Revoke).
- 权限小 (Scope).
OAuth Authentication Basis
- 在 GitHub Developer Settings 中备案第三方应用, 拿到属于它的客户端 ID 和客户端密钥 (3rd-Party Server vs Resource Owner)
- 在自己的第三方网站提供一个 GitHub 登录链接,
用户点击该链接后会跳转到 GitHub OAuth API
https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize/?client_id=${clientID}. - 用户跳转到 GitHub, 通过验证并同意使用 GitHub 身份登录第三方网站, 此时就会带着授权码 Code 跳回第三方网站.
- 第三方网站收到授权码, 利用授权码, 客户端 ID, 客户端密钥向 GitHub 请求
access_token令牌https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token?client_id=${clientID}&client_secret=${clientSecret}&code=${code}(3rd-Party Server vs Authorization Server) - 第三方网站收到令牌, 可以暂时拥有 GitHub 一些请求的权限比如用户信息,
https://api.github.com/user?access_token=${accessToken}或者 Request HeaderAuthorization: token ${accessToken}. 可以构建第三方网站自己的 Token, 做进一步相关鉴权操作 (如 Session Cookie). (3rd-Party Server vs Resource Server)
OAuth 2.0
OAuth 2.0 允许自动更新令牌. 资源所有者颁发令牌时一次性颁发两个令牌, 一个用于获取数据 (Access Token), 另一个用于获取新的令牌 (Refresh Token). 令牌到期前, 第三方网站使用 Refresh Token 发请求更新令牌:
https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token
?client_id=CLIENT_ID
&client_secret=CLIENT_SECRET
&grant_type=refresh_token
&refresh_token=REFRESH_TOKEN
OAuth Usage
- Modern guide to OAuth.
Single Sign On
单点登录 (SSO) 要求不同域下的系统一次登录, 全线通用,
通常由独立的 SSO 系统记录登录状态, 下发 ticket,
各业务系统配合存储和认证 ticket:
- 用户访问系统 1 的受保护资源, 系统 1 发现用户未登录, 跳转至
SSO认证中心, 并将自己的地址作为参数. SSO认证中心发现用户未登录, 将用户引导至登录页面.- 用户输入用户名密码提交登录申请.
SSO认证中心校验用户信息, 创建用户与SSO认证中心之间的会话, 称为全局会话, 同时创建授权令牌.SSO认证中心带着令牌跳转会最初的请求地址 (系统 1).- 系统 1 拿到令牌, 去
SSO认证中心校验令牌是否有效. SSO认证中心校验令牌, 返回有效, 注册系统 1 .- 系统 1 使用该令牌创建与用户的会话, 称为局部会话, 返回受保护资源.
- 用户访问系统 2 的受保护资源.
- 系统 2 发现用户未登录, 跳转至
SSO认证中心, 并将自己的地址作为参数. SSO认证中心发现用户已登录, 跳转回系统 2 的地址, 并附上令牌.- 系统 2 拿到令牌, 去
SSO认证中心校验令牌是否有效. SSO认证中心校验令牌, 返回有效, 注册系统 2 .- 系统 2 使用该令牌创建与用户的局部会话, 返回受保护资源.
用户登录成功之后,
用户与 SSO 认证中心建立的会话称为全局会话,
用户与各个子系统建立的会话称为局部会话,
局部会话建立之后, 用户访问子系统受保护资源将不再通过 SSO 认证中心:
- 局部会话存在, 全局会话一定存在.
- 全局会话存在, 局部会话不一定存在.
- 全局会话销毁, 局部会话必须销毁.
Web Operation and Deployment
Static Assets
Fingerprinting is a technique that makes the name of a file, dependent on the contents of the file, not on the timestamp differ from servers. When the file contents change, the filename is also changed. For content that is static or infrequently changed, this provides an easy way to tell whether two versions of a file are identical, even across different servers or deployment dates.
When a filename is unique and based on its content, HTTP headers
can be set to encourage caches(code: 200) everywhere
(whether at CDNs, at ISPs, in networking equipment, or in web browsers)
to keep their own copy of the content.
When the content is updated(),
the fingerprint will change.
This will cause the remote clients to request a new copy of the content.
This is generally known as cache busting.
CI System
- Full builds upon continuous deployment.
- Incremental builds are a product of time.
Docker Deployment
FROM node:16-alpine as builder
WORKDIR /code
ADD package.json package-lock.json /code/
RUN npm install
ADD . /code
RUN npm run build
# 选择更小体积的基础镜像
FROM nginx:alpine
# 将构建产物移至 Nginx
COPY code/build/ /usr/share/nginx/html/
Nginx Configuration
子域名设置:
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/blog/html
sudo chown -R $USER:$USER /var/www/blog/html
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www
sudo cp /etc/nginx/sites-available/default /etc/nginx/sites-available/blog
# change 'root' and 'server_name' config, remove 'default_server' config
sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/blog
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/blog /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo nginx -t
sudo systemctl restart nginx
A/B Testing
- Improves customer experience: by testing different options, businesses can find out what their customers prefer and make their websites or products more enjoyable to use.
- Increases sales: if a business knows which version of a webpage leads to more sales or sign-ups, they can use that version for everyone, potentially making more money.
- Reduces risks: before making big changes, like redesigning a website, businesses can test small changes to see how people react. This way, they avoid making big investments that might not pay off.
- Informs decisions: Instead of relying on gut feelings, businesses can make informed decisions that are backed up by actual user behavior.
// A/B test causing Flash of Unstyled Content (FoUC):
// - SEO impact.
// - User experience impact.
// - Web performance impact.
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react'
const imageUrlA = 'https://fakeimg.pl/150x150/0000FF/808080?text=Variant+A'
const imageUrlB = 'https://fakeimg.pl/150x150/FF0000/FFFFFF?text=Variant+B'
const VariantA = () => <img src={imageUrlA} alt="Variant A" />
const VariantB = () => <img src={imageUrlB} alt="Variant B" />
export default function ABTestComponent() {
const [variant, setVariant] = useState('loading')
useEffect(() => {
// Simulate reading from localStorage with a delay
const timeout = setTimeout(() => {
const randomVariant = Math.random() < 0.5 ? 'A' : 'B'
const storedVariant = localStorage.getItem('userVariant') ?? randomVariant
localStorage.setItem('userVariant', storedVariant)
setVariant(storedVariant)
}, 500) // 500ms second delay to simulate a flicker effect
return () => clearTimeout(timeout)
}, [])
return (
<div>
{variant === 'loading' && <div>Loading variant...</div>}
{variant === 'A' && <VariantA />}
{variant === 'B' && <VariantB />}
</div>
)
}
Blue Green Deployment
两套系统, 一套稳定的绿色系统, 一套即将发布的蓝色系统. 不断切换并迭代发布到生产环境中.
Rolling Update
多个集群实例的服务中, 在不影响服务的情况下, 停止一个或多个实例, 逐步进行版本更新.
Gray Release
Gray Release Introduction
Canary Release: 全量或增量部署新文件, 并逐步把流量切换至新 CDN URL. 根据灰度白名单, 将灰度测试用户的 CDN Assets 更换至不同 Version Number 或者 Fingerprint 的新版本前端页面文件.
Gray Release Solution
通过灰度发布收集用户反馈 (转化率等指标), 决定后续是否全面将所有流量切至新版本, 或者完全放弃新版本, 亦或是通过 FLAGS 结合用户特征图像, (如用户级别, UA, Cookie Location, IP, Feature List 等) 只向部分流量投放新版本. 可以实现千人千页, 每个用户获得由不同的功能 (FLAGS 开启关闭) 组成的不同页面.
业界成熟的灰度方案:
- 简单灰度逻辑通过 Nginx 配置做规则判断(路由, 参数, IP, Cookie 等), upstream 到不同的服务器:
- 新代码部署到 A 边.
- 符合灰度策略的小部分流量切到 A 边, 剩余大部分流量仍去往 B 边
- 验证 A 边功能是否正常可用/好用
- 验证无误后, 大部分流量转到 A 边, 灰度流量去往 B 边
- 验证 B 边功能是否正常可用/好用
- 验证无误后, 流量像往常一样均分到 AB 边
# Canary Deployment
map $COOKIE_canary $group {
# canary account
~*devui$ server_canary;
default server_default;
}
# 流量均分, 注释掉其中某一边, 另一边为灰度流量访问边
upstream server_canary {
server 11.11.11.11:8000 weight=1 max_fails=1 fail_timeout=30s;
server 22.22.22.22 weight=1 max_fails=1 fail_timeout=30s;
}
# 流量均分, 注释掉其中某一边, 另一边为正常流量访问边
upstream server_default {
server 11.11.11.11:8000 weight=2 max_fails=1 fail_timeout=30s;
server 22.22.22.22 weight=2 max_fails=1 fail_timeout=30s;
}
# 配置 8000 端口的转发规则, 并且 expose port
server {
listen 8000;
server_name _;
root /var/canaryDemo;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
root /var/canaryDemo;
index index.html;
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
}
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name _;
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
root /var/canaryDemo;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
proxy_pass http://$group;
# root /var/canaryDemo;
# index index.html;
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.h
}
- 复杂灰度逻辑通过 Nginx + Lua 新增一个灰度中心服务, 结合业务来做流量的灰度与切换, 控制 HTML 入口文件, 使灰度规则与业务代码解耦.
Gray Release Performance
-
前端优化: 每一个页面都需要去获取灰度规则, 这个灰度请求将阻塞页面. 可以使用 localStorage 存储这个用户是否为灰度用户, 然后定期的更新 localStorage, 取代大量的请求造成的体验问题.
-
后端优化: 利用 MemCache 在内存中缓存灰度规则与灰度用户列表, 提升灰度发布性能.
DevOps Reference
ESLint
ESLint Flat Config
Flat config compatibility solution.
Babel
babel example.js -o compiled.js
babel src -d lib -s
Babel Node
A read-eval-print loop(REPL) can replace node REPL.
Babel Core
提供 babel 转码 API
npm install babel-core --save
const babel = require('babel-core')
// 字符串转码
babel.transform('code();', options)
// => { code, map, ast }
// 文件转码 (异步)
babel.transformFile('filename.js', options, (err, result) => {
process(err)
return result // => { code, map, ast }
})
// 文件转码 (同步)
babel.transformFileSync('filename.js', options)
// => { code, map, ast }
// Babel AST转码
babel.transformFromAst(ast, code, options)
// => { code, map, ast }
CodeMod Tool
Use Babel to refactor code:
Babel Transform Plugin
- Visitor pattern with Babel.
- Named
babel-plugin-transform-xxx.
{
"main": "index.js"
}
// index.js
module.exports = (babel) => {
const t = babel.types
let isJSXExisted = false
let isMeactContextEnabled = false
return {
visitor: {
Program: {
exit(path) {
if (isJSXExisted === true && isMeactContextEnabled === false)
throw path.buildCodeFrameError(`Meact isn't in current context!`)
},
},
ImportDeclaration(path, state) {
if (path.node.specifiers[0].local.name === 'Meact')
isMeactContextEnabled = true
},
MemberExpression(path, state) {
if (
path.node.object.name === 'React'
&& path.node.property.name === 'createElement'
) {
isJSXExisted = true
path.replaceWith(
t.MemberExpression(
t.identifier('Meact'),
t.identifier('createElement')
)
)
}
},
},
}
}
Babel plugins:
- Define plugin.
Babel Preset Plugin
- Just like
.babelrc.js. - Named
babel-preset-xxx.
// package.json
{
"main": "index.js",
"dependencies": {
"babel-plugin-transform-meact-jsx": "^0.1.2",
"@babel/plugin-proposal-object-rest-spread": "^7.0.0",
"@babel/plugin-transform-react-jsx": "^7.0.0",
"@babel/plugin-transform-runtime": "^7.0.0",
"@babel/preset-env": "^7.0.0"
}
}
// index.js
const defaultTargets = {
android: 30,
chrome: 35,
edge: 14,
explorer: 9,
firefox: 52,
safari: 8,
ucandroid: 1,
}
function buildTargets(options) {
return Object.assign({}, defaultTargets, options.additionalTargets)
}
module.exports = function buildMeactPreset(context, options) {
const transpileTargets
= (options && options.targets) || buildTargets(options || {})
return {
presets: [
require('@babel/preset-env').default(null, {
targets: transpileTargets,
modules: false,
}),
],
plugins: [
require('@babel/plugin-proposal-object-rest-spread'),
require('@babel/plugin-transform-react-jsx'),
require('babel-plugin-transform-meact-jsx'),
require('@babel/plugin-transform-runtime'),
].filter(Boolean),
}
}
Webpack
Webpack Workflow
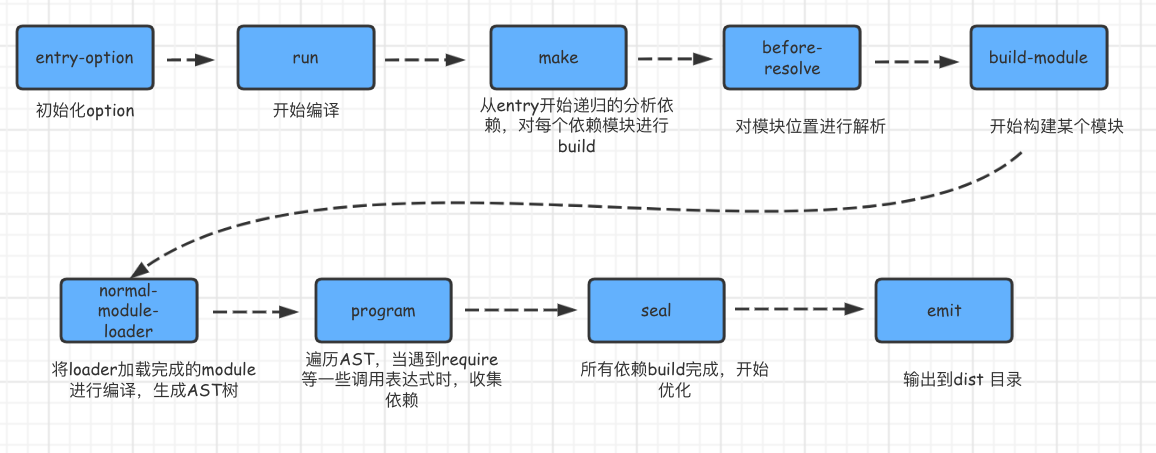
Webpack Configuration Intellisense
Enable webpack configuration types intellisense:
npm i -D webpack webpack-cli webpack-dev-server
Enable devServer type intellisense:
# Add `devServer` type to `webpack.Configuration`
npm i -D @types/webpack-dev-server
/** @type {import('webpack').Configuration} */
module.exports = {
entry: {
main: './src/index.ts',
},
output: {
filename: devMode ? '[name].js' : '[name].[contenthash].js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'build'),
},
mode: devMode ? 'development' : 'production',
devServer: {
hot: true,
open: true,
port: 2333,
},
}
Webpack Hot Module Replacement
HMR:
- 使用 WDS 托管静态资源, 同时以 Runtime 方式注入 HMR 客户端代码 (HMR Runtime).
- 浏览器加载页面后, 与 WDS 建立 WebSocket 连接.
- Webpack 监听到文件变化后, 增量构建发生变更的模块, 并通过 WebSocket 发送 hash 事件.
- 浏览器接收到 hash 事件后, 请求 manifest (
[hash].hot-update.json) 资源文件, 确认增量变更范围. - 浏览器加载发生变更的增量模块.
- 浏览器中注入的 HMR Runtime 触发变更模块的
module.hot.accept回调, 执行代码变更逻辑.
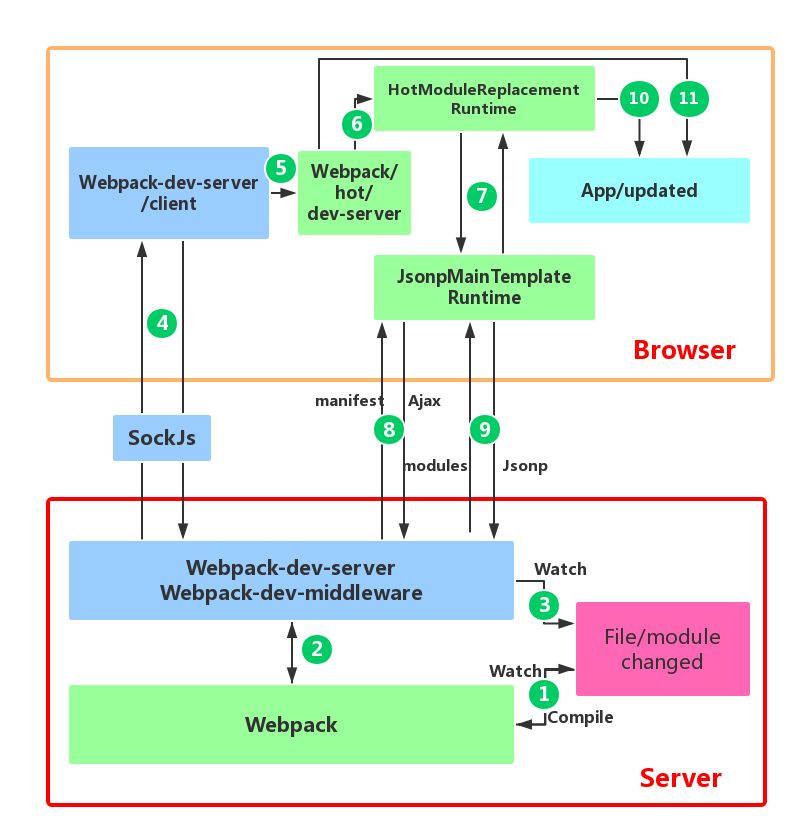
module.hot.accept 有两种调用模式:
- 无参调用模式
module.hot.accept(): 当前文件修改后, 重头执行当前文件代码. - 回调调用模式
module.hot.accept(path, callback): 常用模式, 监听模块变更, 执行代码变更逻辑.
// 该模块修改后, `console.log('bar')` 会重新执行
console.log('bar')
module.hot.accept()
import component from './component'
let demoComponent = component()
document.body.appendChild(demoComponent)
if (module.hot) {
module.hot.accept('./component', () => {
const nextComponent = component()
document.body.replaceChild(nextComponent, demoComponent)
demoComponent = nextComponent
})
}
react-refresh-webpack-plugin/vue-loader/style-loader
利用 module.hot.accept 实现了 HMR (forceUpdate),
无需开发者编写热模块更新逻辑.
Webpack Watch Options
echo fs.notify.max_user_watches=524288 | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf
sudo sysctl -p
Webpack Resolve Path Options
const TsconfigPathsPlugin = require('tsconfig-paths-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
resolve: {
alias: {
'#': path.resolve(__dirname, '/'),
'~': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src'),
'@': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src'),
'~@': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src'),
'vendor': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src/vendor'),
'~component': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src/components'),
'~config': path.resolve(__dirname, 'config'),
},
extensions: ['.tsx', '.ts', '.jsx', '.js'],
plugins: [new TsconfigPathsPlugin({ configFile: './tsconfig.json' })],
},
}
get baseUrland paths from tsconfig.json:
const TsconfigPathsPlugin = require('tsconfig-paths-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
resolve: {
plugins: [new TsconfigPathsPlugin({ configFile: './tsconfig.json' })],
},
}
jsconfig.json for vscode resolve path:
{
"compilerOptions": {
// This must be specified if "paths" is set
"baseUrl": ".",
// Relative to "baseUrl"
"paths": {
"*": ["*", "src/*"]
}
}
}
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2017",
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": false,
"baseUrl": "./",
"paths": {
"Config/*": ["src/config/*"],
"Components/*": ["src/components/*"],
"Ducks/*": ["src/ducks/*"],
"Shared/*": ["src/shared/*"],
"App/*": ["src/*"]
}
},
"exclude": ["node_modules", "dist"]
}
Webpack Flag Options
- --progress
- --colors
- -p
Webpack Devtool Source Map Configuration
| Devtool | Build | Rebuild | Production | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (none) / false | fastest | fastest | yes | bundle |
| eval | fast | fastest | no | generated |
| eval-cheap-source-map | ok | fast | no | transformed |
| eval-cheap-module-source-map | slow | fast | no | lines only |
| eval-source-map | slowest | ok | no | lines + rows |
Webpack Cache Configuration
Webpack Build Cache
cache is set to type: 'memory' in development mode
and disabled in production mode.
cache: true is an alias to cache: { type: 'memory' }.
Accelerate second build time:
module.exports = {
cache: {
type: 'filesystem',
},
}
Webpack Browser Cache
- Webpack caching guide.
- Use
[contenthash]and long-term browser cache to improve second access time.
Webpack Library Configuration
const path = require('node:path')
module.exports = {
entry: {
'bod-cli.min': path.join(__dirname, './src/index.js'),
'bod-cli': path.join(__dirname, './src/index.js'),
},
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, './dist'),
filename: '[name].[contenthash].js',
library: 'bod',
libraryExport: 'default',
libraryTarget: 'esm',
globalObject: 'this',
},
}
Webpack Loader Configuration
Webpack Babel Loader
const config = {
test: /\.(js|mjs|jsx|ts|tsx)$/,
include: path.resolve('src'),
use: [
'thread-loader',
{
loader: require.resolve('babel-loader'),
},
],
options: {
customize: require.resolve('babel-preset-react-app/webpack-overrides'),
plugins: [
[
require.resolve('babel-plugin-named-asset-import'),
{
loaderMap: {
svg: {
ReactComponent: '@svgr/webpack?-svgo,+titleProp,+ref![path]',
},
},
},
],
['lodash'],
],
cacheDirectory: true,
cacheCompression: false,
compact: isEnvProduction,
},
}
Webpack CSS Loader
style-loader将 CSS 动态注入到 DOM 中 (document.createElement('style')), 导致 DOM 重新渲染.production下需利用Webpack将 CSS 提前打包 (mini-css-extract-plugin):- 优先加载 critical CSS in
<head>. - Lazy loading non-critical CSS.
- Split up non-initial page CSS.
- 优先加载 critical CSS in
Next.js不允许:global(.global-class):modules.mode设置为pure.
const CssMinimizerPlugin = require('css-minimizer-webpack-plugin')
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin')
const devMode = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /.s?css$/,
exclude: /node_modules$/,
use: [
devMode ? 'style-loader' : MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,
{
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
modules: {
compileType: 'module',
localIdentName: '[local]__[hash:base64:5]',
},
},
},
'sass-loader',
{
loader: 'postcss-loader',
options: {
postcssOptions: {
plugins: [['autoprefixer']],
},
},
},
],
},
],
},
optimization: {
minimizer: [
// `...`,
new CssMinimizerPlugin(),
],
},
}
Webpack Static Assets Loader
- ImageMin Loader
asset/resourceemits separate file and exports the URL (file-loader).asset/inlineexports data URI of the asset (url-loader).asset/sourceexports source code of the asset (raw-loader).assetautomatically chooses between exporting data URI and separate file (url-loaderwith asset size limit, default8kb).
const config = {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif|jpeg|webp|svg|eot|ttf|woff|woff2)$/,
type: 'asset',
parser: {
dataUrlCondition: {
maxSize: 4 * 1024, // 4kb
},
},
},
],
}
Webpack Resource Assets
const path = require('node:path')
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
filename: 'main.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
assetModuleFilename: 'images/[hash][ext][query]',
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.png/,
type: 'asset/resource',
},
{
test: /\.html/,
type: 'asset/resource',
generator: {
filename: 'static/[hash][ext][query]',
},
},
],
},
}
import mainImage from './images/main.png'
img.src = mainImage // '/dist/151cfcfa1bd74779aadb.png'
Webpack Inline Assets
const path = require('node:path')
const svgToMiniDataURI = require('mini-svg-data-uri')
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
filename: 'main.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.svg/,
type: 'asset/inline',
generator: {
dataUrl: (content) => {
content = content.toString()
return svgToMiniDataURI(content)
},
},
},
],
},
}
import metroMap from './images/metro.svg'
block.style.background = `url(${metroMap})`
// => url(data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB4bW0iaHR0cDo...vc3ZnPgo=)
Webpack Source Assets
const path = require('node:path')
module.exports = {
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
filename: 'main.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.txt/,
type: 'asset/source',
},
],
},
}
import exampleText from './example.txt'
block.textContent = exampleText // 'Hello world'
Webpack Thread Loader
const config = {
rules: [
{
loader: 'thread-loader',
// loaders with equal options will share worker pools
options: {
// the number of spawned workers, defaults to (number of cpus - 1) or
// fallback to 1 when require('os').cpus() is undefined
workers: 2,
// number of jobs a worker processes in parallel
// defaults to 20
workerParallelJobs: 50,
// additional node.js arguments
workerNodeArgs: ['--max-old-space-size=1024'],
// Allow to respawn a dead worker pool
// respawning slows down the entire compilation
// and should be set to false for development
poolRespawn: false,
// timeout for killing the worker processes when idle
// defaults to 500 (ms)
// can be set to Infinity for watching builds to keep workers alive
poolTimeout: 2000,
// number of jobs the poll distributes to the workers
// defaults to 200
// decrease of less efficient but more fair distribution
poolParallelJobs: 50,
// name of the pool
// can be used to create different pools with elseWise identical options
name: 'my-pool',
},
},
// your expensive loader (e.g babel-loader)
],
}
const threadLoader = require('thread-loader')
threadLoader.warmup(
{
// pool options, like passed to loader options
// must match loader options to boot the correct pool
},
[
// modules to load
// can be any module, i. e.
'babel-loader',
'babel-preset-es2015',
'sass-loader',
]
)
Webpack Web Worker Loader
npm i -D worker-loader
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.worker\.js$/,
use: { loader: 'worker-loader' },
},
],
},
}
Webpack Optimization
- CDN.
- 服务器端渲染.
- 提取公共库.
- 代码压缩.
- 代码分割: Chunks.
- 代码分割: 按需加载.
- 优化构建速度:
- 缩小文件搜索范围:
- 优化
loader配置:include/exclude. - 优化
module.noParse配置: 忽略对部分没采用模块化的文件的递归解析处理. - 优化
resolve.modules配置: 第三方模块. - 优化
resolve.alias配置. - 优化
resolve.mainFields配置. - 优化
resolve.extensions配置: 后缀列表.
- 优化
- 减少打包文件:
- 提取公共代码.
- 动态链接
DllPlugin. externals.- Tree shaking.
- 缓存:
- 持久化缓存.
babel缓存cacheDirectory: true.cache-loader.
- 多进程:
thread-loader.
- 缩小文件搜索范围:
- JD Webpack optimization guide.
Common Libraries
{
"externals": {
"moment": "window.moment",
"antd": "window.antd",
"lodash": "window._",
"react": "window.React",
"react-dom": "window.ReactDOM"
}
}
Common Chunks
const config = new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
name: string, // or
names: [string],
// The chunk name of the commons chunk.
// An existing chunk can be selected by passing a name of an existing chunk.
// If an array of strings is passed this is equal to
// invoking the plugin multiple times for each chunk name.
// If omitted and `options.async` or `options.children`
// is set all chunks are used, otherwise `options.filename`
// is used as chunk name.
// When using `options.async` to create common chunks
// from other async chunks you must specify an entry-point
// chunk name here instead of omitting the `option.name`.
filename: string,
// The filename template for the commons chunk.
// Can contain the same placeholders as `output.filename`.
// If omitted the original filename is not modified
// (usually `output.filename` or `output.chunkFilename`).
// This option is not permitted if you're using `options.async` as well,
// see below for more details.
minChunks: number | Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY | fn,
// (module, count) => boolean,
// The minimum number of chunks which need to contain a module
// before it's moved into the commons chunk.
// The number must be greater than or equal 2
// and lower than or equal to the number of chunks.
// Passing `Infinity` creates the commons chunk, but moves no modules into it.
// By providing a `function` you can add custom logic.
// (Defaults to the number of chunks)
chunks: [string],
// Select the source chunks by chunk names.
// The chunk must be a child of the commons chunk.
// If omitted all entry chunks are selected.
children: boolean,
// If `true` all children of the commons chunk are selected
deepChildren: boolean,
// If `true` all descendants of the commons chunk are selected
async: boolean | string,
// If `true` a new async commons chunk is created
// as child of `options.name` and sibling of `options.chunks`.
// It is loaded in parallel with `options.chunks`.
// Instead of using `option.filename`,
// it is possible to change the name of the output file by providing
// the desired string here instead of `true`.
minSize: number,
// Minimum size of all common module before a commons chunk is created.
})
Code Minimization
const CssMinimizerPlugin = require('css-minimizer-webpack-plugin')
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin')
const TerserPlugin = require('terser-webpack-plugin')
const isEnvProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
const isEnvProductionProfile
= isEnvProduction && process.argv.includes('--profile')
const shouldUseSourceMap = process.env.GENERATE_SOURCEMAP !== 'false'
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(js|mjs|jsx|ts|tsx)$/,
include: path.resolve('src'),
use: [
'thread-loader',
{
loader: require.resolve('babel-loader'),
},
],
},
{
test: /.s?css$/,
use: [MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader, 'css-loader', 'sass-loader'],
},
],
},
optimization: {
minimize: true,
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
parallel: true,
terserOptions: {
parse: {
ecma: 8,
},
compress: {
ecma: 5,
warnings: false,
drop_console: true,
comparisons: false,
inline: 2,
},
mangle: {
safari10: true,
},
keep_classnames: isEnvProductionProfile,
keep_fnames: isEnvProductionProfile,
output: {
ecma: 5,
comments: false,
ascii_only: true,
},
},
}),
new CssMinimizerPlugin(),
],
},
}
Code Splitting
Huge bundle downside:
- Cache invalid: one line code make whole cache invalid.
- Useless code: only use
1/Nofbundle.js.
Code splitting methods:
require.ensure([], () => {});.- async/await
import. React.SuspenseandReact.lazy.- Route-based code splitting.
vendor.[hash].chunk.js(document.createElement('script')promise): splitting vendor and application code is to enable long term caching techniques Since vendor code tends to change less often than the actual application code, browser will be able to cache them separately, and won't re-download them each time the app code changes.
Split chunks configuration:
- chunks:
- async: 只提取异步加载的模块出来打包到一个文件中.
- initial: 提取同步加载和异步加载模块, 分别打包到不同的文件中.
- all: 不管异步加载还是同步加载的模块都提取出来, 打包到一个文件中.
- minSize: 超过 minSize 才会被提取.
- maxSize: 超过 maxSize 会被进一步分割.
- minChunks: 引用次数 >= minChunks 值才被提取.
- maxAsyncRequests: 最大的按需 (异步) 加载次数 (default: 6).
- maxInitialRequests: 入口文件加载最大数 (default: 4).
- automaticNameDelimiter: 文件名分割符.
- name: chunk 文件名.
- cacheGroups: 配置提取模块的方案, 里面每一项代表一个提取模块的方案.
- priority: 值越大优先级越大.
- test: 匹配模块路径或名称.
- reuseExistingChunk:
true/false. - enforce:
true/false.
module.exports = {
optimization: {
runtimeChunk: true,
splitChunks: {
chunks: 'async',
minSize: 30000,
maxSize: 200000,
minChunks: 1,
maxAsyncRequests: 6,
maxInitialRequests: 4,
automaticNameDelimiter: '-',
cacheGroups: {
vendors: {
name: 'chunk-vendors',
priority: -10,
chunks: 'initial',
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
},
common: {
name: 'chunk-common',
priority: -20,
chunks: 'initial',
minChunks: 2,
reuseExistingChunk: true,
},
element: {
name: 'element-ui',
priority: 0,
chunks: 'all',
test: /[\\/]element-ui[\\/]/,
},
api: {
name: 'api',
priority: 0,
test: /[\\/]api[\\/]/,
},
subApi: {
name: 'subApi',
priority: 10,
minChunks: 2,
test: /[\\/]api[\\/]subApi[\\/]/,
},
mixin: {
name: 'mixin',
priority: 0,
test: /[\\/]mixin[\\/]/,
},
},
},
},
}
Next.js granular chunking configuration:
module.exports = {
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
chunks: chunk => !/^polyfills|main|pages\/_app$/.test(chunk.name),
cacheGroups: {
framework: {
chunks: 'all',
name: 'framework',
test(module) {
const resource = module.nameForCondition?.()
return resource
? topLevelFrameworkPaths.some(pkgPath =>
resource.startsWith(pkgPath)
)
: false
},
priority: 40,
enforce: true,
},
lib: {
test(module: {
size: Function
nameForCondition: Function
}): boolean {
return (
module.size() > 160000
&& /node_modules[/\\]/.test(module.nameForCondition() || '')
)
},
name(module: {
type: string
libIdent?: Function
updateHash: (hash: crypto.Hash) => void
}): string {
const hash = crypto.createHash('sha1')
if (isModuleCSS(module)) {
module.updateHash(hash)
} else {
if (!module.libIdent) {
throw new Error(
`Encountered unknown module type: ${module.type}.`
)
}
hash.update(module.libIdent({ context: dir }))
}
return hash.digest('hex').substring(0, 8)
},
priority: 30,
minChunks: 1,
reuseExistingChunk: true,
},
},
maxInitialRequests: 25,
minSize: 20000,
},
},
}
Tree Shaking
Webpack tree shaking includes:
usedExportsOptimization: Remove unused export variables from modules, thereby further eliminating related side-effect-free statements. Inlib.js, variablebis unused, so related code is removed from the final output.sideEffectsOptimization: Remove modules from the module graph where export variables are not used. Inutil.js, no export variables are used and entire module are side-effect-free. soutil.jsmodule is removed from the final output.- DCE (Dead Code Elimination) Optimization:
Remove dead code by by general minification tools.
In
bootstrap.js, theconsole.log('bad')statement will not execute, so related code is removed from the final output.
// index.js
import { a } from './lib'
import { c } from './util'
import './bootstrap'
console.log(a)
// lib.js
export const a = 1
export const b = 2
// util.js
export const c = 3
export const d = 4
// bootstrap.js
console.log('bootstrap')
if (false)
console.log('bad')
else
console.log('good')
Write tree-shakable code:
- 避免无意义的赋值.
- 尽量不写带有副作用的代码: 诸如编写了立即执行函数, 在函数里又使用了外部变量等.
- 如果对 ES6 语义特性要求不是特别严格, 可以开启 babel 的 loose 模式 etc. 是否真的要不可枚举 class 的属性 (babel 将 Class 转化为 ES5 过程中会产生 Side Effect, 导致 Tree Shaking 失效).
- 禁止 Babel 将模块导入导出语句转译成
CommonJS形式.@babel/preset-env: always{ "modules": false }.- Babel 作为编译器不应该处理
modules类型的转换. - Webpack 要依赖
esm模块进行 tree shaking.
- 如果是开发 JavaScript 库, 使用
rollup(ES6 module export + code flow static analysis), 并且提供 ES6 module 的版本, 入口文件地址设置到package.json的 module 字段. - 如果 JavaScript 库开发中, 难以避免的产生各种副作用代码, 可以将功能函数或者组件, 打包成单独的文件或目录, 以便于用户可以通过目录去加载. 如有条件, 也可为自己的库开发单独的 webpack-loader, 便于用户按需加载.
- 优化导出粒度, 保持导出值颗粒度和原子性:
export { foo, bar }better thanexport default alls. - 使用支持
Tree Shaking的包:lodash-esorbabel-plugin-lodash.
Building Caches
const config = new HardSourceWebpackPlugin({
// Either an absolute path or relative to webpack options.context.
cacheDirectory: 'node_modules/.cache/hard-source/[confighash]',
// Either a string of object hash function given a webpack config.
configHash: (webpackConfig) => {
// node-object-hash on npm can be used to build this.
return require('node-object-hash')({ sort: false }).hash(webpackConfig)
},
// Either false, a string, an object, or a project hashing function.
environmentHash: {
root: process.cwd(),
directories: [],
files: ['package-lock.json', 'yarn.lock'],
},
// An object.
info: {
// 'none' or 'test'.
mode: 'none',
// 'debug', 'log', 'info', 'warn', or 'error'.
level: 'debug',
},
// Clean up large, old caches automatically.
cachePrune: {
// Caches younger than `maxAge` are not considered for deletion. They must
// be at least this (default: 2 days) old in milliseconds.
maxAge: 2 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000,
// All caches together must be larger than `sizeThreshold` before any
// caches will be deleted. Together they must be at least this
// (default: 50 MB) big in bytes.
sizeThreshold: 50 * 1024 * 1024,
},
})
Webpack 5
const config = {
cache: {
type: 'memory',
},
}
const config = {
cache: {
type: 'filesystem',
buildDependencies: {
config: [__filename],
},
},
}
Webpack Perf Profiling
const SpeedMeasurePlugin = require('speed-measure-webpack-plugin')
const smp = new SpeedMeasurePlugin()
const webpackConfig = smp.wrap({
plugins: [new MyPlugin(), new MyOtherPlugin()],
})
npx webpack --mode production --profile --json > stats.json
Commit Linter
{
"husky": {
"hooks": {
"commit-msg": "commitlint -e -V",
"pre-commit": "lint-staged"
}
},
"lint-staged": {
"src/**/*.{js,jsx, ts, tsx}": ["eslint --fix", "git add"],
"src/**/*.{css, scss}": ["stylelint --fix", "git add"]
}
}
Webpack Plugins
Webpack HTML Plugins
Webpack JavaScript Plugins
- UglifyJS Terser Plugin
- JavaScript Obfuscator
- Circular Dependency Plugin
- TypeScript React Components Properties Parser
Webpack CSS Plugins
Webpack Images Plugins
Webpack Building Work Plugins
Webpack Bundles UI Plugins
Webpack DLL Plugins
Webpack 5 support out of box cache.
Webpack Misc Plugins
- PreLoad plugin
- PreFetch plugin
- Define Plugin
- Provide Plugin
- Webpack Merge
Webpack Custom Plugin
module.exports = {
plugins: [
function () {
this.hooks.done.tap('done', (stats) => {
if (
stats.compilation.errors
&& stats.compilation.errors.length
&& !process.argv.includes('--watch')
) {
// Process build errors.
process.exit(1)
}
})
},
],
}
const childProcess = require('node:child_process')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const branch = childProcess
.execSync('git rev-parse --abbrev-ref HEAD')
.toString()
.replace(/\s+/, '')
const version = branch.split('/')[1]
const scripts = [
'https://cdn.bootcss.com/react-dom/16.9.0-rc.0/umd/react-dom.production.min.js',
'https://cdn.bootcss.com/react/16.9.0/umd/react.production.min.js',
]
class HotLoad {
apply(compiler) {
compiler.hooks.beforeRun.tap('UpdateVersion', (compilation) => {
compilation.options.output.publicPath = `./${version}/`
})
compiler.hooks.compilation.tap('HotLoadPlugin', (compilation) => {
HtmlWebpackPlugin.getHooks(compilation).alterAssetTags.tapAsync(
'HotLoadPlugin',
(data, cb) => {
scripts.forEach(src => [
data.assetTags.scripts.unshift({
tagName: 'script',
voidTag: false,
attributes: { src },
}),
])
cb(null, data)
}
)
})
}
}
module.exports = HotLoad
Typed webpack plugin from laravel-mix/:
const readline = require('node:readline')
const chalk = require('chalk')
const Table = require('cli-table3')
const _ = require('lodash')
const stripAnsi = require('strip-ansi')
const { formatSize } = require('webpack/lib/SizeFormatHelpers')
const { version } = require('../../package.json')
/**
* @typedef {object} BuildOutputOptions
* @property {boolean} clearConsole console cleared
* @property {boolean} showRelated show related
*/
/**
* @typedef {object} StatsAsset
* @property {string} name name
* @property {number} size size
* @property {StatsAsset[]|{}} related related
*/
/**
* @typedef {object} StatsData
* @property {StatsAsset[]} assets assets
*/
class BuildOutputPlugin {
/**
*
* @param {BuildOutputOptions} options
*/
constructor(options) {
this.options = options
this.patched = false
}
/**
* Apply the plugin.
*
* @param {import('webpack').Compiler} compiler
*/
apply(compiler) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'test')
return
compiler.hooks.done.tap('BuildOutputPlugin', (stats) => {
if (stats.hasErrors())
return false
if (this.options.clearConsole)
this.clearConsole()
const data = stats.toJson({
assets: true,
builtAt: true,
hash: true,
performance: true,
relatedAssets: this.options.showRelated,
})
this.heading(`Laravel Mix v${version}`)
console.log(
chalk.green.bold(`✔ Compiled Successfully in ${data.time}ms`)
)
if (data.assets.length)
console.log(this.statsTable(data))
})
}
/**
* Print a block section heading.
*
* @param {string} text
*/
heading(text) {
console.log()
console.log(chalk.bgBlue.white.bold(this.section(text)))
console.log()
}
/**
* Create a block section.
*
* @param {string} text
*/
section(text) {
const padLength = 3
const padding = ' '.repeat(padLength)
text = `${padding}${text}${padding}`
const line = ' '.repeat(text.length)
return `${line}\n${text}\n${line}`
}
/**
* Generate the stats table.
*
* @param {StatsData} data
* @returns {string} return
*/
statsTable(data) {
const assets = this.sortAssets(data)
const table = new Table({
head: [chalk.bold('File'), chalk.bold('Size')],
colWidths: [35],
colAligns: ['right'],
style: {
head: [],
compact: true,
},
})
for (const asset of assets)
table.push([chalk.green(asset.name), formatSize(asset.size)])
this.extendTableWidth(table)
this.monkeyPatchTruncate()
return table.toString()
}
/**
*
* @param {StatsData} data
*/
sortAssets(data) {
let assets = data.assets
assets = _.flatMap(assets, asset => [
asset,
...(Array.isArray(asset.related) ? asset.related : []),
])
assets = _.orderBy(assets, ['name', 'size'], ['asc', 'asc'])
return assets
}
/**
* Clear the entire screen.
*/
clearConsole() {
const blank = '\n'.repeat(process.stdout.rows)
console.log(blank)
readline.cursorTo(process.stdout, 0, 0)
readline.clearScreenDown(process.stdout)
}
/**
* Extend the width of the table
*
* Currently only increases the file column size
*
* @param {import('cli-table3').Table} table
* @param {number|null} targetWidth
* @param {number} maxWidth
*/
extendTableWidth(
table,
targetWidth = null,
maxWidth = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY
) {
targetWidth = targetWidth === null ? process.stdout.columns : targetWidth
if (!targetWidth)
return
const tableWidth = this.calculateTableWidth(table)
const fileColIncrease = Math.min(
targetWidth - tableWidth,
maxWidth - tableWidth
)
if (fileColIncrease <= 0)
return
// @ts-expect-error Should error
table.options.colWidths[0] += fileColIncrease
}
monkeyPatchTruncate() {
if (this.patched)
return
this.patched = true
// @ts-expect-error Should error
const utils = require('cli-table3/src/utils')
const oldTruncate = utils.truncate
/**
*
* @param {string} str
* @param {number} desiredLength
* @param {string} truncateChar
*/
utils.truncate = (str, desiredLength, truncateChar) => {
if (stripAnsi(str).length > desiredLength)
str = `…${str.substr(-desiredLength + 2)}`
return oldTruncate(str, desiredLength, truncateChar)
}
}
/**
* Calculate the width of the CLI Table
*
* `table.width` does not report the correct width
* because it includes ANSI control characters
*
* @internal
* @param {import('cli-table3').Table} table
*/
calculateTableWidth(table) {
const firstRow = table.toString().split('\n')[0]
return stripAnsi(firstRow).length
}
}
module.exports = BuildOutputPlugin
Webpack Migrate to 5
Make sure there's no webpack deprecation warnings.
node --trace-deprecation node_modules/webpack/bin/webpack.js
Webpack Reference
Rollup
import commonjs from '@rollup/plugin-commonjs'
import resolve from '@rollup/plugin-node-resolve'
import typescript from '@rollup/plugin-typescript'
import { defineConfig } from 'rollup'
import dts from 'rollup-plugin-dts'
import external from 'rollup-plugin-peer-deps-external'
import postcss from 'rollup-plugin-postcss'
import { terser } from 'rollup-plugin-terser'
import pkg from './package.json'
export default defineConfig([
{
input: 'src/index.ts',
output: [
{
file: pkg.main,
format: 'cjs',
sourcemap: true,
name: 'react-lib',
},
{
file: pkg.module,
format: 'esm',
sourcemap: true,
},
],
plugins: [
external(),
resolve(),
commonjs(),
typescript({ tsconfig: './tsconfig.json' }),
postcss(),
terser(),
],
},
{
input: 'dist/esm/types/index.d.ts',
output: [{ file: 'dist/index.d.ts', format: 'esm' }],
external: [/\.css$/],
plugins: [dts()],
},
])
Vite
import path from 'node:path'
import react from '@vitejs/plugin-react'
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import dts from 'vite-plugin-dts'
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
react(),
dts({
insertTypesEntry: true,
}),
],
build: {
lib: {
entry: path.resolve(__dirname, 'src/lib/index.ts'),
name: 'SafeView',
formats: ['es', 'umd'],
fileName: format => `SafeView.${format}.js`,
},
rollupOptions: {
external: ['react', 'react-dom'],
output: {
globals: {
'react': 'React',
'react-dom': 'ReactDOM',
},
},
},
minify: true,
sourcemap: true,
},
})
ESBuild
ESBuild build configuration:
// build.js
const esbuild = require('esbuild')
const inlineImage = require('esbuild-plugin-inline-image')
esbuild
.build({
entryPoints: ['./src/index.js'],
outfile: './public/js/app.js',
minify: true,
bundle: true,
loader: {
'.js': 'jsx',
},
plugins: [inlineImage()],
})
.catch(() => process.exit(1))
ESBuild serve configuration:
// serve.js
const esbuild = require('esbuild')
const inlineImage = require('esbuild-plugin-inline-image')
esbuild
.serve(
{
servedir: 'public',
port: 8000,
},
{
entryPoints: ['./src/index.js'],
outfile: './public/js/app.js',
bundle: true,
loader: {
'.js': 'jsx',
},
plugins: [inlineImage()],
}
)
.catch(() => process.exit())
ESBuild webpack configuration:
const { ESBuildMinifyPlugin } = require('esbuild-loader')
module.exports = {
rules: [
{
test: /.js$/,
loader: 'esbuild-loader',
options: {
loader: 'jsx',
target: 'es2015',
},
},
],
optimization: {
minimizer: [
new ESBuildMinifyPlugin({
target: 'es2015',
}),
],
},
}